Chapter 21
Magnetism
By Boundless
An electric current will produce a magnetic field, which can be visualized as a series of circular field lines around a wire segment.
Permanent magnets are objects made from ferromagnetic material that produce a persistent magnetic field.
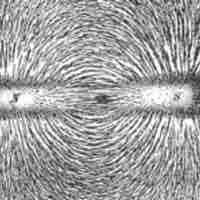
Magnetic field lines are useful for visually representing the strength and direction of the magnetic field.
Earth's magnetic field is caused by electric currents in the molten outer core and varies with time.
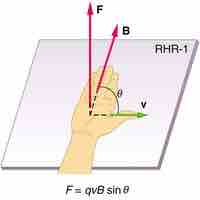
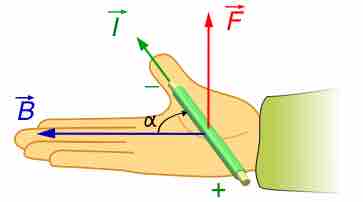
The magnetic force on a charged particle q moving in a magnetic field B with a velocity v (at angle θ to B) is
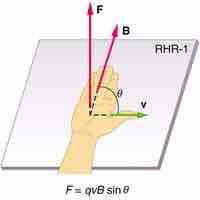
The right hand rule is used to determine the direction of the magnetic force on a positive charge.
Electric and magnetic forces both affect the trajectory of charged particles, but in qualitatively different ways.

If a charged particle's velocity is parallel to the magnetic field, there is no net force and the particle moves in a straight line.

Since the magnetic force is always perpendicular to the velocity of a charged particle, the particle will undergo circular motion.
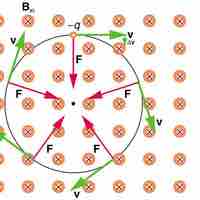
Helical motion results when the velocity vector is not perpendicular to the magnetic field vector.
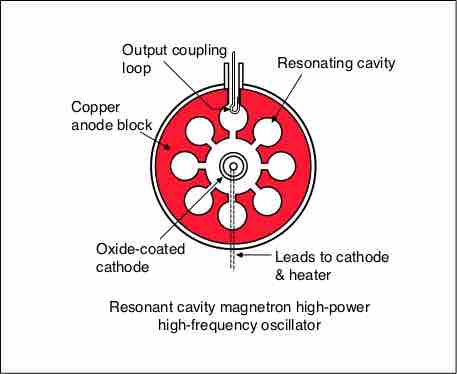
Cyclotrons, magnetrons, and mass spectrometers represent practical technological applications of electromagnetic fields.
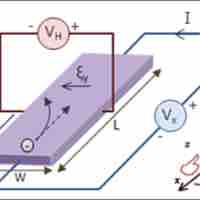
When current runs through a wire exposed to a magnetic field a potential is produced across the conductor that is transverse to the current.
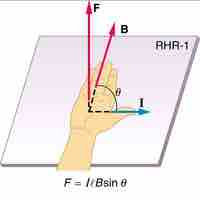
When an electrical wire is exposed to a magnet, the current in that wire will experience a force—the result of a magnet field.
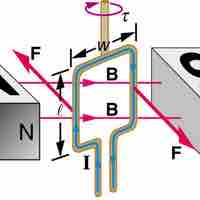
A current-carrying loop exposed to a magnetic field experiences a torque, which can be used to power a motor.
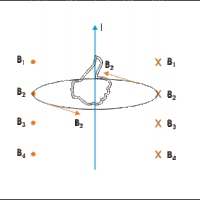
Current running through a wire will produce a magnetic field that can be calculated using the Biot-Savart Law.
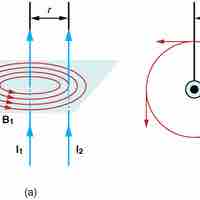
Parallel wires carrying current produce significant magnetic fields, which in turn produce significant forces on currents.
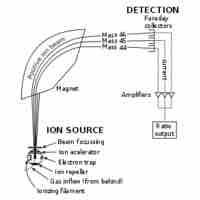
Mass spectrometers use electric or magnetic fields to identify different materials.

Ferromagnetism is the property of certain materials that enables them to form magnets and be attracted to magnets.

Paramagnetism is the attraction of material while in a magnetic field, and diamagnetism is the repulsion of magnetic fields.
Solenoids are loops of wire around a metallic core, and can be used to create controlled magnetic fields.