Chapter 12
Temperature and Kinetic Theory
By Boundless
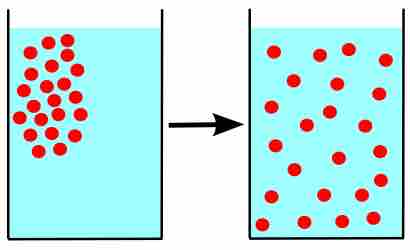
The kinetic theory of gases describes a gas as a large number of small particles (atoms and molecules) in constant, random motion.
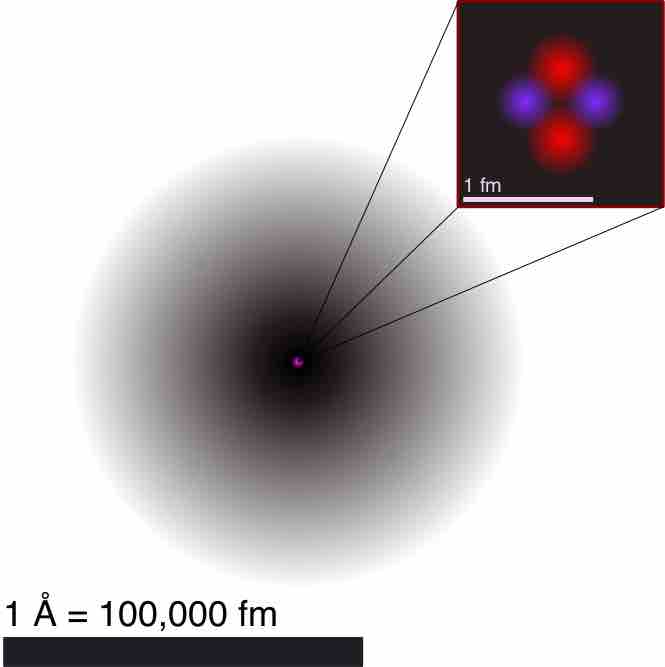
Atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms.

Celsius, or centigrade, is a scale and unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the most commonly used temperature units.

In the Fahrenheit scale, the freezing of water is defined at 32 degrees, while the boiling point of water is defined to be 212 degrees.
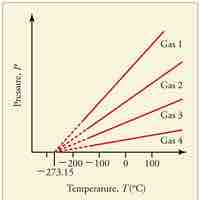
Absolute zero is the coldest possible temperature; formally, it is the temperature at which entropy reaches its minimum value.
The kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature; the null point of the Kelvin scale is absolute zero, the lowest possible temperature.

Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change in volume in response to a change in temperature.
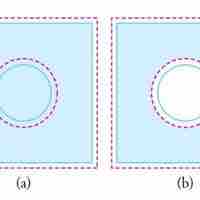
Objects expand in all dimensions. That is, their areas and volumes, as well as their lengths, increase with temperature.
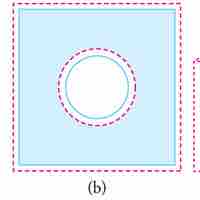
Substances expand or contract when their temperature changes, with expansion or contraction occurring in all directions.
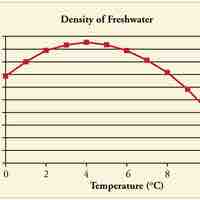
Objects will expand with increasing temperature, but water is the most important exception to the general rule.

The ideal gas law is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas (in which there is no molecule to molecule interaction).
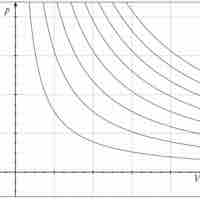
An isothermal process is a change of a system in which the temperature remains constant: ΔT = 0.
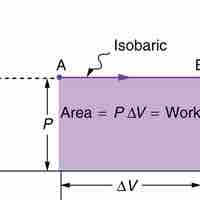
Isobaric processis a thermodynamic process in which the pressure stays constant (at constant pressure, work done by a gas is

With the ideal gas law we can figure pressure, volume or temperature, and the number of moles of gases under ideal thermodynamic conditions.
The number of molecules in a mole is called Avogadro's number (NA)—defined as 6.02x 1023 mol-1.
Absolute temperature is the most commoly used thermodyanmic temperature unit and is the standard unit of temperature.
Pressure is explained by kinetic theory as arising from the force exerted by molecules or atoms impacting on the walls of a container.
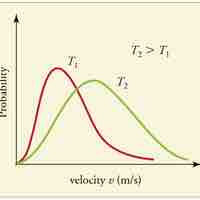
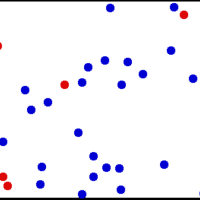
A gas of many molecules has a predictable distribution of molecular speeds, known as the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution.
Temperature is directly proportional to the average translational kinetic energy of molecules in an ideal gas.

Internal energy is the total energy contained by a thermodynamic system, and has two major components: kinetic energy and potential energy.

During a phase transition, certain properties of the medium change, often discontinuously, as a result of some external condition.
The amount of water vapor in air is a result of evaporation or boiling, until an equilibrium is reached.