Section 2
The Rate Law: Concentration and Time
Book
Version 33
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Chemistry
Chemistry
by Boundless
6 concepts
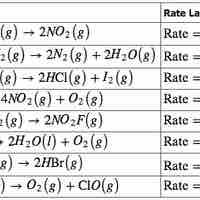
The Rate Law
The rate law for a chemical reaction relates the reaction rate with the concentrations or partial pressures of the reactants.
First-Order Reactions
A first-order reaction depends on the concentration of one reactant, and the rate law is:
Second-Order Reactions
A second-order reaction is second-order in only one reactant, or first-order in two reactants.
Zero-Order Reactions
A zero-order reaction has a constant rate that is independent of the concentration of the reactant(s); the rate law is simply
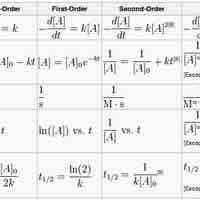
The Integrated Rate Law
The integrated rate laws derive from calculus, and they relate the concentrations of reactants with time.
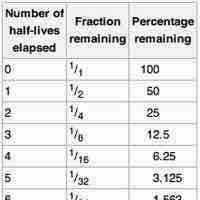
Half-Life
The half-life of a reaction is the amount of time it takes for the concentration of a reactant to decrease to one-half of its initial value.