This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Travis Boylls. Travis Boylls is a Technology Writer and Editor for wikiHow. Travis has experience writing technology-related articles, providing software customer service, and in graphic design. He specializes in Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, and Linux platforms. He studied graphic design at Pikes Peak Community College.
This article has been viewed 1,384 times.
Learn more...
Do you want to know how to enhance your bass using Audiotool? Audiotool is an excellent program that allows you to create and collaborate on music tracks from within your web browser. There are a variety of effects you can use to enhance the bass in Audiotool. This wikiHow teaches you how to enhance the bass in Audiotool.
Steps
What Are the Best Bass Instruments?
-
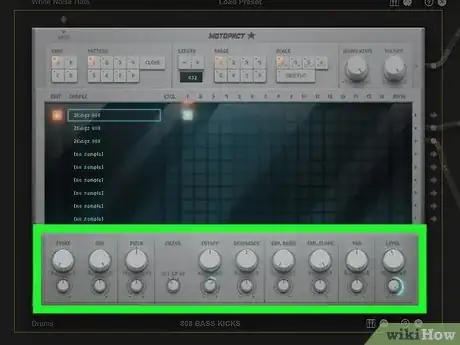
There are tons of instruments and sounds in Audiotool. Audiotool has 5 programmable synthesizers and 3 programmable drum machines. They each have their own presets and settings. The amount of sounds you can get out each of these is infinite. You can sample different presets to see which sounds you like best. What gives you the best bass will depend on your personal preferences and what style of music you are creating. Sample different presets to see what you like best.
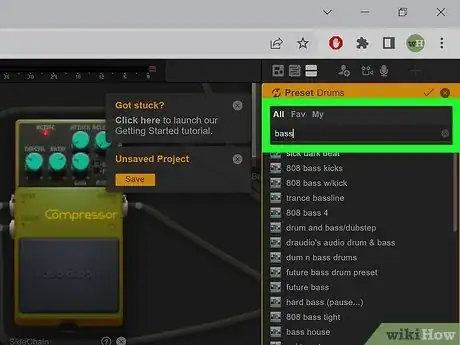
- To load a preset, right-click a synthesizer or drum machine and select Presets. Then click Load. Type "Bass" in the search bar at the top of the presets menu to the right. Click one of the presets to hear a sample of it. Double-click the preset to apply it.
- The Machinste is the easiest drum machine to program. Simply click the square next to the drum you want to add to a pattern on the beat you want to to play. Click and drag to make that drum louder or quieter. The beat will replay on a loop. You can adjust how long of a loop you want to use.
What are the Different Ways to Change the Bass Tone in Audiotool?
-
There are a variety of knobs and adjustments you can make in Audiotool. You see these on a variety of instruments and effects in Audiotool as well as in other digital audio workstations. Some of the knobs and adjustments you might run into are as follows:
- Volume/Level: When you see a knob labeled "Volume" or "Level", it simply changes the loudness of the sound output after the sound has been processed. It may be applied to an individual instrument, synthesizer drum, drum machine, channel, or your entire mix. One of the easiest ways to increase the bass volume is to turn on the volume on your bass instruments and/or the channels they are connected to.
- Gain: Gain is similar to volume, except that it effects how loud a sound is before it has been processed. In addition to making a sound louder, adding gain can also add distortion to a sound, giving it a crunchy or dirty sound. Increasing the gain on bass synthesizer or tracks can also enhance your bass tone as well as add a bit of white noise to the mix. Adding too much gain can cause it to sound distorted and dirty.[1] X Research source
- Wave form: Wave form is the the shape of the sound wave that a synthesizer creates. The most common wave forms are square wave, saw wave, and sine wave. Try using a square wave or sine wave to create your bass tones.
- Pitch: The pitch is the tone an instrument makes. On a synthesizer, it is the note that is played. On a drum machine, it is the tone a drum makes when it is hit.
- Octave: A synthesizer can produce 12 notes that are represented on a keyboard. These notes repeat at higher and lower frequencies, which are called octaves. The higher the octave, the higher the pitch. The lower the octave, the lower the pitch. Most bass tones are in the low octave ranges from octave 0 to 2.
- Modulation: Modulation just means change. It can mean a variety of things in music production. It can be a change in pitch, sound, wave form, or frequency.
- Attack: When a note is hit on a synthesizer, it goes through 4 phases: attack, decay, sustain, and release. Attack is how long (in milliseconds) it takes for a sound wave to go from silence to it's peak amplitude.
- Decay: Decay is how long it takes for a sound wave on a synthesizer to drop from it's peak amplitude to a sustained tone.
- Sustain: Sustain is how long a sound wave on a synthesizer is held while the key is pressed.
- Release: Release is how long it takes a sound wave on a synthesizer to ring out after the key has been released.
What Effects Can I Use to Enhance the Bass?
-
Audiotool has many effects you can use to increase the bass. The following are just a couple:[2] X Research source
- Tube Distortion: The Tube Distortion effect is another way you can add additional gain to an instrument or drum machine. You can find the Tube Distortion pedal in the Devices panel under Effects. Drag it onto your desktop and connect your drum machine or synthesizer to the input on the Tube Distortion effect and then connect it to a channel on your Centroid mixer. Use Drive knob to adjust the level of distortion and use the Gain knob to enhance the gain.
- Compression: Compression is another good way to enhance the sound of your bass. You can find the Compressor pedal in the Devices panel under "Effects." Drag the compressor pedal onto your desktop and connect your drum machine or synthesizer to the input of the Compressor pedal. Then connector the compressor pedal to one of the tracks on your Centroid mixer.
- Exciter: The Exciter effect can also be used to enhance bass. It can be used to adjust the tone and power of a sound. You can find the Exciter effect in the Devices panel under "Effects."
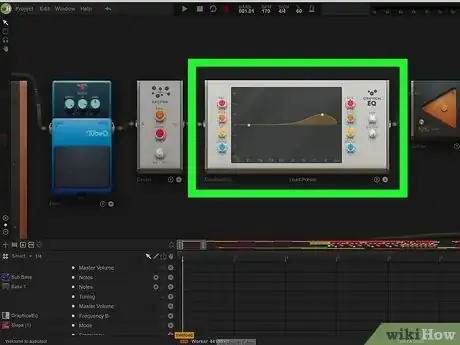
- Graphic EQ: Use a GraphicEQ to enhance the low frequencies. The GraphicEQ allows you to adjust the high and low frequencies at the same time. The knobs on the left adjust the low frequencies, and the knobs on the right adjust the high frequencies. Use the "Freq" knob to adjust the frequency you want to adjust. Use the yellow knob to adjust the width of the frequency (how much of the overall frequency is affected). Use the "Gain" knob to increase or decrease the frequency. Graphic EQ can be applied to individual instruments or your entire mix. To apply it to your entire, mix, connect the output on your mixer to the input on the Graphic EQ. Then connect the Output on your GraphicEQ to the input on your Stereo Output.
Can I Record a Bass Guitar in AudioTool?
-
Audiotool does not allow you to connect external instruments. The Probe sample audio editor allows you to record a sample using your computer mic, but it does not work with an audio interface, which is what is needed to record using a guitar or bass. However, you can record a sample using a guitar or bass using another program and upload it to the cloud.
- To record a sample using a guitar or bass guitar, you need to have an audio interface that you can use to connect your guitar or bass to your computer. Then you need recording software to record with. Free audio recording software includes Audacity and Reaper.
- It's recommended you use a metronome when recording outside of Audiotool so that you can match the tempo of your Audiotool mix.
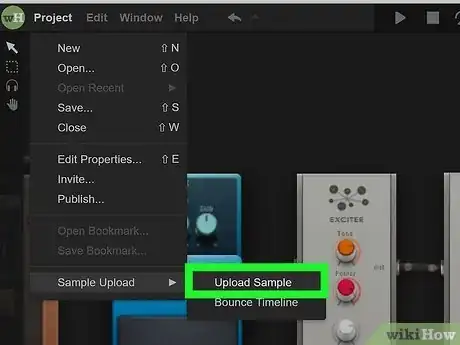
- To open the Probe sample editor in another browser tab, click Project in the upper-right corner of Audiotool. Then click Sample Upload followed by Upload Sample. Then click Understand to agree to the terms and conditions. To upload a pre-recorded sample, click File in the menu bar at the top. Then click Browse. Select the audio file for your sample and click Open. To upload the sample to the cloud, click File and then click Upload. You can only upload a maximum of 30 seconds.
How Do I Get the Best Bass Sound On My Computer?
-
You need a decent set of headphones or computer speakers. Most laptop speakers do not have strong bass sound. For good bass, you want a decent set of computer speakers with a subwoofer or you need a good pair of headphones.
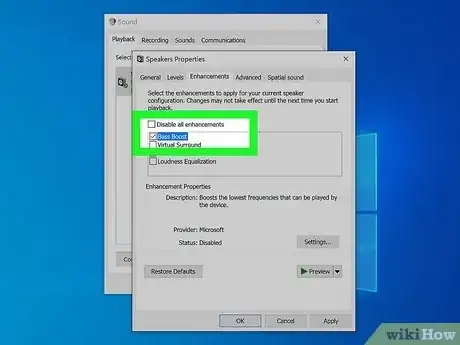
- If you are using a desktop computer, you can turn on bass boost in the Windows Sound Settings menu. Alternatively, you can use third-party EQ software to enhance the bass on your PC or Mac.
- If you have 2.1 or 5.1 PC speakers with subwoofer, the best place to put the subwoofer is on the floor next to the desk (not under it) about 8-12 inches from the wall.[3] X Research source
Other wikiHows

 How to Relieve & Prevent Headaches & Migraines Fast
How to Relieve & Prevent Headaches & Migraines Fast
 Best Ways to Unclog a Toilet
Best Ways to Unclog a Toilet
 How to Take a Screenshot on a Windows PC: 8 Simple Tricks
How to Take a Screenshot on a Windows PC: 8 Simple Tricks

 How to Take Care of Potted Orchids
How to Take Care of Potted Orchids

References
About This Article