Chapter 16
Acid-Base Equilibria
By Boundless
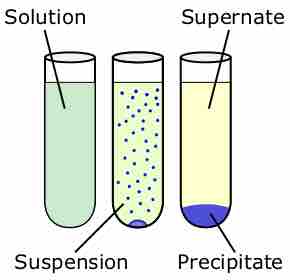
The equilibrium constants for homogeneous and heterogeneous solutions need to be calculated differently.

The common ion effect describes the changes that occur with the introduction of ions to a solution containing that same ion.

A buffer is a solution of weak acid and conjugate base or weak base and conjugate acid used to resist pH change with added solute.
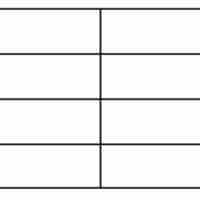
The pH of a buffer solution can be calculated from the equilibrium constant and the initial concentration of the acid.
The Henderson–Hasselbalch equation connects the measurable value of the pH of a solution with the theoretical value pKa.
The changed pH of a buffer solution in response to the addition of an acid or a base can be calculated.
An alkaline buffer can be made from a mixture of the base and its conjugate acid, but the formulas for determining pH take a different form.

The pH of a buffer depends on the ratio [base]/[acid] rather than on the particular concentration of a specific solution.

For an effective buffer, there must be enough acid/conjugate base to consume all newly added ions so that the pH is maintained.
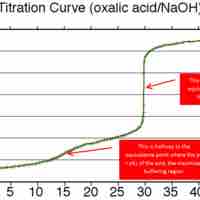
A buffer's capacity is the pH range where it works as an effective buffer, preventing large changes in pH upon addition of an acid or base.
A strong acid will react with a strong base to form a neutral (pH = 7) solution.
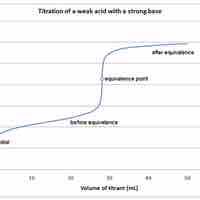
A weak acid will react with a strong base to form a basic (pH > 7) solution.
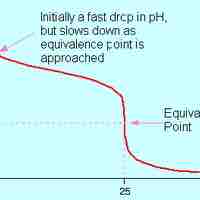
A strong acid will react with a weak base to form an acidic (pH < 7) solution.
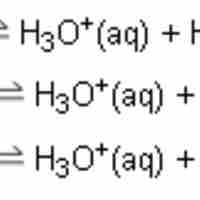
Polyprotic acids, also known as polybasic acids, are able to donate more than one proton per acid molecule.
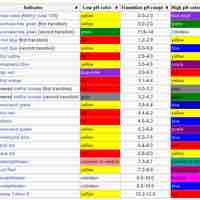
An indicator is a weak acid (or a weak base) that has different colors in its dissociated and undissociated states.
2.jpg)
The solubility product is the equilibrium constant representing the maximum amount of solid that can be dissolved in aqueous solution.

Molar solubility is the number of moles of a solute that can be dissolved per liter of solution before the solution becomes saturated.
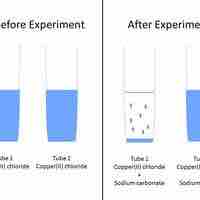
A set of rules can be used to predict whether a combination of cations and anions in solution will recombine and precipitate.
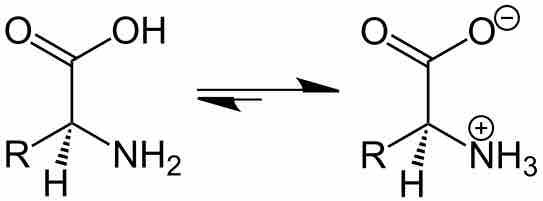
By changing the pH of the solution, you can change the charge state of the solute.

Fractional precipitation can be used to determine which ions are present in a solution by taking advantage of their different solubilities.

Adding a common ion decreases the solubility of a solute, causing it to precipitate.