Chapter 18
Electric Potential and Electric Field
By Boundless
Electric potential and field are related in that potential is a property of the field that describes the field's action.
Electric potential energy results from forces between charges; potential difference is the energy needed to move a charge from point A to B.
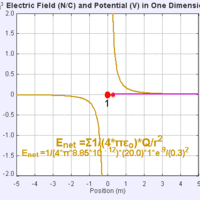
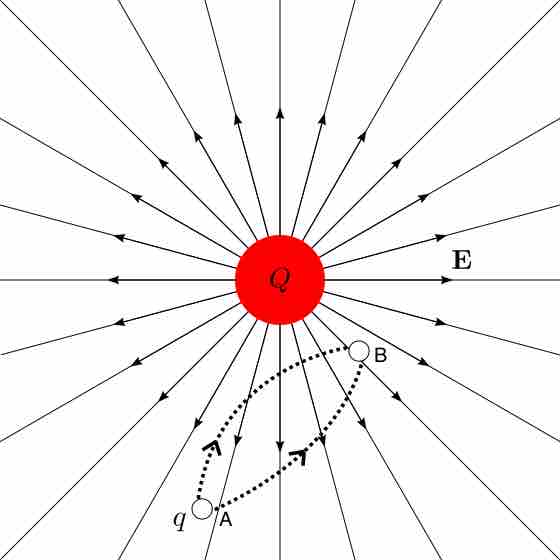
Electric field is the gradient of potential, which depends inversely upon distance of a given point of interest from a charge.
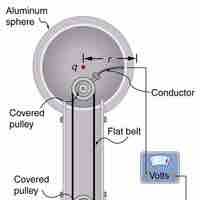
Electric potential within a charged conductor is equal to zero, but can be calculated as a nonzero value outside of a charged conductor.
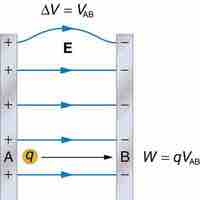
An electric field that is uniform is one that reaches the unattainable consistency of being constant throughout.
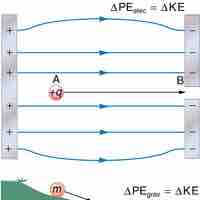
Energy is conserved in the movement of a charged particle through an electric field, as it is in every other physical situation.

The electron volt is a unit of energy useful in the physics of elementary charges and electricity.
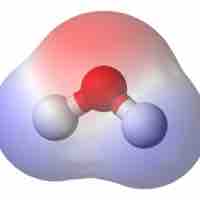
The electric dipole moment is a measure of polarity in a system.
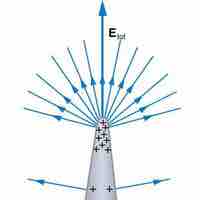
An ideal conductor exists only in the world of theory; it has "ideal" properties that make calculations easy to perform.

Electric potentials are commonly found in the body, across cell membranes and in the firing of neurons.
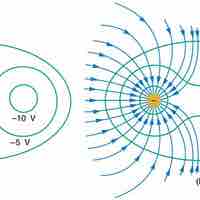
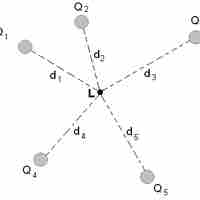
Equipotential lines depict one-dimensional regions in which the electric potential created by one or more nearby charges is constant.
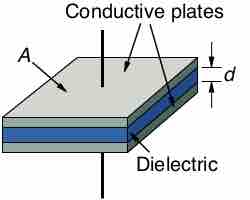
Capacitance is the measure of an object's ability to store electric charge.
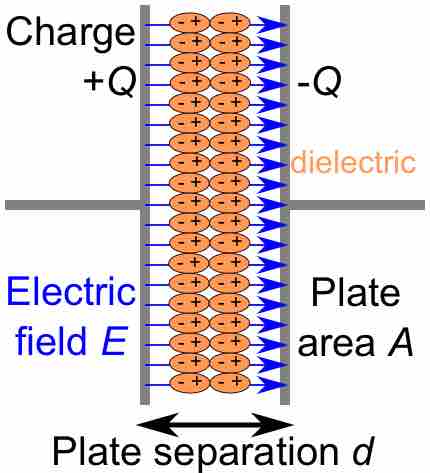
A dielectric partially opposes a capacitor's electric field but can increase capacitance and prevent the capacitor's plates from touching.
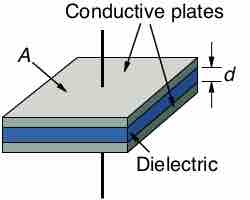
The parallel-plate capacitor is one that includes two conductor plates, each connected to wires, separated from one another by a thin space.
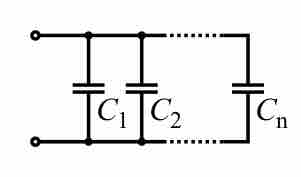
Like any other form of electrical circuitry device, capacitors can be used in series and/or in parallel within circuits.

Dielectric breakdown is the phenomenon in which a dielectric loses its ability to insulate, and instead becomes a conductor.