Chapter 20
Circuits and Direct Currents
By Boundless
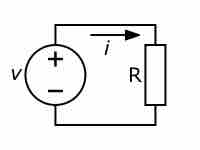
An electrical circuit is an interconnection of electrical elements that has a closed loop giving a return path for the current.

Electromotive force (EMF) is the voltage voltage generated by a battery or by the magnetic force according to Faraday's Law of Induction.
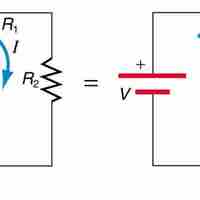
The total resistance in the circuit with resistors connected in series is equal to the sum of the individual resistances.
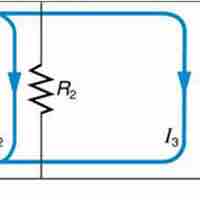
The total resistance in a parallel circuit is equal to the sum of the inverse of each individual resistances.
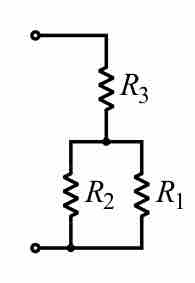
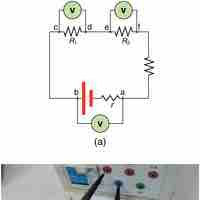
A combination circuit can be broken up into similar parts that are either series or parallel.
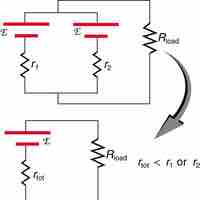
When voltage sources are connected in series, their emfs and internal resistances are additive; in parallel, they stay the same.
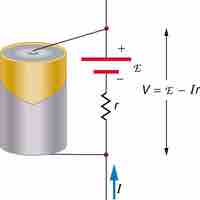
The output, or terminal voltage of a voltage source such as a battery, depends on its electromotive force and its internal resistance.
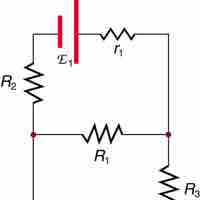
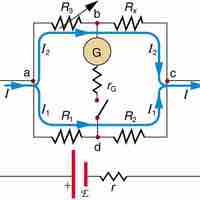
Kirchhoff's circuit laws are two equations that address the conservation of energy and charge in the context of electrical circuits.

Kirchhoff's junction rule states that at any circuit junction, the sum of the currents flowing into and out of that junction are equal.
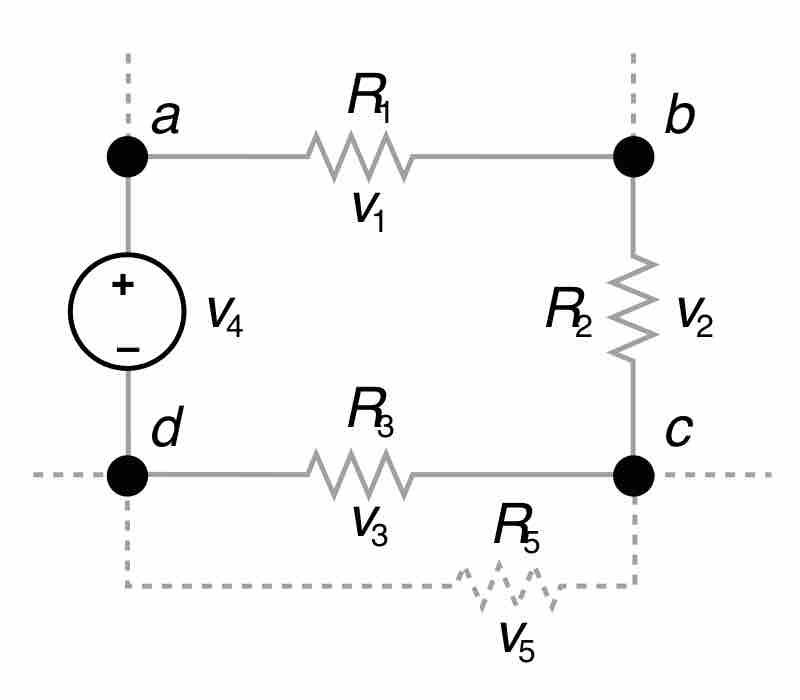
Kirchhoff's loop rule states that the sum of the emf values in any closed loop is equal to the sum of the potential drops in that loop.
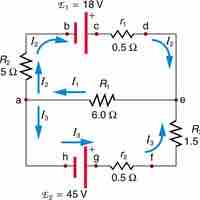
Kirchhoff's rules can be used to analyze any circuit and modified for those with EMFs, resistors, capacitors and more.
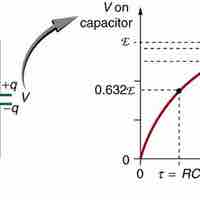
An RC circuit has a resistor and a capacitor and when connected to a DC voltage source, and the capacitor is charged exponentially in time.
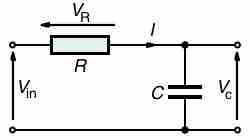
Impedance is the measure of the opposition that a circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied.
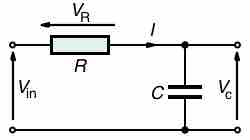
In a series RC circuit connected to an AC voltage source, voltage and current maintain a phase difference.