Chapter 17
Thermodynamics
By Boundless
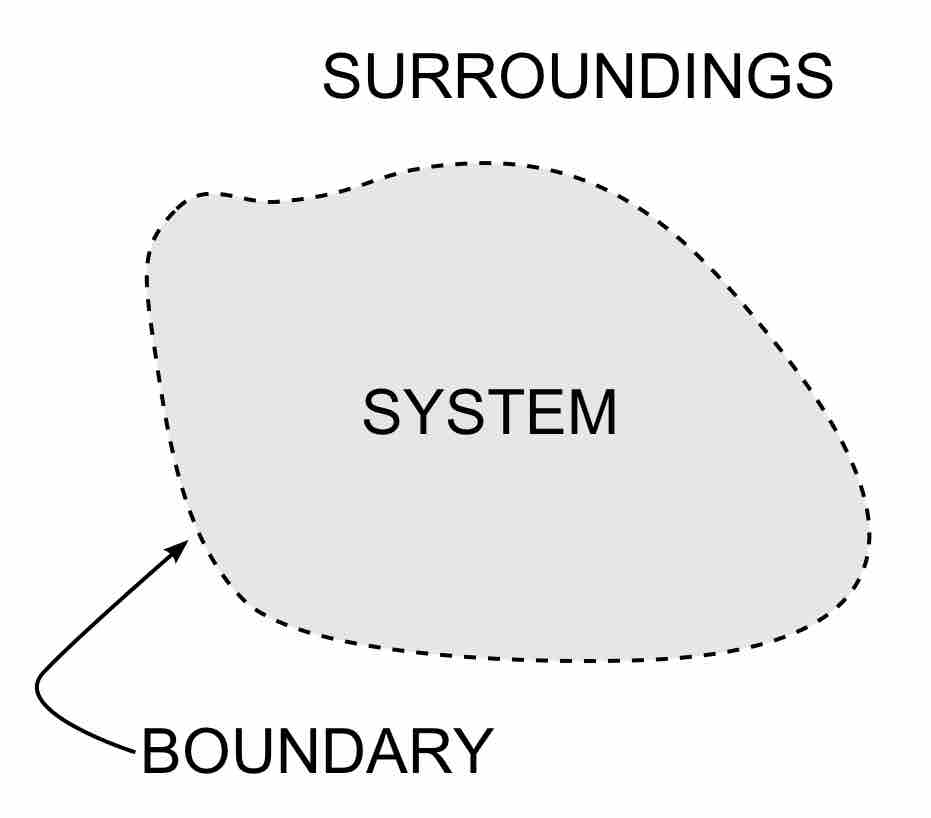
The laws of thermodynamics define fundamental physical quantities (temperature, energy, and entropy) that characterize thermodynamic systems.
Spontaneous processes do not require energy input to proceed, whereas nonspontaneous processes do.
Energy can be shared between microstates of a system. With more available microstates, the entropy of a system increases.

The concept of entropy can be described qualitatively as a measure of energy dispersal at a specific temperature.
The standard entropy of a substance (its entropy at 1 atmospheric pressure) helps determine if a reaction will take place spontaneously.
Irreversible reactions result in a change in entropy to the surroundings.
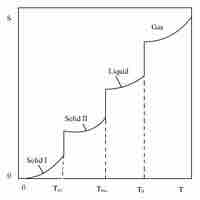
The third law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of a system approaches a constant value as the temperature approaches absolute zero.
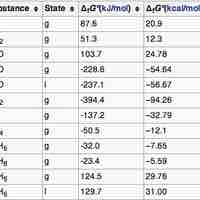
The standard Gibbs Free Energy is calculated using the free energy of formation of each component of a reaction at standard pressure.
ΔG determines the direction and extent of chemical change.
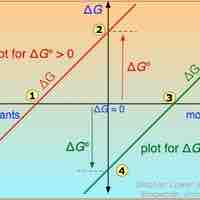
A single reaction can have an infinite number of ΔG values, reflecting the infinite possible compositions between reactants and products.

Gibbs free energy is dependent on pressure.
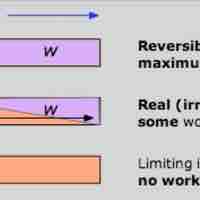
The Gibbs free energy is the maximum amount of non-expansion work that can be extracted from a closed system.