This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Nicole Levine, MFA. Nicole Levine is a Technology Writer and Editor for wikiHow. She has more than 20 years of experience creating technical documentation and leading support teams at major web hosting and software companies. Nicole also holds an MFA in Creative Writing from Portland State University and teaches composition, fiction-writing, and zine-making at various institutions.
The wikiHow Tech Team also followed the article's instructions and verified that they work.
This article has been viewed 1,381,317 times.
Learn more...
Software like Thunderbird and Outlook make sending e-mail seem like magic. Well, until your e-mail never arrives at its destination. How can you find out what really happens when you click “Send?” One option is to send a test message from your e-mail provider's outbound server with telnet, a tiny application that came with your computer. You may catch an error message that your e-mail software didn't.
Steps
Connecting to the Mail Server with Telnet
-
1Get telnet. If you’re using MacOS or Windows XP, your version of telnet is ready to use. If you have Windows Vista, 2008 server, 7, 8.1 or 10, you’ll need to enable telnet before you can use it.
- Windows Vista, 2008 server, 7 and 8.1: Click on the Start Menu and then select Control Panel. Click Programs, and select “Turn Windows features on or off.” This will bring up a list of Windows Features. Scroll down until you see “Telnet Client,” and put a check in that box. Click “OK.” [1]
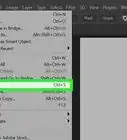
- Windows 10: Right-click the Start menu and select Programs and Features. Click “Turn Windows features on or off” in the left menu. In the list that pops up, put a check in the box next to “Telnet client” and click “OK.”
-
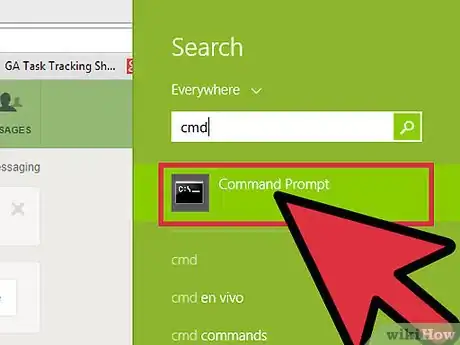
2Open a terminal window. This is a little different between Windows and Mac.
- Any version of Windows: Press ⊞ Win+R , type
cmd, then press ↵ Enter. - Mac: In Finder, select “Applications,” then “Utilities.” Double-click the “Terminal” icon. [2] You can also access Terminal by typing it into Launchpad and clicking it.
Advertisement - Any version of Windows: Press ⊞ Win+R , type
-
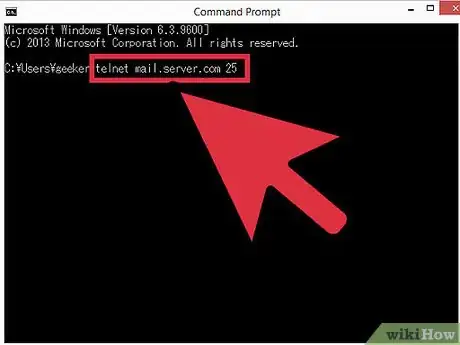
3Open a telnet connection. Type
telnet mail.server.com 25where "mail.server.com" is the name of the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) server of your email provider (such as smtp-server.austin.rr.com) and 25 is the port number used by the SMTP service.- You should receive a reply like "220 mail.server.com.”
- Port 25 is the port for most mail servers, but some network administrators move SMTP to a different port, like 465 (a secure port) or 587 (for Microsoft Outlook users) [3] . Ask your administrator (or check your account information) for the correct port.
- If you receive an error message, such as "Cannot connect to host on port 25," and you are sure that port 25 is the correct port, the mail server is likely experiencing an issue.
Sending Your Message
-
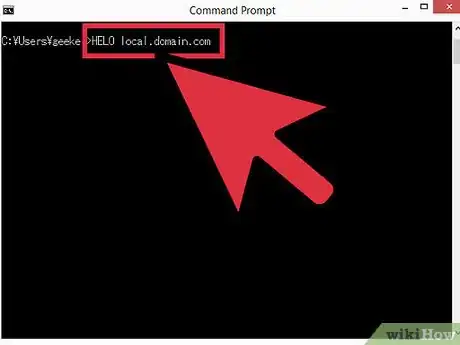
1Greet the server. The rest of the steps are the same no matter which operating system you're using. Type
HELO yourdomain.comwhere yourdomain.com is the domain name from which you send e-mail. Note that there is only one L in HELO. Press ↵ Enter.- You should receive a reply like "250 mail.server.com Hello yourdomain.com pleased to meet you."
- If you receive no response or an error message, try
EHLOinstead ofHELO. Some servers prefer one to the other.
-
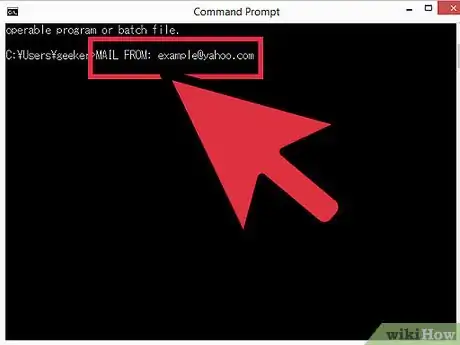
2Enter the sender “header” information. Type
mail from: you@server.com, using your own e-mail address. Make sure there is a space after themail from:. Press ↵ Enter.- You should receive message that says something similar to "250 Sender OK.”
- If you see an error, double-check that you’re using an e-mail address with the same domain as the server. Your server may not allow you to send a message with your yahoo.com address, for example.
-
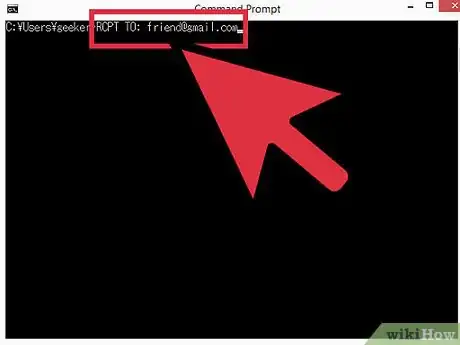
3Enter the e-mail address of the recipient. Type
rcpt to: friend@friendsdomain.com, where the e-mail address is that of your actual recipient. Press ↵ Enter.- You should see a message that says something along the lines of "250 OK – MAIL FROM you@yourdomain.com ".
- If you receive an error, the e-mail address you are trying to send a message to may be blocked.
-
4Compose your message. You’ll need to enter a few commands to format and send the message.
- Type
dataand press ↵ Enter. - On the next line, type
subject: testand press ↵ Enter twice. Replace “test” with your desired subject. - Type your message. When you’re done, press ↵ Enter.
- Type a single . to end the message, then press ↵ Enter. You should see a message that confirms your message was accepted or queued. This message varies across servers.
- If you see any sort of error message, write it down and contact your e-mail provider.
- Type
-
5Type
quitto exit telnet. Press ↵ Enter.
Community Q&A
-
QuestionDoes this process require an internet connection?
 Community AnswerOnly if you are trying to send your email outside of your local network or use an Internet Mail Server for mailing.
Community AnswerOnly if you are trying to send your email outside of your local network or use an Internet Mail Server for mailing.
Warnings
- Using this method to send harassing or illegal messages could easily catch up with you. System administrators closely monitor their outbound mail servers.⧼thumbs_response⧽
Things You'll Need
- Telnet client
- The address of a mail server capable of relaying mails
- Valid email address
References
About This Article
You can both check your server's responsiveness and send an email to a recipient through your computer's Telnet, which is a command line-only feature. Start by opening Command Prompt (Windows) or Terminal (Mac), then type in telnet and press ↵ Enter. You can then enter the command to open the Telnet connection; if the connection is responsive, you'll be able to send an email through Telnet by entering the necessary commands one at a time.