Section 4
Motion of a Charged Particle in a Magnetic Field
Book
Version 3
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Physics
Physics
by Boundless
5 concepts
Electric vs. Magnetic Forces
Electric and magnetic forces both affect the trajectory of charged particles, but in qualitatively different ways.

Constant Velocity Produces a Straight-Line
If a charged particle's velocity is parallel to the magnetic field, there is no net force and the particle moves in a straight line.

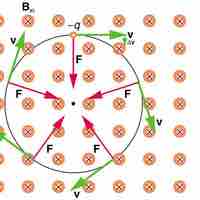
Circular Motion
Since the magnetic force is always perpendicular to the velocity of a charged particle, the particle will undergo circular motion.
Helical Motion
Helical motion results when the velocity vector is not perpendicular to the magnetic field vector.
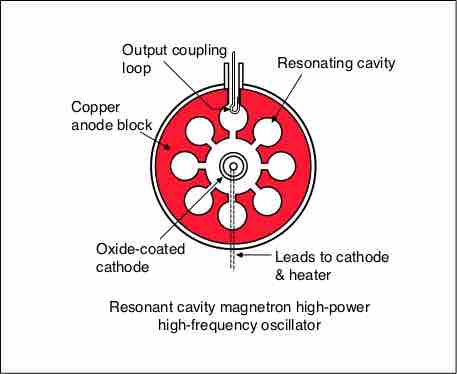
Examples and Applications
Cyclotrons, magnetrons, and mass spectrometers represent practical technological applications of electromagnetic fields.