This article was co-authored by Zora Degrandpre, ND. Dr. Zora Degrandpre is a Natural Health Doctor and Licensed Naturopathic Physician in Vancouver, Washington. She is a grant reviewer for the National Institutes of Health and the National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine. She received her ND from the National College of Natural Medicine in 2007.
There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 21,393 times.
A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot located in your deeper veins, often in your legs or arms. Herbs, such as garlic, green tea, turmeric, and ginkgo biloba, and lifestyle changes may help you avoid DVT. However, check with your doctor before using herbal treatments. Additionally, get immediate medical care if you have symptoms of DVT or pulmonary embolism.
Steps
Incorporating Herbs
-
1Eat garlic and onions to maintain your cholesterol, blood pressure, and glucose. Garlic and onions can help to prevent DVT in a variety of ways, including decreasing cholesterol levels, decreasing blood pressure, and promoting healthy blood glucose levels. To get these benefits, add garlic and onions to recipes or use as a garnish.
- Safe amounts of onions and garlic are those that you would normally use for cooking, so enjoy them at one or more of your meals during the day.
-
2Sip green tea for antioxidants and to prevent blood clots. Green tea is high in antioxidants and also has anti-cancer properties. Green tea has been shown to help prevent mutations and tumor initiation. Green tea also has antiplatelet properties and may reduce blood clotting. Green tea is safe in the amounts normally used in food, so drink some green tea throughout the day. A common recommendation is to drink 3–4 cups a day.
- Keep in mind that green tea contains caffeine. You may drink decaffeinated green tea instead to reap the same benefits.
Advertisement -
3Add ginger to food to help reduce your risk of clots. Ginger decreases platelet aggregation, which may help to prevent blood clots. You can add fresh ginger to recipes, drink it as a tea, or look for a supplement if you are not a fan of the taste.
- Try eating about two to four grams (one to two teaspoons) of fresh ginger per day. Talk to your doctor first if you are taking any prescription blood thinners.
-
4Spice up food with turmeric to relieve inflammation. Turmeric, also known as curcumin, has antioxidant properties and decreases platelet aggregation. You can add curry powder (which contains turmeric) to food or even try adding fresh turmeric to food.
- If you are on blood thinners, make sure to tell your physician. A common recommended daily amount is about 1.5 to three grams of turmeric a day (about one-half to one teaspoon).
-
5Take a ginkgo biloba supplement to reduce blood clotting. Ginkgo biloba inhibits blood clotting and decreases the level of D-dimer, a protein that accompanies blood clots. You can also use ginkgo biloba as a tea.nt, take 120mg twice a day for up to six years.[1] Talk to your doctor first if you are on blood thinners.
-
6Try some Pau d'arco tea to prevent platelets from sticking together. Pau d'arco is a traditional South American medicinal herb that decreases platelet aggregation. This herb is considered safe if used as a tea. Look for Pau d'arco online or look at your local herb store.
- Drink one to two cups a day. Talk to your doctor first, especially if you are on blood thinners.
- Do not use Pau d'arco if you are pregnant or nursing.
-
7Try gotu kola to improve your circulation. Gotu kola, also known as centella asiatica, has been used in Traditional Chinese Medicine for centuries. Recent research has shown that gotu kola can be safe and effective in improving the circulation and decreasing the symptoms of venous insufficiency.[2] Taking gotu kola may also help you to avoid DVT during airplane flights lasting over three hours.
- Try taking 30 mg twice a day. Talk to your doctor first if you are taking any other medications.
-
8Use butcher’s broom as a possible preventative treatment. Butcher’s broom, also known as Ruscus aculeatus, may also help to treat venous insufficiency and reduce the risk of DVT. You can take it alone or combine it with Vitamin C and hesperidin, a substance derived from citrus fruit.
- Capsules of butcher’s broom, Vitamin C, and hesperidin contain 30–150 mg of butcher’s broom. The recommended dosage is two to three capsules taken daily. Talk to your doctor first if you are taking any other medications.
Making Lifestyle Changes
-
1Exercise for at least 30 minutes every day. Part of the reason why people develop DVT is because they are bedridden or otherwise unable to move around. As a result, blood pools in their legs and clots form. Getting regular daily exercise, such as going for quick, frequent walks throughout the day, is a great way to reduce your risk of developing DVT.[3]
-
2Wear compression stockings to prevent DVT in your legs. Compression stockings are often recommended for those who are at risk of developing DVT. These stockings compress your legs, which helps to improve circulation and prevent DVT. You will need to wear the compression hose for a set amount of time each day, according to your doctor’s recommendations.[4]
- If you are at risk of developing DVT and you have not been instructed to wear compression hose, ask your doctor about getting some.
-
3Stay on your medications if you’re taking any. If you are on any blood-thinning medications, then it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions and take them every day until you have been told to stop taking them. Do not try to replace your medications with herbs.
- If you plan to supplement with herbs and you are on medications, make sure that you ask your doctor first to make sure that there are no interactions. Some herbs may increase or reduce the effectiveness of certain medications, especially blood thinners.[5]
-
4Ask for help to quit smoking. Smoking increases your risk of developing DVT as well as many other serious health conditions, so it is important to quit smoking right away. If you are a smoker, ask your doctor for help to quit. Your doctor may be able to prescribe medications that can help and there are smoking cessation programs that may also help you to quit.[6]
-
5Control your blood pressure. High blood pressure is another common risk factor for DVT. To reduce this risk factor, keep your blood pressure under control. Follow your doctor’s recommendations and get your blood pressure checked regularly.[7]
- Common recommendations include following a low sodium diet, getting regular exercise, and taking medications.
-
6Identify your risk factors so you can take preventative steps. Most people will be at risk for DVT at some point, but some people are at a much higher risk due to chronic conditions and lifestyle factors. If you’re at risk, work with your doctor to reverse any risk factors that are preventable, like smoking or carrying extra bodyweight. Then, talk to them about what you can do about your remaining risk factors. Here are the risk factors for DVT:[8]
- Hospitalization
- Infection
- Cancer
- Being over 75 years old
- A recent episode of more than three days in bed
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Cigarette smoking
- High cholesterol levels
- Genetic risk factors, such as clotting factor deficiencies
- Long periods of sitting, such as on an airplane
- Obesity
- Recent surgery
When to Seek Medical Care
-
1Check with your doctor before using herbs for home treatment. While herbs are generally safe to use, they aren’t right for everyone. Additionally, they don’t work the same way for different people. Talk to your doctor before you start using herbal treatments. Make sure that the herbs you’re planning to take are safe for you to consume.[9]
- You may be allergic to some herbs, and herbal treatments may interfere with medications you’re taking or may worsen existing medical conditions. Your doctor can help you use herbal treatments safely.
- Tell your doctor that you’re hoping to prevent DVT. They may be able to recommend additional changes for you to make based on your individual health profile.
-
2Visit your doctor immediately if you have symptoms of DVT. While preventative measures help, there’s no guarantee they’ll work. If you develop DVT, you need prompt medical treatment to help you recover. Otherwise, your blood clot could become life threatening. Don’t worry, but do get immediate medical care if you have the following symptoms:[10]
- Swelling in 1 leg or 1 arm
- Pain in your leg or arm
- Red or discolored skin
- A feeling of warmth around the area
- Tenderness around the area
-
3Get emergency medical care for signs of a pulmonary embolism. In some cases, a DVT blood clot can break free and travel to your lungs, which causes a pulmonary embolism. This is an emergency medical condition that requires immediate medical treatment. Try not to worry because treatment is available. Visit an emergency room if you have the following symptoms:[11]
- Sudden shortness of breath
- Chest pain that worsens when you breathe or cough
- Rapid heartbeat
- Being lightheaded or dizzy
- Coughing up blood
-
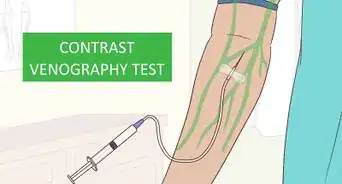
4Expect your doctor to do imaging and blood tests to diagnose DVT. Let your doctor do an ultrasound, venography X-ray, MRI, or CT-scan to create an image of your blood clot. Additionally, get a simple blood test to check for D-Dimer, which is a protein that’s present during blood clots. These tests are easy and painless, though you might experience minor discomfort. Based on the results, your doctor can confirm if you have DVT.[12]
- Your doctor will also consider your symptoms and how long you’ve been having them.
- In some cases, you may need additional tests if your doctor suspects that you don’t actually have a blood clot or DVT.
-
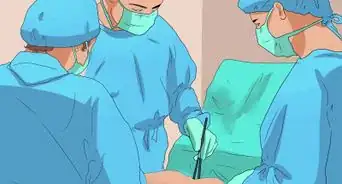
5Ask your doctor about treatment options. If you have DVT, your doctor will help you create a treatment plan to break up the clot and prevent it from traveling to your lungs. You may be able to treat your DVT using medication alone. However, your doctor may recommend a minor procedure if your clot is large or may travel to your lungs. Talk to your doctor to learn more about these treatment options:[13]
- Blood thinners to slowly break down your clot and prevent new ones.
- Clot busters that are administered via IV for big clots.
- Filters that go into your veins to prevent clots from traveling to your lungs.
- Compression stockings to prevent swelling and clotting.
Warnings
- Some herbs may interact with other medications that you are taking. Be sure to check with your doctor before adding a supplement to your regimen.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ https://www.drugs.com/mtm/ginkgo-biloba.html
- ↑ http://www.researchgate.net/publication/236085039_A_Systematic_Review_of_the_Efficacy_of_Centella_asiatica_for_Improvement_of_the_Signs_and_Symptoms_of_Chronic_Venous_Insufficiency
- ↑ https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16911-deep-vein-thrombosis-dvt
- ↑ https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16911-deep-vein-thrombosis-dvt
- ↑ https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16911-deep-vein-thrombosis-dvt
- ↑ https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/deep-vein-thrombosis-dvt/
- ↑ https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/deep-vein-thrombosis/
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470215/
- ↑ https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/herbal-medicine
-Step-2.webp)
-Step-3.webp)
-Step-4.webp)
-Step-5.webp)
-Step-6.webp)
-Step-7.webp)
-Step-8.webp)
-Step-9.webp)
-Step-10.webp)
-Step-11.webp)
-Step-12.webp)
-Step-13.webp)
-Step-14.webp)
-Step-17.webp)
-Step-1.webp)
-Step-15.webp)
-Step-16.webp)








-Step-13.webp)












































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...