Chapter 1
Building Blocks of Calculus
By Boundless
Functions relate a set of inputs to a set of outputs such that each input is related to exactly one output. Graphs can be used to represent these relationships pictorially.
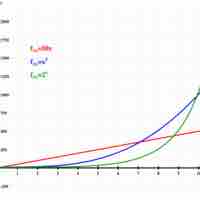
Linear and quadratic functions make lines and a parabola, respectively, when graphed and are some of the simplest functional forms.
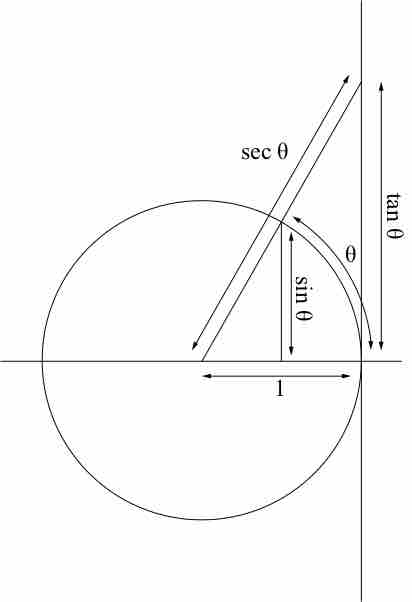
Trigonometric functions are functions of an angle, relating the angles of a triangle to the lengths of the sides of a triangle.
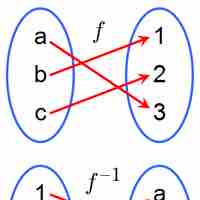
An inverse function is a function that undoes another function: For a function
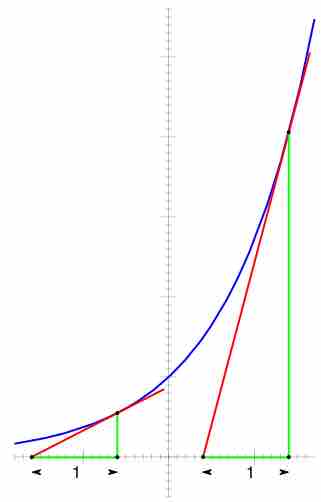
Both exponential and logarithmic functions are widely used in scientific and engineering applications.

For numerical calculations and graphing, scientific calculators and personal computers are commonly used in classes and laboratories.
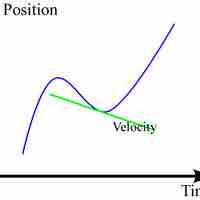
Iinstantaneous velocity can be obtained from a position-time curve of a moving object.
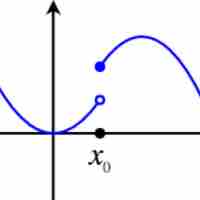
The limit of a function is a fundamental concept in calculus and analysis concerning the behavior of a function near a particular input.
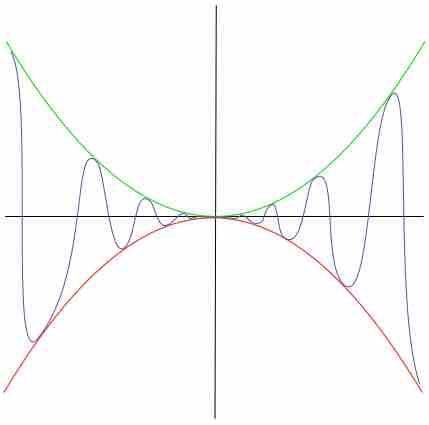
Limits of functions can often be determined using simple laws, such as L'Hôpital's rule and squeeze theorem.
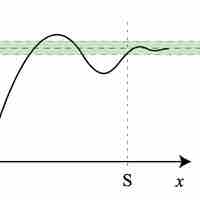
The
A continuous function is a function for which, intuitively, "small" changes in the input result in "small" changes in the output.
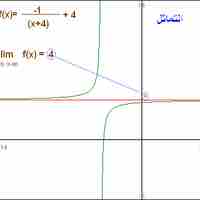
For a real-valued function expressed in terms of other functions, limit values may be computed via algebraic operations.
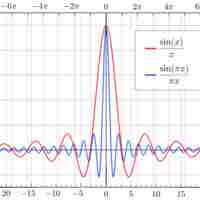
There are several limits of special interest involving trigonometric functions.
For a real-valued continuous function
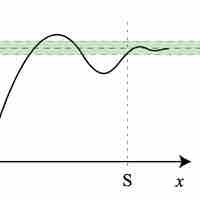
Limits involving infinity can be formally defined using a slight variation of the