wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, 25 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time.
This article has been viewed 547,853 times.
Learn more...
One of the simplest ways to give your laptop more hard drive space, or backup all of your important files without burning them to CD or DVD, is to build your own external hard drive. This hard drive would be able to connect to any computer with a spare USB port. You can easily and quickly transfer large files between computers, and also have a form of backup in the event something ever happens to your computer. This external hard drive will work on computers running Windows 2000/XP, OS X, or Linux.
Steps
-
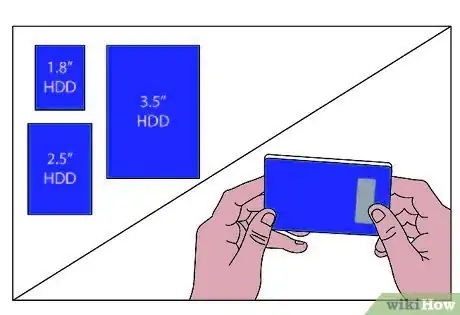
1You must obtain an internal hard drive (from now on referred to as a HDD). The first step is to decide on one of the standard physical sizes for any HDD. If you already have a spare HDD laying around for this project, skip to step 2. There are basically 3 HDD sizes: 1.8", 2.5", and 3.5". 1.8" and 2.5" are the standard sizes for laptop HDD's. Laptop HDD's can be powered by the USB cable, so there is no AC adapter needed. Laptop HDD's are however more expensive than internal PC HDD's, so if you are not worried about size or another power cord, a desktop PC HDD may be the way to go.
-
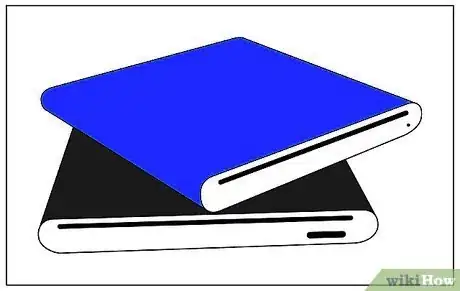
2Choose and purchase a compatible enclosure. Take into consideration the physical size of your HDD, as well as its interface (ATA100, ATA133, Serial ATA150, Serial ATA II, etc.). Decide on a connection type that suits the needs of all computers that will be connected. USB2.0 is currently a good standard, and it will work on any computer or laptop with a free USB connection. FireWire (IEEE1394) is even faster, however it is not as common in all computers yet. Be sure to also compare fan noise levels (if it has a fan, and if the noise level is displayed). For a HDD that will be running whenever your computer is turned on, a fan will be most likely a good thing to have, while HDD's used primarily for backup usually won't need one. Also check to see if there is a power switch on 3.5" enclosures. Without one, you will need to unplug the adapter to power down the drive. For backup this isn't a big deal, but some people using their drive for secondary storage might find it annoying to plug and unplug every time they start and shut down their computers.Advertisement
-
3Unwrap both your enclosure and HDD.
-
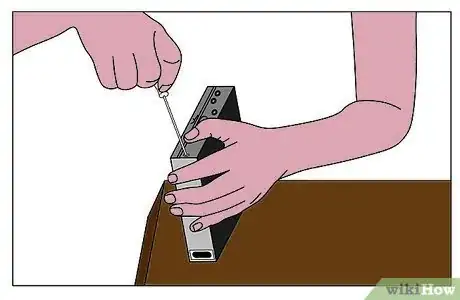
4Follow your instructions on how to correctly open your enclosure.
-
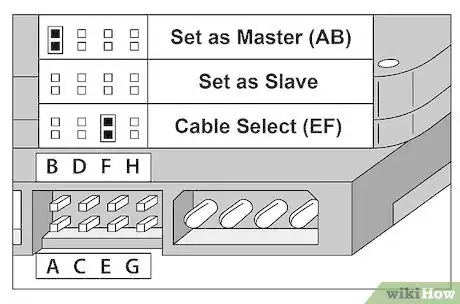
5Set your HDD to the Master setting (or Master/No Slave if one exists). This jumper setting is located between the Molex power connector (4 large round pins) and the ATA/SATA connector. You will see 2 rows of four or five small pins, and a small clip (jumper) connected to 2 of them. Pull out the jumper with a tool such as tweezers or a pencil, and place it in the Master position if it is not already there. A diagram of the different jumper settings can usually be found right on the top label of the HDD.
-
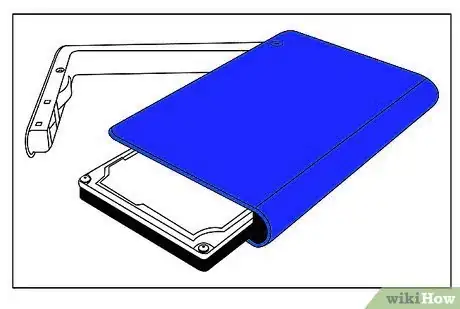
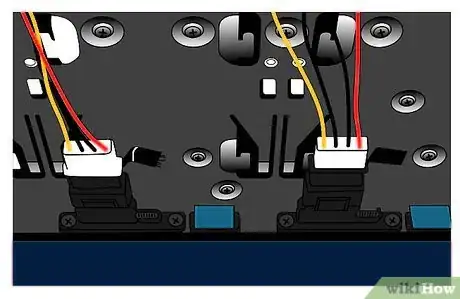
6Connect your enclosure's Molex power connector and ATA/SATA ribbon cable to your HDD. Although it would be very hard to accidentally plug these in upside-down, take a moment to make sure that the ribbon cable and power connector are properly aligned before inserting them.
-
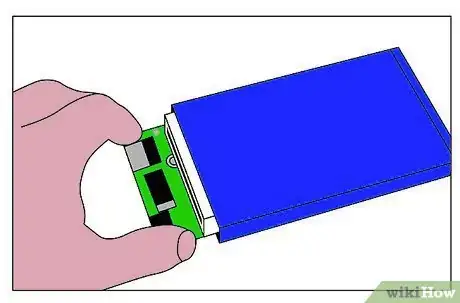
7Screw the HDD into the enclosure. 4 or more screws were supplied with the enclosure. There will be 4 holes, 2 on each side of the HDD, and corresponding holes inside the enclosure.
-
8Take one last look at the inside before you close it. Make sure you did not forget to connect anything. Read your instructions (you HAVE been reading them too, haven't you? :) and make sure you covered all of the steps. It will be a pain to open it all over again because you forgot to change the jumper to Master or something.
-
9Close the enclosure.
-
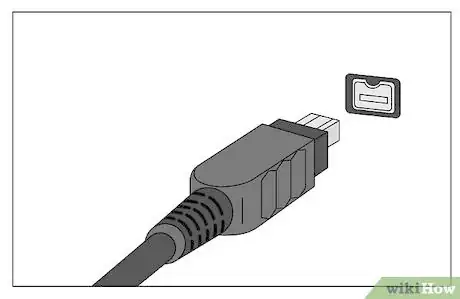
10Connect the power cord (if one is necessary) and the USB or FireWire cord to your drive.
-
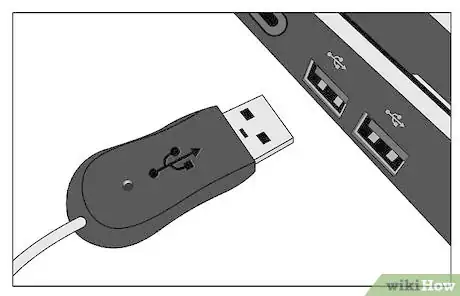
11USB and FireWire are Plug-and-Play, meaning that you do not need to turn off the computer before connecting your drive. Connect the other ends of these cords to your computer and surge protector (you ARE using a surge protector, right? :).
-
12Turn your computer on if it is not already. Go to My Computer (or Computer for Windows Vista or Windows 7). It is most likely on your desktop, but can also be found in the Start menu.
-
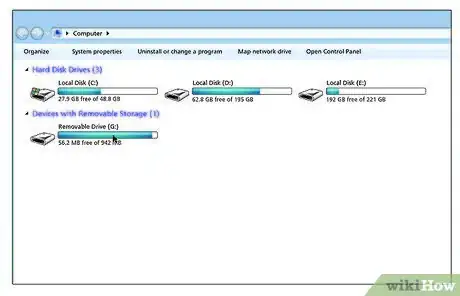
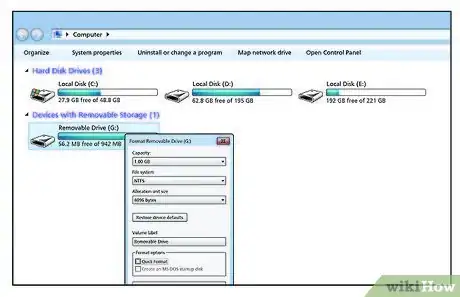
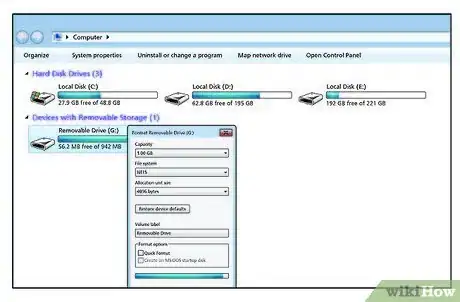
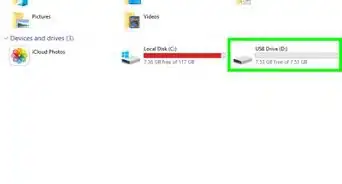
13You should see a new device in the 'Devices with Removable Storage' section.
-
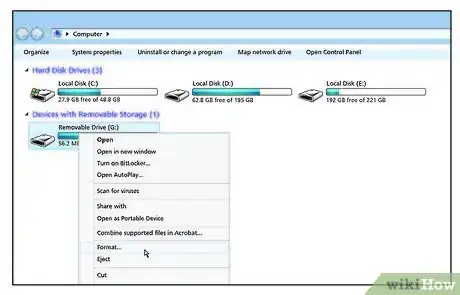
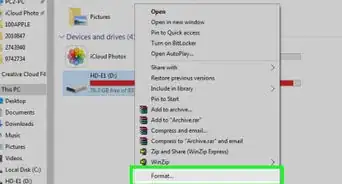
14Right click on it and select Format (about halfway down the list).
-
15Format the drive using NTFS for use in Windows (ext3 or ext4 is good for Linux) as the File System. To read and write from both Linux and Windows, use fat32. You can give it a Volume Label if you wish. Example: External, Secondary, Backup, etc. Be sure Quick Format is not selected. This will allow any bad sectors to be recognized and to be roped off from any data being stored later on.
-
16Wait for formatting to complete. This may take longer for large drives.
-
17Good Job! You have successfully built your own external hard drive.
Community Q&A
-
QuestionHow do I connect these?
 Community AnswerWith an adapter that connects your hard drive with a USB port.
Community AnswerWith an adapter that connects your hard drive with a USB port. -
QuestionWhat is the disk in a disk drive made of?
 Community AnswerThe disks spinning inside your hard drive are actually made of aluminium. Make sure you do not drop your hard drive, or you might risk data loss.
Community AnswerThe disks spinning inside your hard drive are actually made of aluminium. Make sure you do not drop your hard drive, or you might risk data loss. -
QuestionCan I purchase an regular HDD, or will it need to be a Toshiba drive?
 Community AnswerThe same size/interface drive from any manufacturer will work.
Community AnswerThe same size/interface drive from any manufacturer will work.
Warnings
- Never force the ribbon cable! There should be some resistance when connecting it, but if it won't go in, the pins may not be lined up correctly. If you do manage to bend the pins (hopefully not too many of them), take time to straighten them using a pair of needlenose pliers.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- HDD's are very easy to damage when dropped onto a hard surface. The read/write heads can crash onto the platter/s and leave physical damage on the platter, rendering that space on the disk useless as well as making the unit as a whole too damaged for use.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- You should always use all 4 screws when adding a HDD to any computer or enclosure, and make them tight. HDD's spin at a high RPM, and vibrations may occur if the drive is not properly secured. These vibrations can cause an annoying humming noise, and even damage to the drive over time.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Keep movement of the drive to a minimum while it is turned on. This once again causes unnecessary vibrations.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Remember that when the hard drive is outside of the enclosure, it is un-protected from static discharge. So do try to keep it from static and the causes thereof.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Drivers are needed if connecting an external Hard Drive (By USB) on Windows 98 (And 98 SE)⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Make sure your enclosure has no HDD capacity limit (no larger than a certain number of Gigabytes (GB)), or that this limit does not conflict with your drive's capacity. Unfortunately, some older enclosures may have a somewhat low limit (say 132GB) and not advertise this. Be careful! And if you attempt to use a larger HDD, format it to this limit or lower, or you will most likely encounter sector read errors or something :(⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Be sure to use the "Remove Hardware" icon on the task bar before removing the drive from the USB port, Failure to do so may cause the drive to not work properly.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Formatting the drive as ext3 will make it unreadable on a Windows system and formatting as ntfs will make it read-only (you can't copy files onto it) on linux systems without the correct software. Fat32 (called vfat in linux) will be read-write on both operating systems.⧼thumbs_response⧽
Things You'll Need
- Harddrive
- Drive Enclosure
- USB/Firewire cable
- Computer with available USB/Firewire port
- Screwdriver (most likely Phillips)
- (optional) Surge Protector