Chapter 12
Solutions
By Boundless
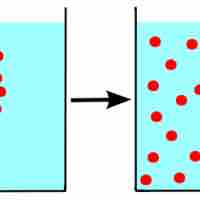
To form a solution, molecules of solute and solvent must be more attracted to each other than themselves.
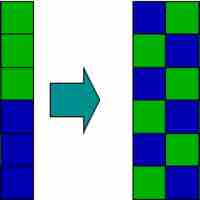
An increase in entropy occurs when a solution is formed, providing one of the many driving forces for this process.
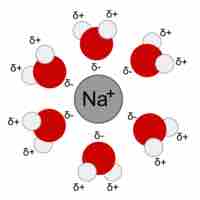
When ions dissolve in water, the stabilizing interactions that result release energy called the "heat of hydration."
Molarity is defined as the moles of a solute per volume of total solution.

Molality is a property of a solution that indicates the moles of solute per kilogram of solvent.
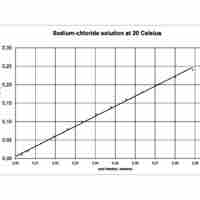
Mole fraction is the number of molecules of a given component in a mixture divided by the total number of moles in the mixture.
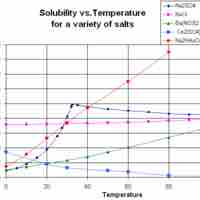
Solubility often depends on temperature; the solubility of many substances increases with increasing temperature.
Solubility of a gas in water tends to decrease with increasing temperature, and solubility of a gas in an organic solvent tends to increase with increasing temperature.

Increasing pressure will increase the solubility of a gas in a solvent.

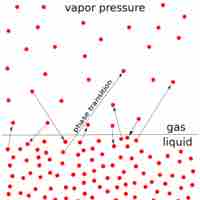
The vapor pressure of a solution is directly influenced by the number of solute molecules present in a given amount of solvent.
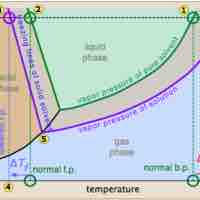
Freezing point depression is a colligative property observed in solutions, brought on by the introduction of solute molecules to a solvent.
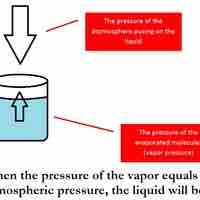
The boiling point of a solvent is elevated in the presence of solutes.
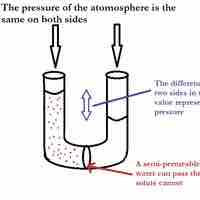
Osmotic pressure is the pressure needed to nullify the effects of osmosis and is directly influenced by the amount of solute in the system.