Chapter 13
Chemical Kinetics
By Boundless
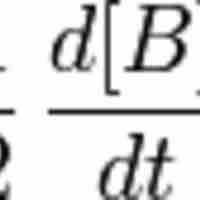
Reaction rates are determined by observing the changes in the concentrations of reactants or products over a specific time frame.
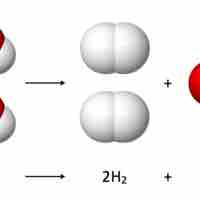
Reaction stoichiometry studies the quantitative relationships between reactants and products within a given chemical reaction.
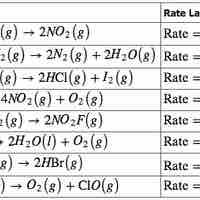
The rate law for a chemical reaction relates the reaction rate with the concentrations or partial pressures of the reactants.
A first-order reaction depends on the concentration of one reactant, and the rate law is:
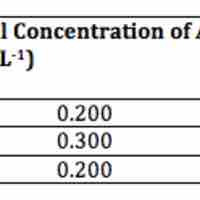
A second-order reaction is second-order in only one reactant, or first-order in two reactants.
A zero-order reaction has a constant rate that is independent of the concentration of the reactant(s); the rate law is simply
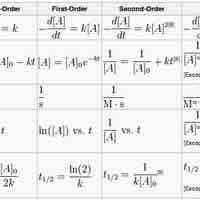
The integrated rate laws derive from calculus, and they relate the concentrations of reactants with time.
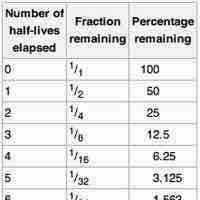
The half-life of a reaction is the amount of time it takes for the concentration of a reactant to decrease to one-half of its initial value.
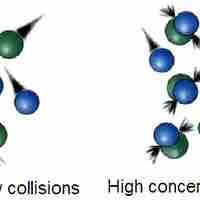
Collision theory provides a qualitative explanation of chemical reactions and the rates at which they occur, appealing to the principle that molecules must collide to react.
The rate of a chemical reaction depends on factors that affect whether reactants can collide with sufficient energy for reaction to occur.

The Arrhenius equation is a formula that describes the temperature-dependence of a reaction rate.
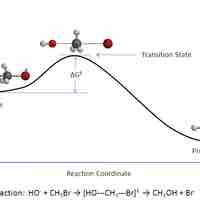
In a given chemical reaction, the hypothetical space that occurs between the reactants and the products is known as the transition state.
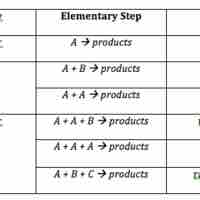
The rate law for an elementary step is derived from the molecularity of that step.

The rate of a multi-step reaction is determined by the slowest elementary step, which is known as the rate-determining step.
Rate laws for reactions are affected by the position of the rate-determining step in the overall reaction mechanism.
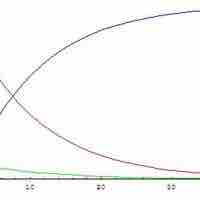
The steady state approximation can be used to determine the overall rate law when the rate-determining step is unknown.
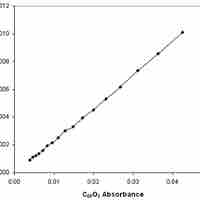
Reaction rates can be determined experimentally by measuring the concentration of a reactant and/or product over time.
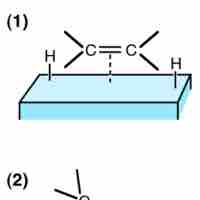
Heterogeneous catalysis is a type of catalysis in which the catalyst occupies a different phase than the reaction mixture.
Homogeneous catalysis is a class of catalysis in which the catalyst occupies the same phase as the reactants.

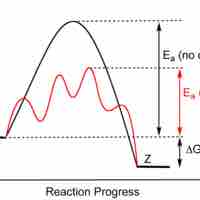
Enzymes are proteins that accelerate biochemical transformations by lowering the activation energy of reactions.