Chapter 19
Electric Current and Resistance
By Boundless

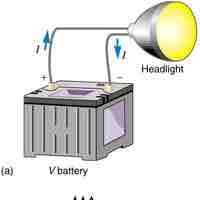
A battery is a device that converts chemical energy directly to electrical energy.
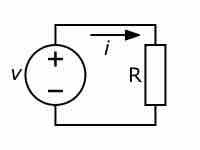
The electrical current is directly proportional to the voltage applied and inversely related to the resistance in a circuit.
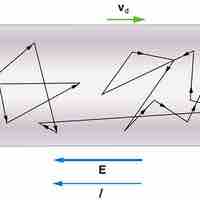
The drift velocity is the average velocity that a particle achieves due to an electric field.
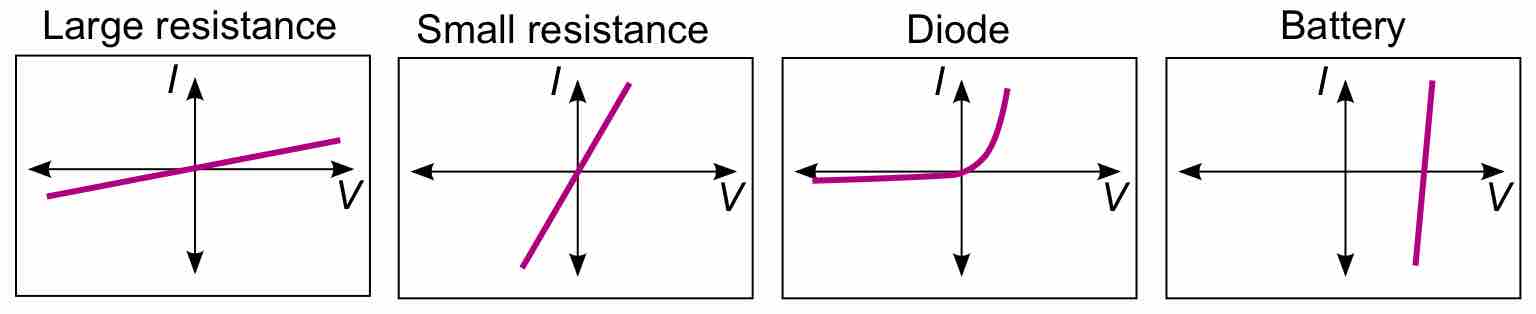
Ohm's Law states that current is proportional to voltage; circuits are ohmic if they obey the relation V=IR.
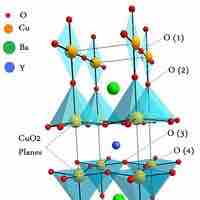
Superconductivity is a phenomenon of zero electrical resistance and expulsion of magnetic fields in certain materials below a critical temp.
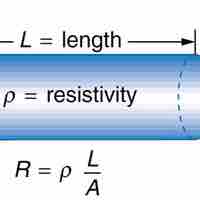
Resistance and resistivity describe the extent to which an object or material impedes the flow of electric current.
Resistivity and resistance depend on temperature with the dependence being linear for small temperature changes and nonlinear for large.

Phasors are used to analyze electrical systems in sinusoidal steady state and with a uniform angular frequency.
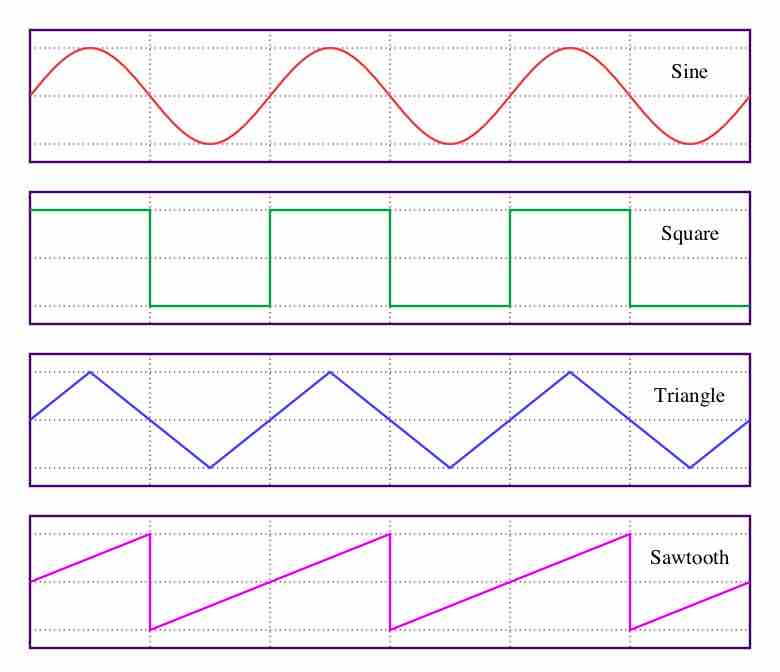
The root mean square (RMS) voltage or current is the time-averaged voltage or current in an AC system.
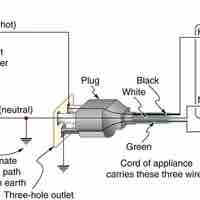
Electrical safety systems and devices are designed and widely used to reduce the risks of thermal and shock hazards.
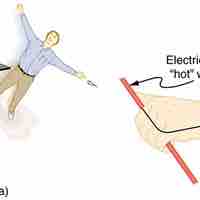
The hazards from electricity can be categorized into thermal and shock hazards.
Voltage pulses along a cell membrane, called action potentials, allow us to sense the world, control parts of our body, and think.
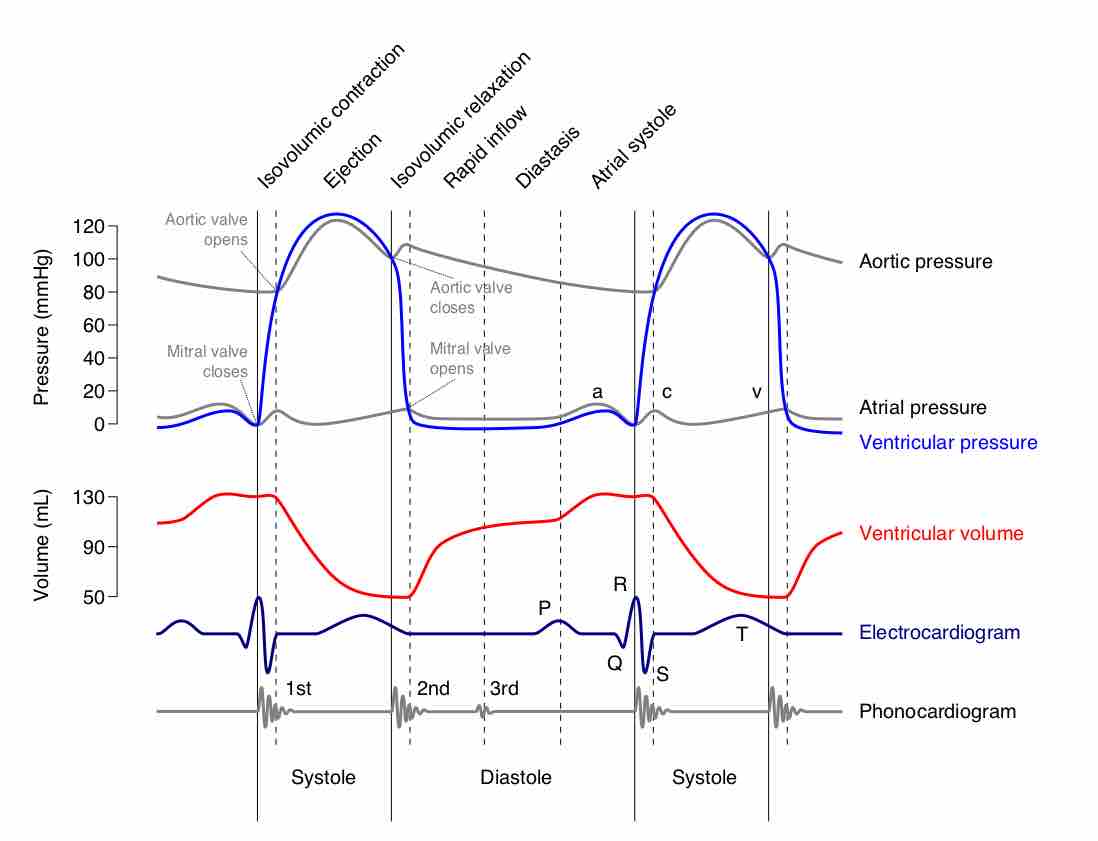
Electric energy stimulating the heart occurs in the sinoatrial node, the heart's pacemaker, and is transmitted partially by Perkinje fibers.