Chapter 22
Induction, AC Circuits, and Electrical Technologies
By Boundless
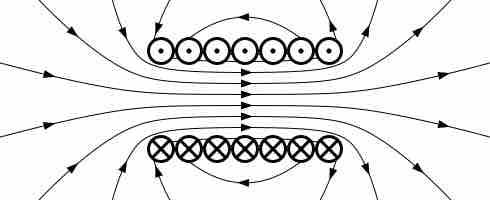
Faraday's law of induction states that an electromotive force is induced by a change in the magnetic flux.
Faraday's law of induction states that the EMF induced by a change in magnetic flux is
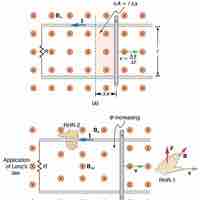
Motion in a magnetic field that is stationary relative to the Earth induces motional EMF (electromotive force).
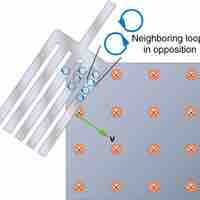
Back EMF, eddy currents, and magnetic damping are all due to induced EMF and can be explained by Faraday's law of induction.
Faraday's law of induction states that changing magnetic field produces an electric field:
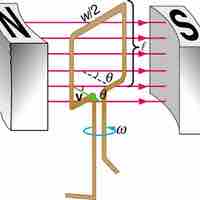
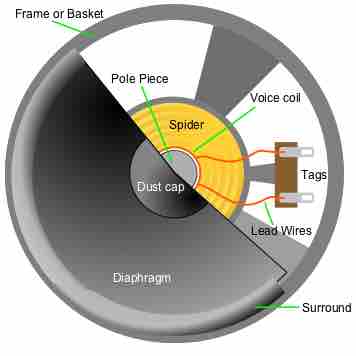
Electric generators convert mechanical energy to electrical energy; they induce an EMF by rotating a coil in a magnetic field.
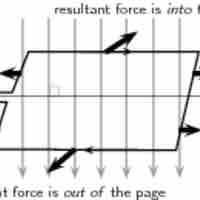
An electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
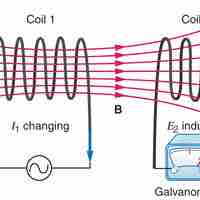
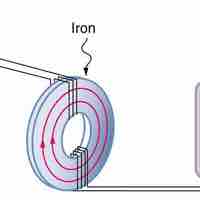
Inductance is the property of a device that tells how effectively it induces an emf in another device or on itself.
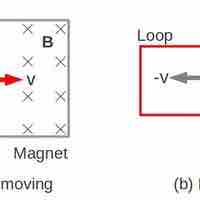
A a motional EMF is an electromotive force (EMF) induced by motion relative to a magnetic field B.
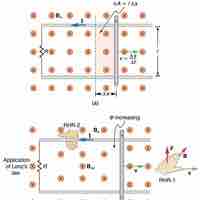
Mechanical work done by an external force to produce motional EMF is converted to heat energy; energy is conserved in the process.
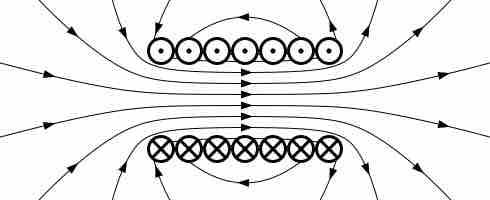
Magnetic field stores energy. The energy density is given as
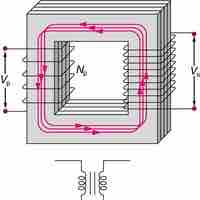
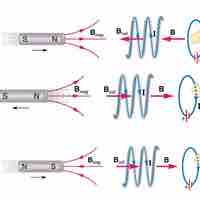
Transformers transform voltages from one value to another; its function is governed by the transformer equation.

Induction is the process in which an emf is induced by changing magnetic flux, such as a change in the current of a conductor.
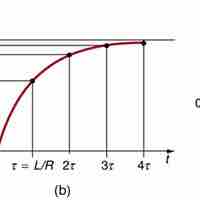
An RL circuit consists of an inductor and a resistor, in series or parallel with each other, with current driven by a voltage source.

Response of an RLC circuit depends on the driving frequency—at large enough frequencies, inductive (capacitive) term dominates.
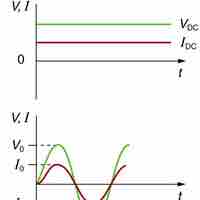
In a circuit with a resistor and an AC power source, Ohm's law still applies (V = IR).
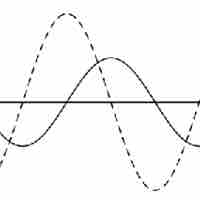
The voltage across a capacitor lags the current. Due to the phase difference, it is useful to introduce phasors to describe these circuits.
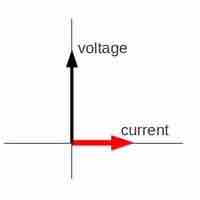
In an AC circuit with an inductor, the voltage across an inductor "leads" the current because of the Lenz' law.
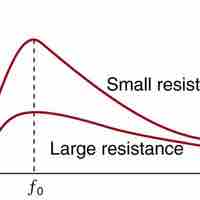
Resonance is the tendency of a system to oscillate with greater amplitude at some frequencies—in an RLC series circuit, it occurs at
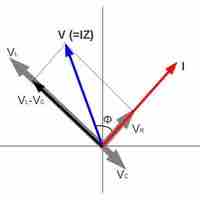
Power delivered to an RLC series AC circuit is dissipated by the resistance in the circuit, and is given as