wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, volunteer authors worked to edit and improve it over time.
This article has been viewed 29,938 times.
Learn more...
When you install Linux onto a computer, the computer's default boot sequence is bypassed or overwritten to allow Linux's Grub/Grub2 bootloader to take control of your boot sequence and run a completely different system than the original bootloader. During the installation, something can go wrong, and the boot sequence is unable to be loaded when the computer powers on again. Grub Rescue then loads to help you recover your computer. If you don't know how to use this prompt, you are completely locked out of your computer, but don't worry! This article will help you get past Grub Rescue.. Go to Step 1 to start.
Steps
-
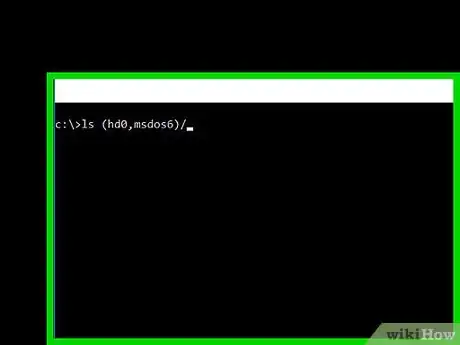
1Locate the right partition. Once the command prompt shows up, type "ls". This command should show a list of partitions that look like this: (hd0), (hd0,msdos1), (hd0,msdos2), (hd0,msdos3), etc. To find a partition's filesystem, type "ls (name partition you want to see)".
- An example would be "ls (hd0, msdos5)". The partition you want to find should have a file system of ext2 or something similar to that. Most, if not all of the others should have an unknown file system.
- For the purposes of this article, "(hd0,msdos6)" will be used to represent the correct partition.
-
2Locate the Grub/Grub2 files. Once you find the partition with the ext2 file system, you will want to find the Grub/Grub2 folder. This will require a little more work than the previous step. First, type "ls (hd0,msdos6)/". Do not forget that slash!
- With the slash right behind it, it should display all the folders contained within the partition. You will want to search through them one by one until you find the Grub or Grub2 folder. (Sometimes, you may end up being extremely lucky and have the grub/grub2 folder displayed immediately. If you aren't, you will have to a bit more searching.)
- Search through the other folders. Type "ls (hd0,msdos6)/foldername/". This will display all subfolders within the selected folder. If you see a "boot" folder, search through that one first, it's the most likely one to contain the files. Continue to search through the folders until you find one that is called "grub" or "grub2". Once you find it, write the path down and continue on.
Advertisement -
3Boot up. Now that you have located the grub/grub2 files, you are now ready to boot up. Simply type "set prefix=(hd0,msdos6)/PathToGrubFiles", "insmod normal", then "normal". Again, this will be different for every computer.
- For example, you may have to type "set prefix=(hd0,msdos6)/grub2/ [enter] insmod normal [enter] normal [enter]", or "set prefix=(hd1,msdos6)/boot/grub/".
Community Q&A
-
QuestionHow do I make Windows 10 handle the dual boot menu instead of Linux?
 rupak chowdhuryCommunity AnswerFirst download and install EasyBCD.exe setup file, then open it and click "Add new Entry." You can see options for which OS you have to choose (in this case it is LinuxBSD). Now select type (in my case GRUB 2), select name (whatever you want, the given name will be displayed at boot menu) and now select your drive in which Linux is installed. After then click "add entry", now select "BCD Deployment" option , and click on "write MBR" to delete GRUB Boot loader, and now restart.
rupak chowdhuryCommunity AnswerFirst download and install EasyBCD.exe setup file, then open it and click "Add new Entry." You can see options for which OS you have to choose (in this case it is LinuxBSD). Now select type (in my case GRUB 2), select name (whatever you want, the given name will be displayed at boot menu) and now select your drive in which Linux is installed. After then click "add entry", now select "BCD Deployment" option , and click on "write MBR" to delete GRUB Boot loader, and now restart. -
QuestionAll hd0 I insert come out as "unknown filesystem". What can I do?
 SomoneCommunity AnswerThat means that the data on the hard drive is corrupt. You may have to take it to a data recovery expert if you have important files you want to salvage.
SomoneCommunity AnswerThat means that the data on the hard drive is corrupt. You may have to take it to a data recovery expert if you have important files you want to salvage.