Chapter 24
Geometric Optics
By Boundless
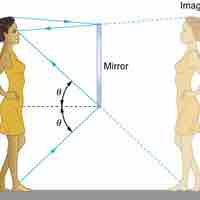
The law of reflection states that the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence.
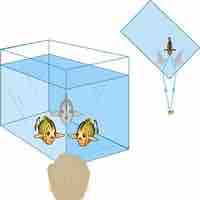
The amount that a light ray changes its direction depends both on the incident angle and the amount that the speed changes.
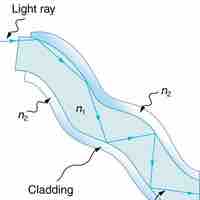
Total internal reflection happens when a propagating wave strikes a medium boundary at an angle larger than a particular critical angle.

Brewster's angle is an angle of incidence at which light with a particular polarization is perfectly transmitted through a surface.
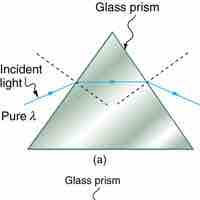
Dispersion is defined as the spreading of white light into its full spectrum of wavelengths.
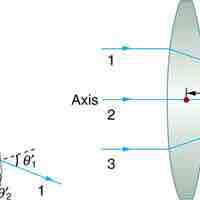
Ray tracing is the technique of determining the paths light rays take; often thin lenses (the light ray bending only once) are assumed.
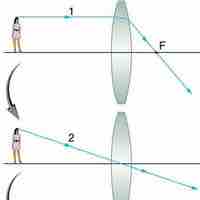
The thin lens equation relates the object distance do, image distance di, and focal length f.
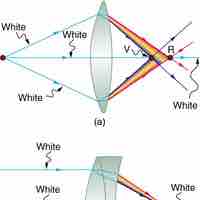
A compound lens is an array of simple lenses with a common axis.
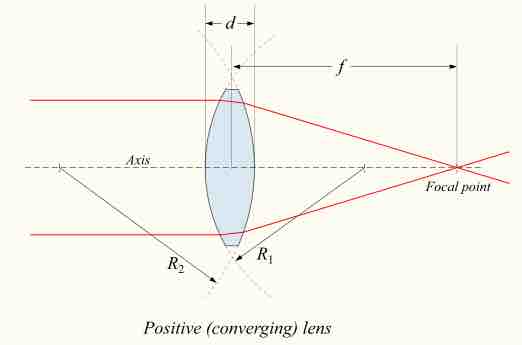
The lensmaker's formula is used to relate the radii of curvature, the thickness, the refractive index, and the focal length of a thick lens.

Because the index of refraction of a lens is greater than air, a ray moves towards the perpendicular as it enters and away as it leaves.
A mirror is a reflective surface that bounces off light, thus producing a real or virtual image.

A mirror is a reflective surface that light does not pass through, made by a layer of silver nitrate or aluminium behind piece of glass.