This article was co-authored by Gonzalo Martinez. Gonzalo Martinez is the President of CleverTech, a tech repair business in San Jose, California founded in 2014. CleverTech LLC specializes in repairing Apple products. CleverTech pursues environmental responsibility by recycling aluminum, display assemblies, and the micro components on motherboards to reuse for future repairs. On average, they save 2 lbs - 3 lbs more electronic waste daily than the average computer repair store.
The wikiHow Tech Team also followed the article's instructions and verified that they work.
This article has been viewed 41,250 times.
If your Mac computer suddenly becomes frozen, or begins to act slow and sluggish, restarting your Mac can help clear its memory and process items at a normal speed upon bootup. There are several methods you can use to restart your Mac, which can be useful in the event you are unable to access certain commands or programs as a result of computer issues.
Steps
Using the Apple Menu
-
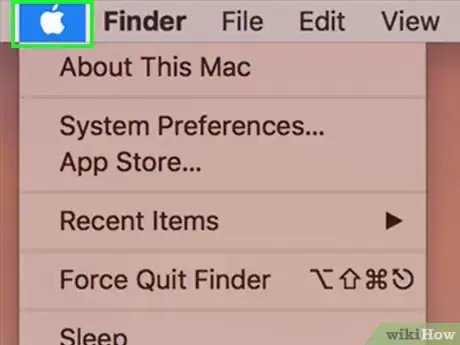
1Click on the Apple logo located within the toolbar of your Mac.
-
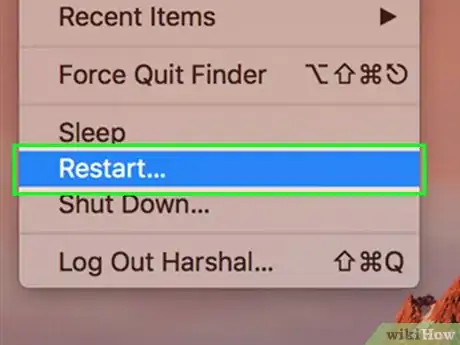
2Click on “Restart.”Advertisement
-
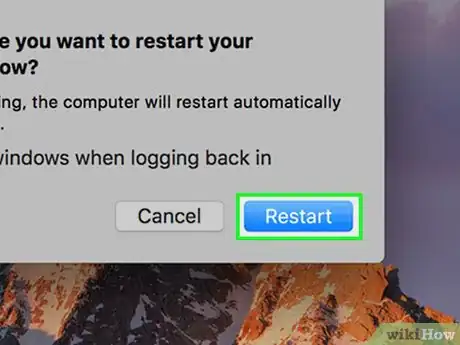
3Click on “Restart” once again when asked to confirm that you want to restart your computer. Your Mac will restart immediately.[1]EXPERT TIPGonzalo Martinez is the President of CleverTech, a tech repair business in San Jose, California founded in 2014. CleverTech LLC specializes in repairing Apple products. CleverTech pursues environmental responsibility by recycling aluminum, display assemblies, and the micro components on motherboards to reuse for future repairs. On average, they save 2 lbs - 3 lbs more electronic waste daily than the average computer repair store.Computer & Phone Repair Specialist

 Gonzalo Martinez
Gonzalo Martinez
Computer & Phone Repair SpecialistRestart your Mac weekly to save memory. Restarting a Mac once a week is recommended to free up memory on your computer. You can use Activity Monitor to check how much memory is being used by other applications and decide when is a good time to restart the Mac. This way, you can use all of the memory that is actually on the computer.
Using the Shutdown Window
Using the Terminal Application
-
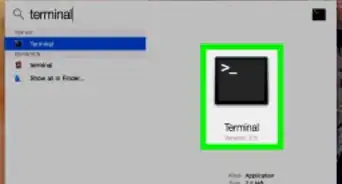
1Open the Applications folder from the Dock of your Mac.
-
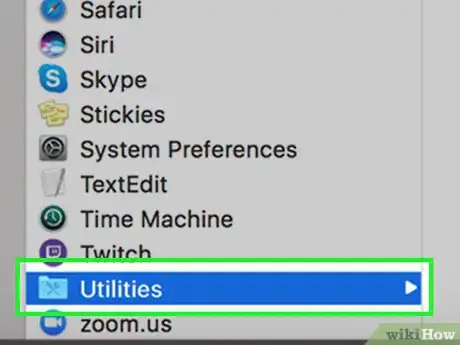
2Open “Utilities.”
-
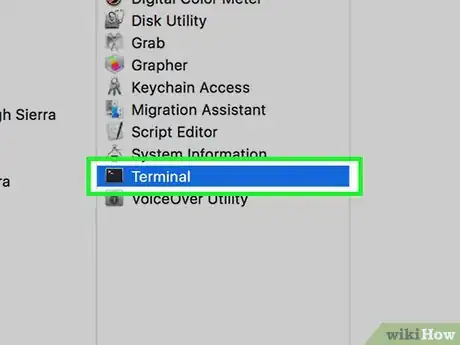
3Click on “Terminal.” The Terminal window will display on-screen.
-
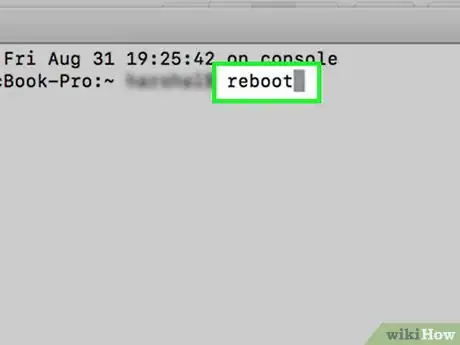
4Type the following command into Terminal: “shutdown -r now”.
- Alternately, you can type the commands, “reboot” or “reboot -q”.
-
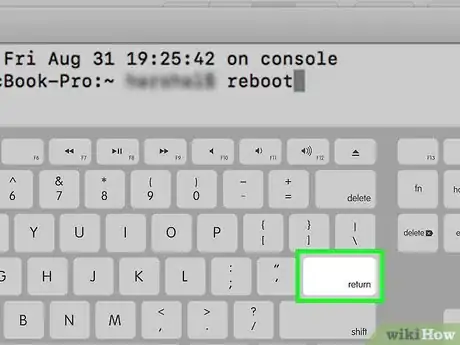
5Press “Enter” on your keyboard. Your Mac will begin the shutdown process and restart immediately.
Performing a Hard Reset
-
1Quit any processes that are requiring use of the hard drive. For example, if you are moving files between a flash drive and the hard drive, wait until the files have finished moving.
-
2Press and hold down the Power button on your Mac until the computer turns off. This process should take between two and three seconds.
-
3Press the Power button again to restart your Mac.
Restarting Using Remote Access
-
1Open the System Preferences application from the Dock of your Mac.
-
2Click on the “Sharing” icon.
-
3Place a checkmark next to “Remote Login.”
-
4Close the System Preferences window.
-
5Open an Internet browser and go to https://google.com.
-
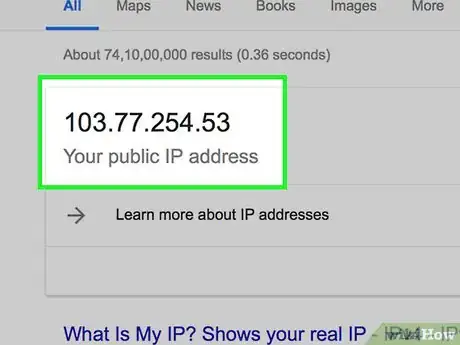
6Type “what is my ip” into the search bar and press “Enter.” Google will display your IP address at the top of search results.
-
7Write down or take note of your IP address.
-
8Go to another computer that is connected to the same network.
-
9Access the Terminal application, or command prompt if using a Windows computer.
-
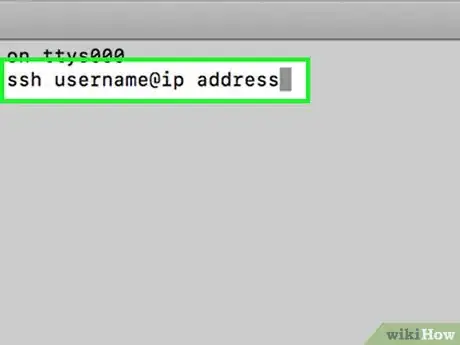
10Type the following command using your IP address into Terminal to log in to your computer remotely: “ssh username@ip_address.”
-
11Type the word “reboot” into Terminal and press “Enter.” Your computer will then restart.
Warnings
- Do not use the hard reset method outlined in method #5 if you are currently accessing your computer’s hard drive. This method could result in physical damage of your computer’s hard drive.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Do not use the Terminal method outlined in method #4 to restart your computer on a regular basis. This method does not give any running processes the time they need to quit normally and save settings, which could result in eventual degradation of the operating system.⧼thumbs_response⧽






-Step-6.webp)