Section 5
Solubility Equilibria
Book
Version 33
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Chemistry
Chemistry
by Boundless
6 concepts
2.jpg)
Solubility Product
The solubility product is the equilibrium constant representing the maximum amount of solid that can be dissolved in aqueous solution.

Molar Solubility and Relative Solubility
Molar solubility is the number of moles of a solute that can be dissolved per liter of solution before the solution becomes saturated.
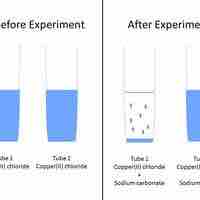
Predicting Precipitation Reactions
A set of rules can be used to predict whether a combination of cations and anions in solution will recombine and precipitate.
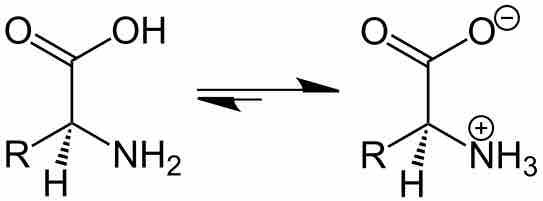
The Effect of pH on Solubility
By changing the pH of the solution, you can change the charge state of the solute.

Ion Separation by Fractional Precipitation
Fractional precipitation can be used to determine which ions are present in a solution by taking advantage of their different solubilities.

Effect of a Common Ion on Solubility
Adding a common ion decreases the solubility of a solute, causing it to precipitate.