This article was co-authored by wikiHow Staff. Our trained team of editors and researchers validate articles for accuracy and comprehensiveness. wikiHow's Content Management Team carefully monitors the work from our editorial staff to ensure that each article is backed by trusted research and meets our high quality standards.
This article has been viewed 219,375 times.
Learn more...
When Windows 7 is unable to show anything but a black screen after returning from hibernation or sleep, there are several potential issues that cause this. This can range from improper configuration for your hardware, video drivers or your computer's BIOS. If your computer does not return from a black screen after a few seconds, you will need to restart your computer to change a few settings to prevent your computer from facing this issue again.
Steps
Resolving Issues With the CPU Fan
-
1Turn off or reboot your computer. If your computer is currently on, but does not display a picture, hold the power button down for a few seconds, this will power off your computer. If the computer continues to not power off, remove any power sources such as turning off the power supply on your desktop or removing the battery on your laptop. Turn the computer back on to initiate the bootup sequence.
-
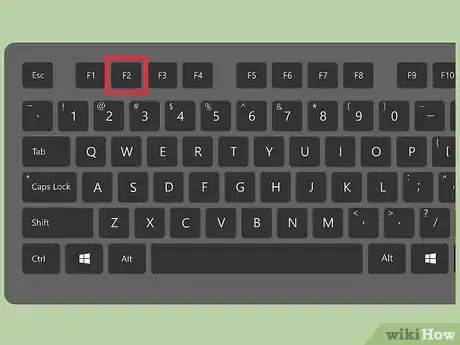
2Open the BIOS Settings. The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) of your computer allows you to change the settings of your computer including the CPU (Central Processing Unit) fan speed. During the bootup sequence of your computer, you will have to hit one of the function keys, either F2, F8 or F10 depending on your manufacturer to get to the Setup Menu.
- If the computer is pre-built, check the user’s guide on how to activate the BIOS Setup Screen.
- You may also see the function key to press on the BIOS splash screen during start up.
- Try pressing the key repeatedly during the startup sequence to activate the menu.
Advertisement -
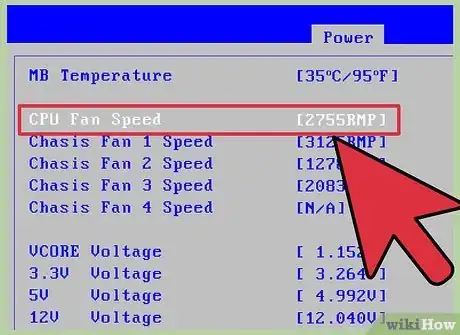
3Identify the CPU Fan Speed. When you activate the BIOS setup screen, find the listing of the CPU fan speed by navigating to the ‘’Hardware Monitor’’ using the arrow keys on your keyboard then pressing ↵ Enter. The BIOS may show an alert if the fan speed is too slow. If there is no warning, identify what if the CPU fan speed is. Ensure the BIOS is set to automatically change the fan speed.
- BIOS settings will vary for most motherboards, refer to your computer or motherboard's manual for where the settings are located.
-
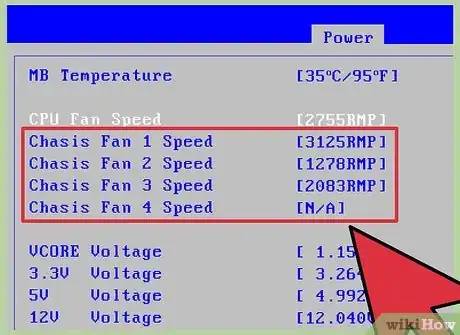
4Change the CPU Fan Speed. In the hardware monitor, use the arrow keys to navigate to the CPU fan settings. Press ↵ Enter then use the arrow keys to change the fan profile information to match automatic or optimal settings then press ↵ Enter again.
- Verify the recommended fan setting in the user guide of your motherboard or computer.
- If the CPU fan speed is set at the recommended setting and is operating normally, the issue may be related to the graphics driver.
-
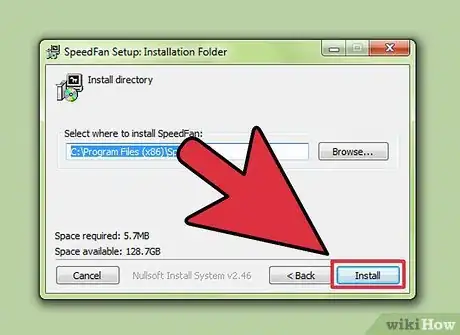
5Download and install fan-controlling software. You can also try controlling your fan's speed outside of the BIOS using a third party application such as SpeedFan if your computer supports these programs.[1]
- Ensure that your computer is compatible with fan controlling software by checking with the compatibility documentation on the developer's website.
- You may not be able to use these programs within Windows as the BIOS will likely override any settings.
- If using a pre-built computer, check the user's guide or support to see if there are any programs dedicated to controlling the fans from pre-installed software.
-
6Repair or replace the CPU fan on your computer. If the fan is damaged or is not achieving appropriate speeds identified by the computer, it may need to be cleaned, repaired or replaced.
- You can attempt to overclock your CPU which will cause the fan speed to speed up from within the BIOS, however this will cause more wear on your CPU and give it a shorter lifespan.
Installing Updates to System BIOS and Graphics Drivers
-
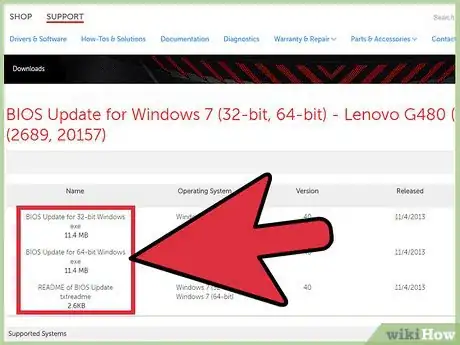
1Update the graphics drivers or system BIOS. Make sure the graphics driver is up-to-date as the issue may have been resolved in a later update. The BIOS may be facing difficulties communicating with Windows that are causing the system to not be able to resume from sleeping or hibernating. Check the website of the manufacturer of your computer, motherboard and video card for any updates.
- It is also possible the current update for the BIOS or graphics drivers are facing problems and may require you to rollback to a previous update or prevent an update from happening. Check with your computer or device manufacturer’s website for any significant updates and how to return to a previous driver or BIOS update.
- Windows 7 will allow you to rollback your device drivers in case you need to return to a previous version, navigate to the “Control Panel” from the Start Menu. Search for or open the “Device Manager” which opens a new window that lists the different drivers associated with each device. In this new window, locate and expand the "Display adapters" from the list, right click your video card device to bring up a menu, click on “Properties.” In the new window click on the “Driver” tab then click on the “Roll Back Driver” button.
-
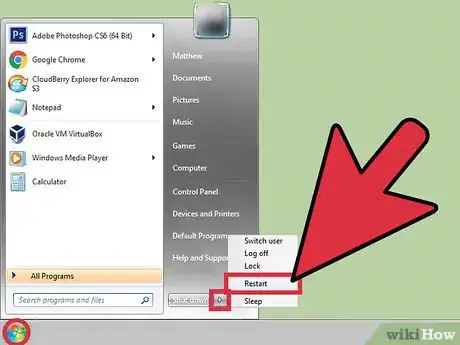
2Turn off or reboot your computer. This ensures that any updates installed on your computer are operating correctly. If the issue persists, continue through the instructions on how to activate a diagnostic mode for Windows 7.
- If you continue to not see a picture after putting the computer into sleep or hibernation mode, you can hold the power button down for a few seconds, turn off the power supply for your desktop, or remove the battery on your laptop to turn off the computer.
-
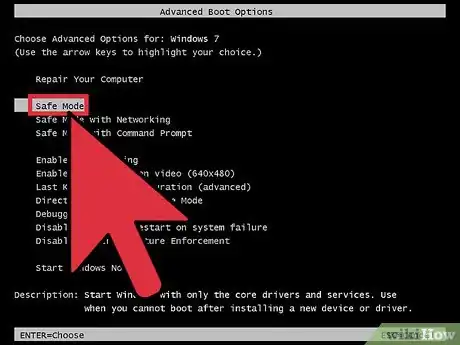
3Turn on your computer and boot Windows 7 into safe mode. This will allow you to start Windows into a diagnostic mode that is useful for identifying significant errors on your computer. During the Windows 7 startup sequence, press a function key, either F8 or F10. Use your computer’s user’s guide to identify the function key to press to access the Windows Accessibility Menu. Select safe mode from this menu using the arrow keys and pressing ↵ Enter.
-
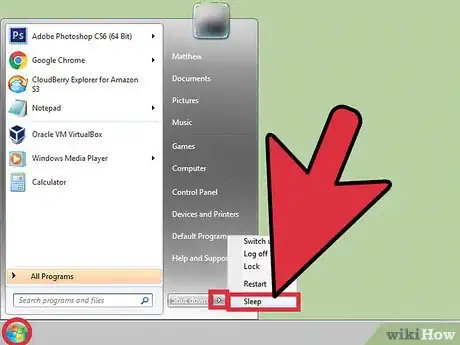
4Log in to your desktop and set the computer into sleep or hibernation mode. After you access the desktop of your computer in safe mode, activate the hibernation mode or sleep mode.
- Laptops can be set in hibernation mode by closing the lid if this setting is activated.
- For desktops or laptops you can use the Start Menu and choose to "Hibernate" or "Sleep". Let the computer sit for two or three minutes.
-
5Resume from the Sleep or Hibernate Mode. If the computer’s desktop resumes normally and the graphics driver was updated, the issue may be due to your computer lacking RAM resources or there may have been a corruption during the installation of the Windows 7 operating system.[2]
Resolving RAM Issues on Your Computer
-
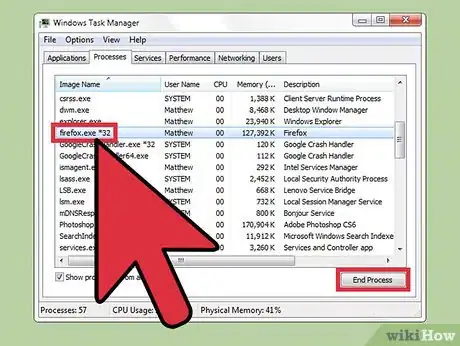
1Close programs that use high amounts of RAM. Programs that either make high use of RAM or cause memory leaks may cause Windows to have difficulties returning from hibernation. Use Task Manager by right clicking the Start bar then selecting “Task Manager” and identify user-opened programs such as Firefox to identify programs that can be closed to free more RAM.[3]
-
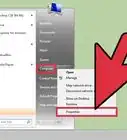
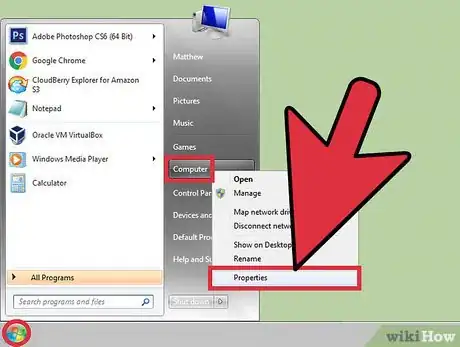
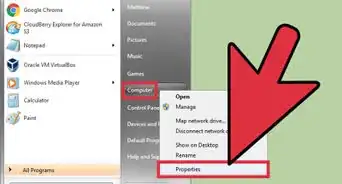
2Investigate the physical RAM usage. You will need to confirm the page file size is greater than your physical RAM. Windows will make use of your hard drive to cache RAM for applications if it exceeds the limits of RAM on your computer. If your computer is running programs with high RAM usage and tries to wake up after sleep or hibernation, Windows may not have enough resources to return to your desktop. Access the Start Menu by clicking on start which is typically in the lower left corner of the screen, then right-click on "My Computer," and select "Properties".
-
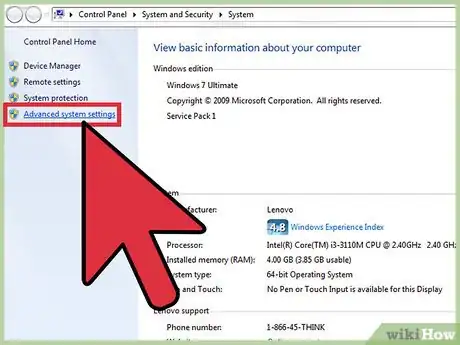
3Navigate to Advanced system settings. In the left column of the new window choose "Advanced system settings."
-
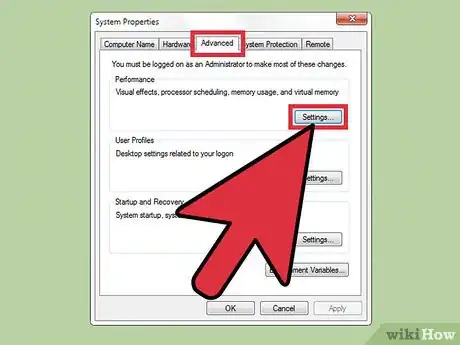
4Navigate to the Performance settings. Select the "Advanced" tab, then under the “Performance” section, select "Settings".
-
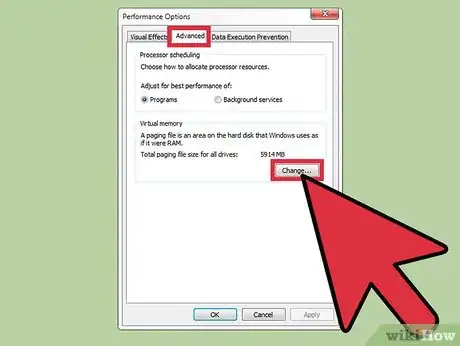
5Change the Virtual Memory settings. Select "Advanced" tab in the new window. Then click on the "Change" button to open a new window.
-
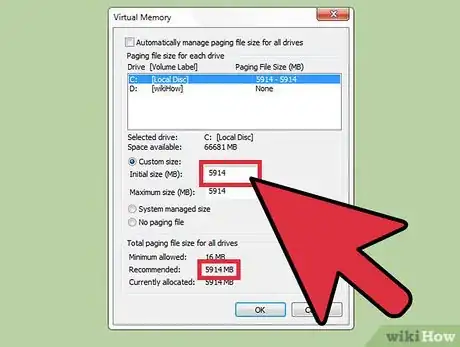
6Set the page file size. Choose a local hard drive, preferably a hard drive you consider your primary or the hard drive Windows is contained on," then choose "Custom Size" and set the size to the same value as displayed in the "Recommended" value shown at the bottom of the window, then click on “OK” to return to the previous window. Then click on “Apply” then click on “OK” to save the changes.[4]
Community Q&A
-
QuestionWhen cleaning the CPU cooling fan, should I remove and clean the attached heat sink/cooling unit?
 Community AnswerI do when I clean my CPU cooling fan, though it depends on how dirty/dusty the heat sink is. I use Q-tips and pipe cleaners to clean between the fins.
Community AnswerI do when I clean my CPU cooling fan, though it depends on how dirty/dusty the heat sink is. I use Q-tips and pipe cleaners to clean between the fins.
References
- ↑ http://lifehacker.com/5866009/control-your-computers-fan-speeds-for-better-performance-when-you-need-it-silence-when-you-dont
- ↑ http://superuser.com/questions/602610/windows-7-shows-blank-screen-after-resuming-it-from-sleep-mode
- ↑ http://www.techrepublic.com/article/wake-up-troubleshoot-laptop-hibernation-and-standby-issues/
- ↑ http://www.online-tech-tips.com/computer-tips/simple-ways-to-increase-your-computers-performace-configuring-the-paging-file/
- ↑ http://windows.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/using-last-known-good-configuration#1TC=windows-7

-Step-55-Version-2.webp)