Chapter 23
Electromagnetic Waves
By Boundless
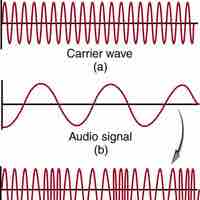
Radio waves are EM (Electromagnetic)waves that have wavelengths between 1 millimeter and 100 kilometers (or 300 GHz and 3 kHz in frequency).
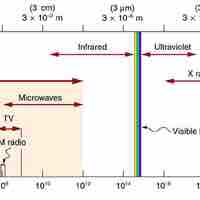
Microwaves are electromagnetic waves with wavelengths ranging from one meter to one millimeter (frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz).
Infrared (IR) light is EM radiation with wavelengths longer than those of visible light from 0.74 µm to 1 mm (300 GHz to 1 THz).
Visible light is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye, ranging from roughly 390 to 750 nm.
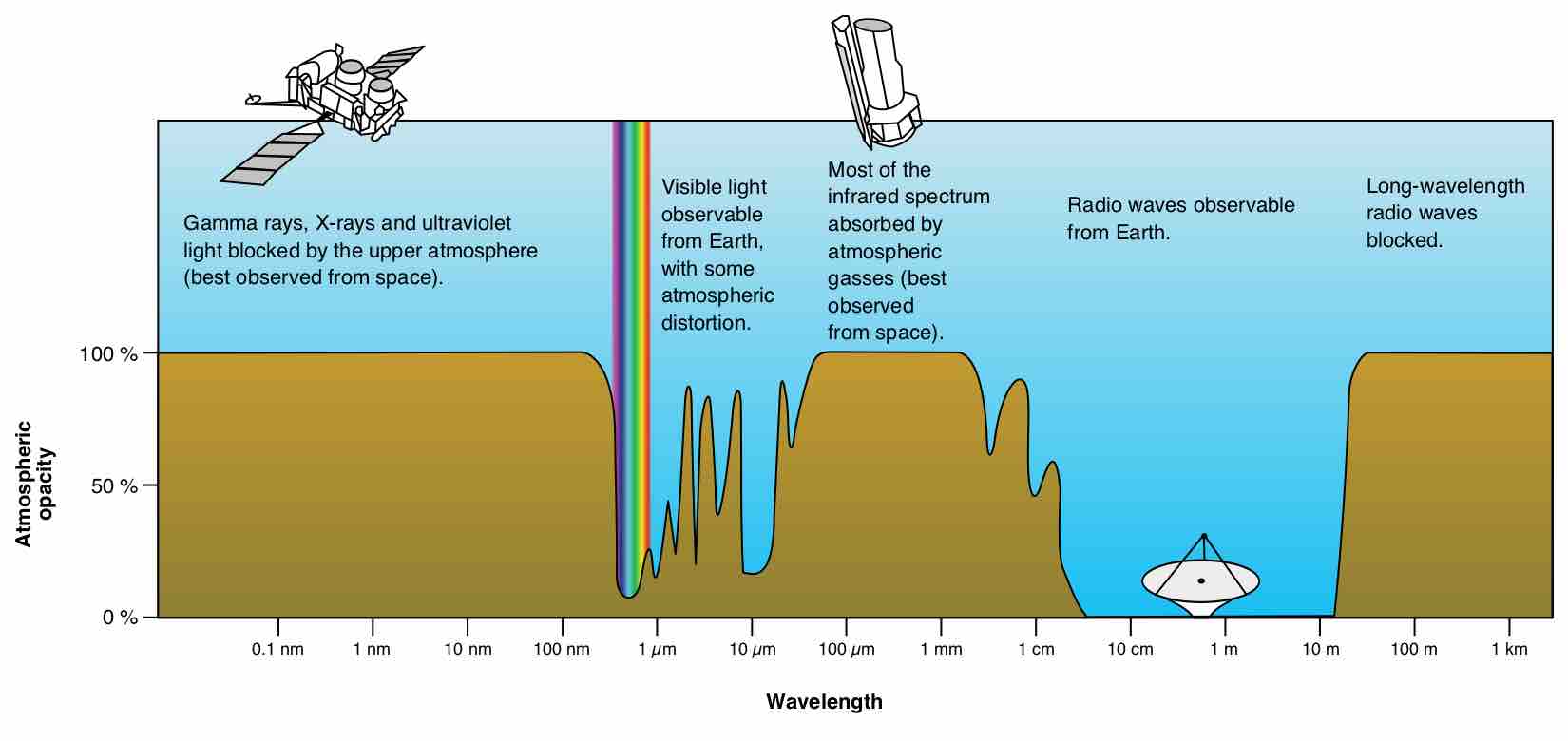
Ultraviolet (UV) light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light in the range 10 nm to 400 nm.

X-rays are electromagnetic waves with wavelengths in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers and energies in the range of 100 eV to 100 keV.
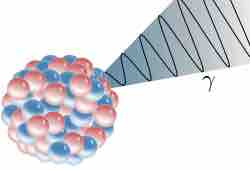
Gamma rays are very high frequency electromagnetic waves usually emitted from radioactive decay with frequencies greater than 1019 Hz.

Maxwell's equations help form the foundation of classical electrodynamics, optics, and electric circuits.

Electromagnetic waves are the combination of electric and magnetic field waves produced by moving charges.
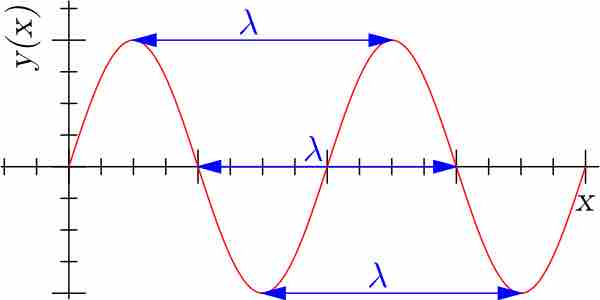
Electromagnetic waves have energy and momentum that are both associated with their wavelength and frequency.

The speed of light in a vacuum is one of the most fundamental constant in physics, playing a pivotal role in modern physics.
The Doppler Effect is the change in a wave's perceived frequency that results from the source's motion, the observer, and the medium.

Radiation pressure is the pressure exerted upon any surface exposed to electromagnetic (EM) radiation.
