Chapter 15
Acids and Bases
By Boundless

Acids and bases will neutralize one another to form liquid water and a salt.
An Arrhenius acid dissociates in water to form hydrogen ions, while an Arrhenius base dissociates in water to form hydroxide ions.
A Brønsted-Lowry acid is any species capable of donating a proton; a Brønsted-Lowry base is any species capable of accepting a proton.
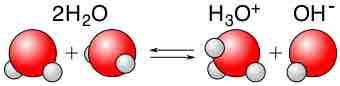
Water is capable of acting as either an acid or a base and can undergo self-ionization.
The acid dissociation constant (Ka) is the measure of the strength of an acid in solution.
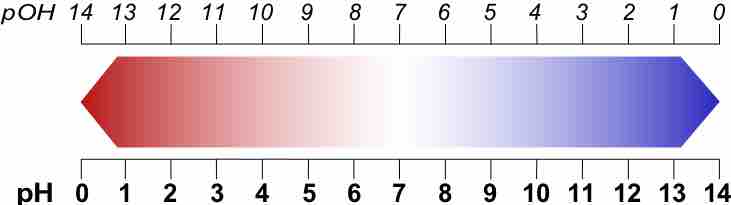
A p-scale is a negative logarithmic scale.
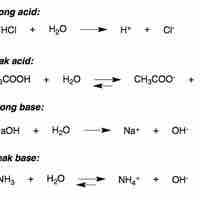
In water, strong acids completely dissociate into free protons and their conjugate base.

A weak acid only partially dissociates in solution.
Percent dissociation represents an acid's strength and can be calculated using the Ka value and the solution's pH.

Strong bases either dissociate completely in solution to yield hydroxide ions, or deprotonate water to yield hydroxide ions.
In aqueous solution, a weak base reacts incompletely with water to yield hydroxide ions.

The base dissociation constant (Kb) measures a base's relative strength.
.jpg)
When dissolved in water, a basic salt yields a solution with pH greater than 7.0.
When dissolved in water, acidic salts form solutions with pH less than 7.0.
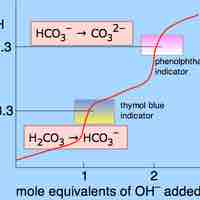
Some salts, such as ammonium bicarbonate (NH4HCO3), contain cations and anions that can both undergo hydrolysis.