This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Jack Lloyd. Jack Lloyd is a Technology Writer and Editor for wikiHow. He has over two years of experience writing and editing technology-related articles. He is technology enthusiast and an English teacher.
This article has been viewed 382,373 times.
Learn more...
This wikiHow teaches you how to enable access to the Registry Editor on a Windows computer. Whether your Registry Editor has been disabled by an administrator on your school network or a virus is preventing you from opening it, there are a few ways you can attempt to bring the Registry Editor back online.
Steps
Using Run
-
1
-
2Type run into Start. This will search your computer for the "Run" app.Advertisement
-
3Click Run. It's at the top of the Start window. Run will open.
- If you're on a computer where Run is disabled, you won't be able to open Run.
-
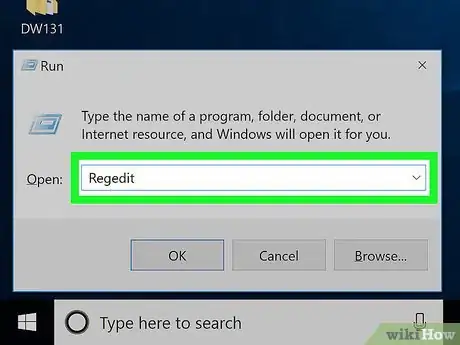
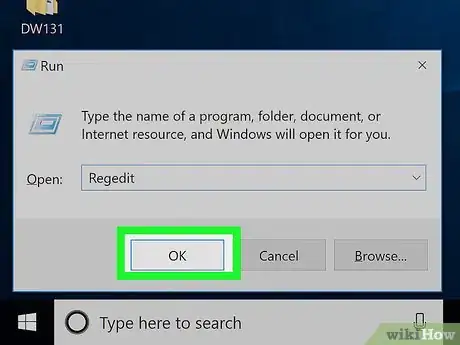
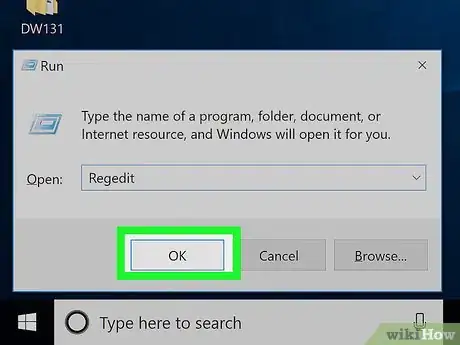
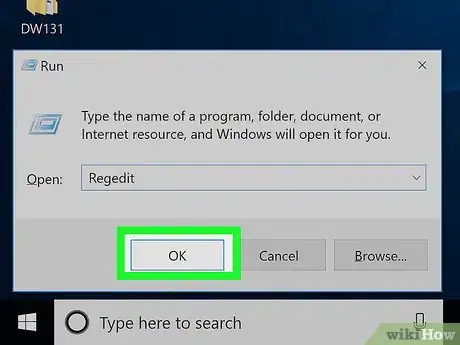
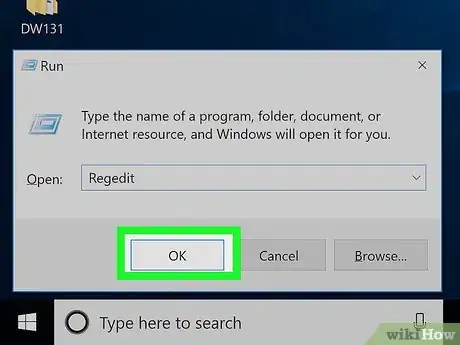
4Type regedit into Run. This is the command to open the Registry Editor.
-
5Click OK. Doing so will run the Registry Editor open command. If the Registry Editor prompts you for permission and then opens when you click Yes, your problem is fixed.
- If the Registry Editor doesn't open, you'll need to try another method in this article.
- If you receive a pop-up window that says "Registry editing has been disabled by your administrator", you'll need to edit your Group Policy settings. This will only work if you control the Group Policy Editor on your network.
Running a Security Scan
-
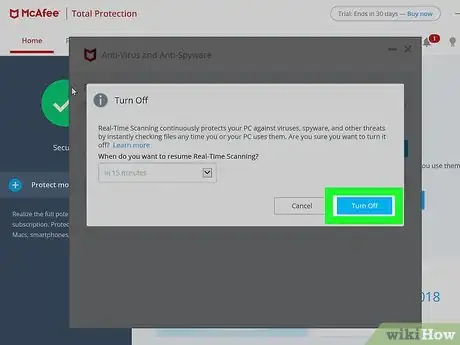
1Disable any third-party antivirus programs. Third-party antivirus programs—that is, any antivirus program that isn't Windows Defender—can cause several different problems with your computer. Because of this, disable all antivirus protection that isn't Windows Defender before continuing.
-
2
-
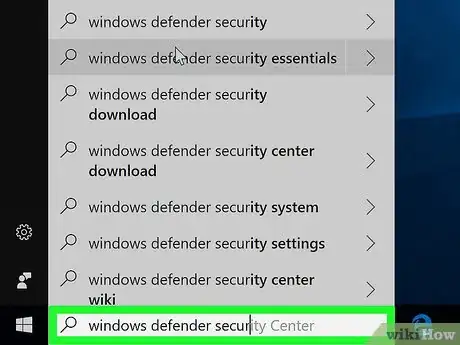
3Type windows defender security center into Start. This will search your computer for the Windows Defender application.
- On some versions of Windows, this may show up simply as Windows Defender instead.
-
4Click Windows Defender Security Center. It's a white shield on a grey background. You'll see it at the top of the Start window.
-
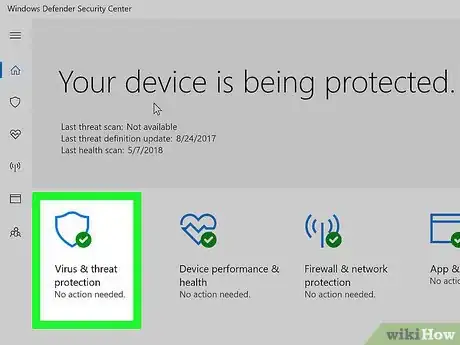
5Click the shield icon. This icon is in the upper-left corner of the Windows Defender page.
- When expanded, this option is called Virus & threat protection.
-
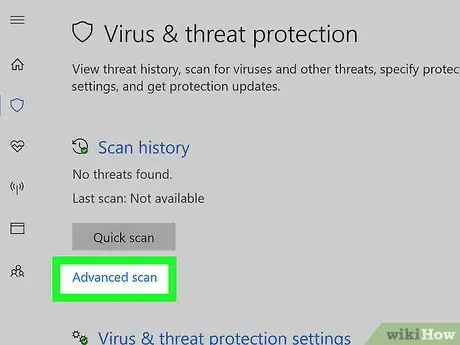
6Click Advanced scan. It's a link below the Quick scan button in the middle of the page.
- On some versions of Windows Defender, click the Home tab instead as there is no Advanced Scan section.
-
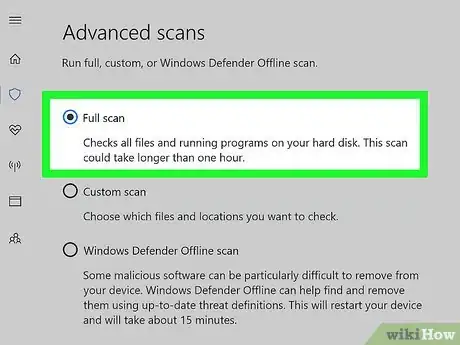
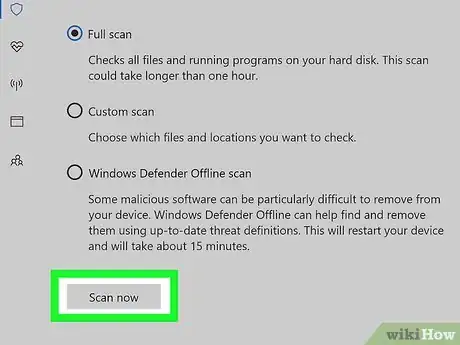
7Make sure "Full scan" is checked. Click the circle to the left of "Full scan" at the top of the page if it isn't already filled in.
-
8Click Scan now. It's in the middle of the page. Windows Defender will start scanning your computer for malicious software that might be preventing Registry access.
-
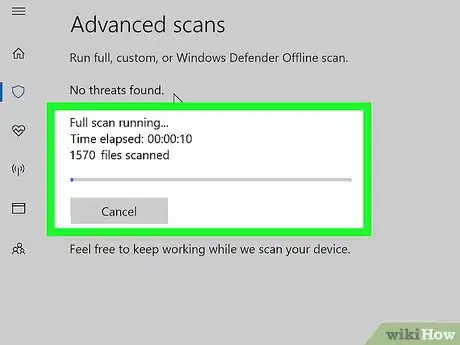
9Wait for the scan to complete. If anything malicious turns up during the scan, Windows Defender will alert you and give you the option of removing the dangerous items.
- If this scan doesn't find anything, repeat the scan with "Windows Defender Offline scan" checked instead of "Full scan" checked.
-
10Try to open Registry Editor. Once the scan completes, open Start, type in regedit, and press ↵ Enter. If the Registry Editor still doesn't open, you'll need to try a different method.
- You may need to restart your computer before you can access Registry Editor after the scan.
Using Command Prompt
-
1
-
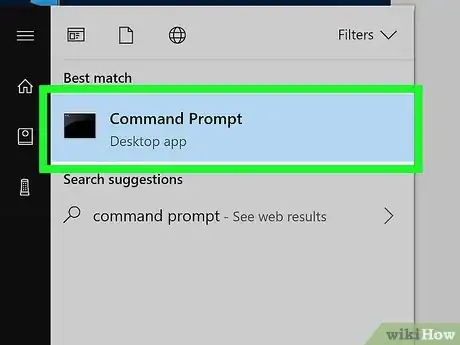
2Type command prompt into Start. This will bring up the Command Prompt icon in the Start menu.
-
3
-
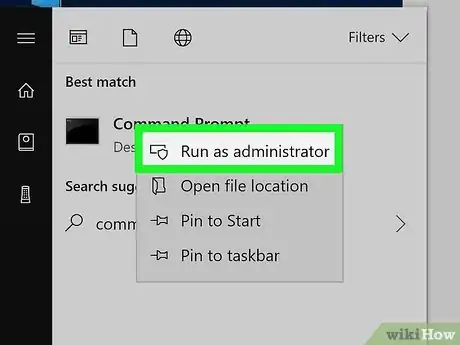
4Click Run as administrator. It's an option in the drop-down menu.
- If you aren't an administrator on this computer, you won't be able to complete this method.
-
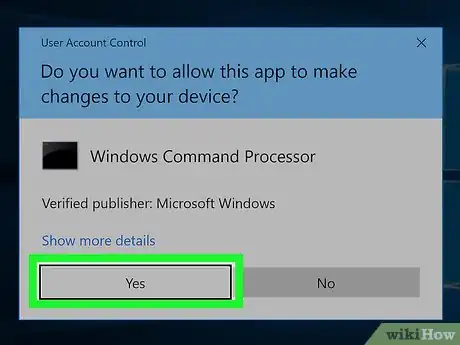
5Click Yes when prompted. Doing so will open Command Prompt in Administrator mode.
-
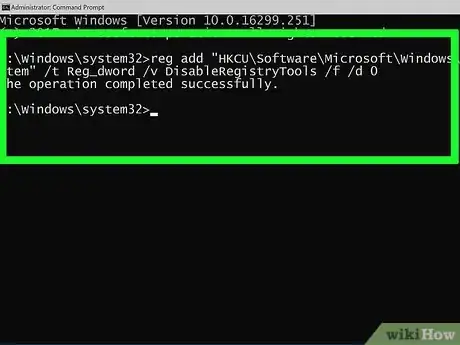
6Enter the Registry refresh command. Type reg add "HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System" /t Reg_dword /v DisableRegistryTools /f /d 0 into Command Prompt, then press ↵ Enter.
-
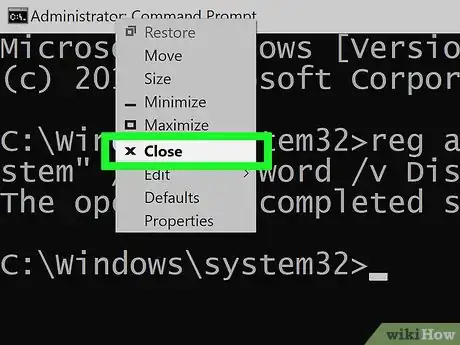
7Close Command Prompt. Your command should have re-enabled the Registry Editor.
-
8Try to open Registry Editor. Open Start, type in regedit, and press ↵ Enter. If the Registry Editor doesn't open, proceed to the next step.
-
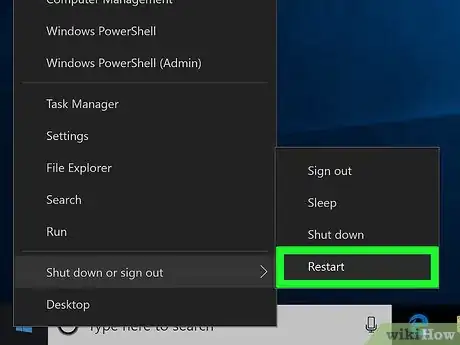
9Restart your computer. Open Start, click the Power icon , and click Restart. Once your computer finishes restarting, you can try opening Registry Editor again.
- If Registry Editor still won't open, you may be able to use a script to force it to open.
Using Group Policy Editor
-
1
-
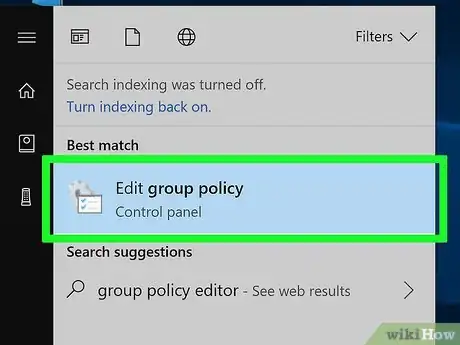
2Type group policy editor into Start. This will search your computer for the Group Policy Editor program.
-
3Click the Group Policy Editor icon. It's at the top of the Start menu. Group Policy Editor will open.
- On some versions of Windows it may read Edit group policy instead.
-
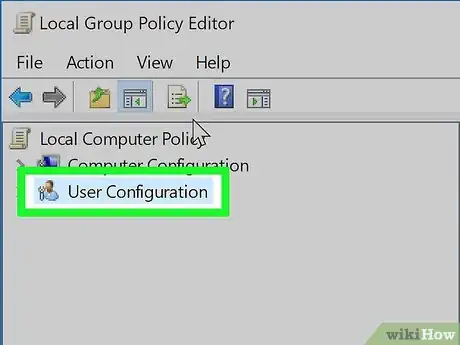
4Double-click User Configuration. Doing so will expand this item to display the folders below it.
- Skip this step if User Configuration is already expanded.
- If you don't see this option, first double-click the Local Computer Policy item at the top of the sidebar.
-
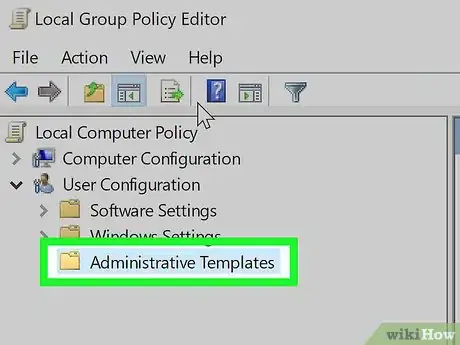
5Click Administrative Templates. This folder is near the bottom of the User Configuration list of folders.
-
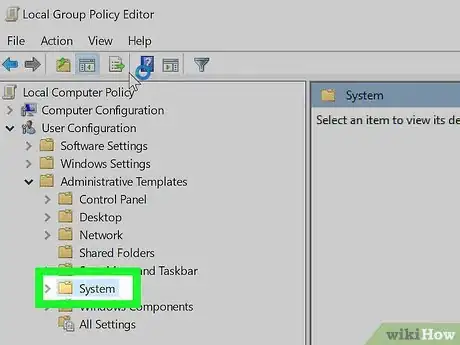
6Double-click the System folder. It's on the right side of the Group Policy Editor window.
-
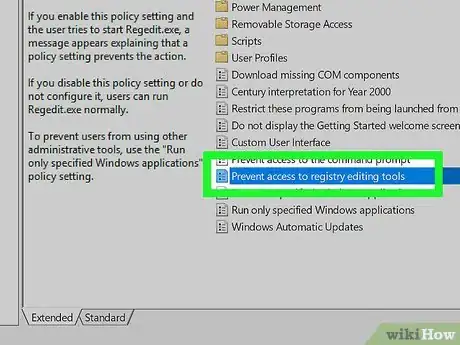
7Double-click Prevent access to registry editing tools. You'll find this item on the right side of the window.
- You may have to scroll down to find it.
-
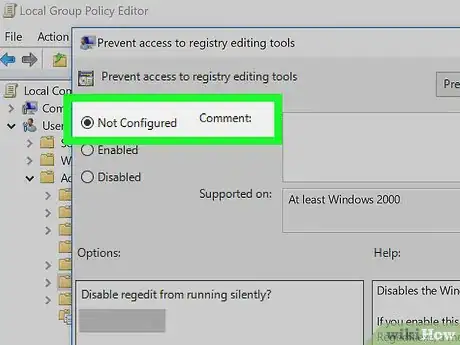
8Check the "Not Configured" box. It's in the upper-left side of the pop-up window.
-
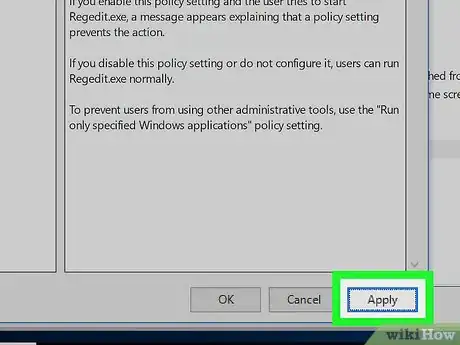
9Click Apply, then click OK. These are both at the bottom of the window. Doing so should re-enable Registry Editor on your computer.
-
10Try to open Registry Editor. Open Start, type in regedit, and press ↵ Enter. If Registry Editor opens, you have successfully bypassed the Group Policy Editor restrictions.
Using a Visual Basic Script
-
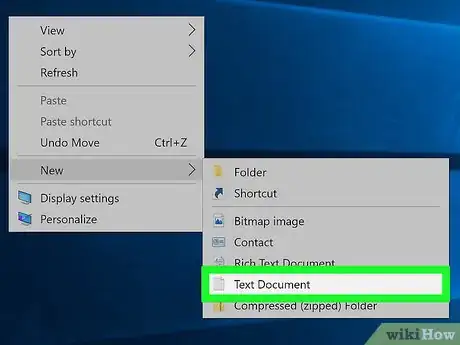
1Open a new Notepad document. Open Start, type notepad in, and click the blue Notepad app. This will open a new Notepad document.
-
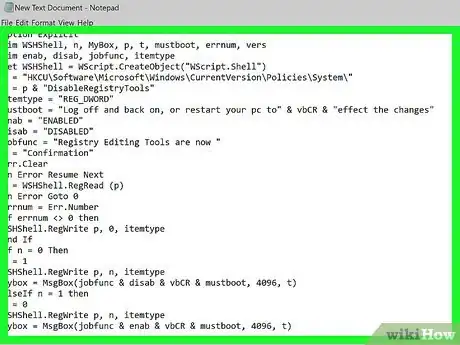
2Copy the following code into the Notepad document:
Option Explicit
Dim WSHShell, n, MyBox, p, t, mustboot, errnum, vers
Dim enab, disab, jobfunc, itemtype
Set WSHShell = WScript.CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
p = "HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System\"
p = p & "DisableRegistryTools"
itemtype = "REG_DWORD"
mustboot = "Log off and back on, or restart your pc to" & vbCR & "effect the changes"
enab = "ENABLED"
disab = "DISABLED"
jobfunc = "Registry Editing Tools are now "
t = "Confirmation"
Err.Clear
On Error Resume Next
n = WSHShell.RegRead (p)
On Error Goto 0
errnum = Err.Number
if errnum <> 0 then
WSHShell.RegWrite p, 0, itemtype
End If
If n = 0 Then
n = 1
WSHShell.RegWrite p, n, itemtype
Mybox = MsgBox(jobfunc & disab & vbCR & mustboot, 4096, t)
ElseIf n = 1 then
n = 0
WSHShell.RegWrite p, n, itemtype
Mybox = MsgBox(jobfunc & enab & vbCR & mustboot, 4096, t)
End If -
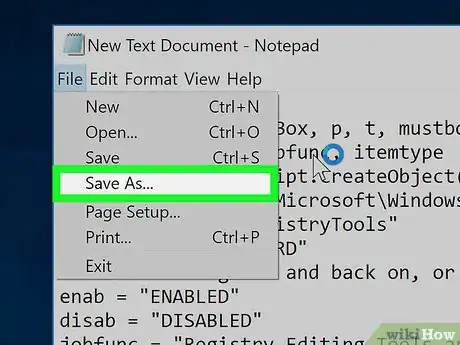
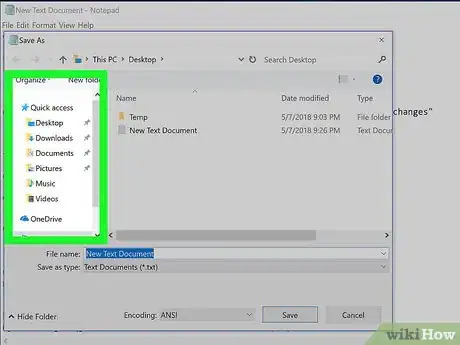
3Click File. It's in the top-left side of the Notepad window.
-
4Click Save As…. This option is near the top of the File drop-down menu.
-
5Select a save location. Click the Desktop folder on the left side of the Save As window.
-
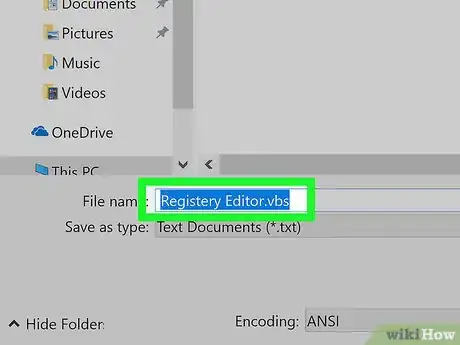
6Enter
Registry Editor.vbsas the file name. Do this in the "File name:" field. -
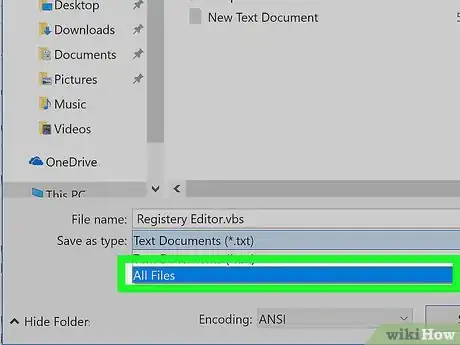
7Select a file type. Click the drop-down box next to "Save as type:", then click All Files. This will save your document in the correct file format.
-
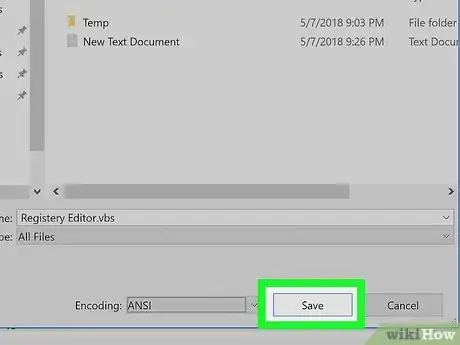
8Click Save. It's in the bottom-right corner of the Save As window. This will create your file.
-
9Close Notepad. Click the X in the top-right corner of Notepad to do so.
-
10Double-click the VBS file. Doing so will prompt the script to run.
- This script will switch the registry editor's disabled/enabled setting. Do not run it a second time, or the registry editor will be disabled again.
-
11Try to open Registry Editor. Open Start, type in regedit, and press ↵ Enter. If the Registry Editor still won't open, you may need to take your computer into a tech department to have a professional look at it.
Community Q&A
-
QuestionHow do I enable task manager?
 Reyhan PalakkaCommunity AnswerPress Ctrl+Shift+Esc in the same time.
Reyhan PalakkaCommunity AnswerPress Ctrl+Shift+Esc in the same time. -
QuestionBoth regedit and cmd are disabled, what can I do?
 Community AnswerIt may be because you do not have administration privileges. Ask your system administrator if it is a work computer, or log into the main account if it's a home PC.
Community AnswerIt may be because you do not have administration privileges. Ask your system administrator if it is a work computer, or log into the main account if it's a home PC. -
QuestionI changed my install location through regedit from c drive to e drive. After restarting regedit, task manger is not opening, there are some extra downloaded files, and it is showing invalid path. What can I do?
 Community AnswerThere will be a lot of mis-entries in the registry due to the different applications you have used. Use a registry repair app and restore the registry file.
Community AnswerThere will be a lot of mis-entries in the registry due to the different applications you have used. Use a registry repair app and restore the registry file.
Warnings
- Never edit the registry unless you know exactly what you are doing. A mistake could make your operating system unusable.⧼thumbs_response⧽
About This Article
1. Open the Windows search bar.
2. Type Run.
3. Click Run.
4. Type Regedit.
5. Click OK.