This article was co-authored by Zora Degrandpre, ND. Dr. Zora Degrandpre is a Natural Health Doctor and Licensed Naturopathic Physician in Vancouver, Washington. She is a grant reviewer for the National Institutes of Health and the National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine. She received her ND from the National College of Natural Medicine in 2007.
There are 14 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 31,583 times.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is when a blood clot forms in your deep veins, often in your legs or arms. While this is a serious medical condition, you may be able to prevent it naturally using supplements. However, check with your doctor before using supplements to make sure they’re safe for you to use. Additionally, get immediate medical care if you have symptoms of DVT and seek emergency care if you notice symptoms of a pulmonary embolism.
Steps
Choosing Supplements
-
1Take a nattokinase supplement to help break down clots. Nattokinase is an enzyme derived from fermented soybeans. This enzyme acts directly on clots to break them up and it also balances the levels of other chemicals that affect clot formation.[1] [2] There no known side effects of this supplement, but you may want to talk to your doctor about taking it, especially if you are on other medications.
- Follow the package instructions, but a common dosage is 100mg of nattokinase taken three times a day.
-
2Consider taking lumbrokinase supplements for clot prevention. Lumbrokinase is another type of enzyme derived from earthworms. This enzyme works like nattokinase by breaking up any blood clots that may form in the veins. Lumbrokinase may cause mild nausea and bloating. Be sure to talk to your doctor before you begin supplementing with lumbrokinase.
- Follow the package instructions or consult your doctor for a recommendation, but a common dosage amount is 40-80 mg taken twice a day.
Advertisement -
3Add omega-3 fish oils to your diet so platelets can’t stick together. Omega-3 oils contain EPA and DHA, which are omega-3 essential fatty acids. Your body uses these acids for many different purposes, including anti-inflammatory purposes. EPA and DHA prevent platelets from clumping together, which can help to reduce clotting.
- Try taking an omega-3 supplement or get your omega-3s from seafood like sardines, salmon, mackerel, cod, tuna, and shellfish.
-
4Try evening primrose oil because it may help prevent clots. Evening primrose oil (EPO) contains gamma-linoleic acid, which is an omega-6 essential fatty acid. The way that EPO works to prevent DVT is not clear, but it has been shown to help to reduce clot formation.[3] [4] EPO may also cause mild nausea and diarrhea.
- Follow the package instructions, but a common dosage is 300mg taken three times a day. Also, make sure that you talk to your doctor if you are on anti-seizure medications, blood pressure medications, antidepressants or blood pressure medications. EPO may interact with some of these.
-
5Prevent venous insufficiency with bioflavonoids. Venous insufficiency may cause DVT, so taking supplements that act against this condition may be helpful as well. Bioflavonoids can help with venous insufficiency. Bioflavonoids are plant components that give berries their color, which is why berries are good sources of bioflavonoids. These antioxidants act on the veins to improve circulation, decrease micro-bleeds in capillaries, and reduce inflammation and swelling.
-
6Reduce your risk of venous deficiency with digestive enzymes. Bromelain is an enzyme that is derived from pineapples. You can also get bromelain from eating fresh pineapple. Bromelain may increase prothrombin time (PT), which may help prevent coagulation.
- Talk to your doctor about supplementing with bromelain and for a dosage recommendation. The recommended dosage varies from 80-320 mg two to three times a day.
Taking Other Steps to Avoid DVT
-
1Take frequent walks so blood doesn’t pool in your legs. Part of the reason why people develop DVT is because they are bedridden or otherwise unable to move around. As a result, blood pools in their legs and clots form. Getting regular daily exercise, such as going for quick frequent walks throughout the day, is a great way to reduce your risk of developing DVT.[7]
-
2Quit smoking because it’s a risk factor for DVT. Smoking increases your risk of developing DVT as well as many other serious health conditions. If you are a smoker, ask your doctor for help to quit. Your doctor may be able to prescribe medications that can help and there are smoking cessation programs that may also help you to quit.[8]
-
3Keep your blood pressure under control. High blood pressure is another risk factor for DVT. Keep your blood pressure under control by getting it checked regularly and following your doctor’s recommendations for reducing blood pressure.[9]
- Common recommendations include following a low sodium diet, getting regular exercise, and taking medications.
-
4Take your medications as directed. If you are on any blood thinning medications, then it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions and take them every day until you have been told to stop taking them. If you plan to supplement and you are on other medications, make sure that you ask your doctor first to make sure that there are not interactions.[10]
-
5Wear compression stockings to improve your circulation. Compression stockings are often recommended for those who are at risk of developing DVT. These stockings help prevent DVT by compressing your legs and improving circulation.[11]
- If you are at risk of developing DVT, ask your doctor about compression hose.
- If you have been told to wear compression hose, make sure that you do.
-
6Try to reduce your risk factors for DVT. There are many risk factors for DVT, and it helps to know if you are at higher risk so you can take extra preventative measures. Some of these risk factors include:[12]
- Hospitalization
- Infection
- Cancer
- Being over 75 years old
- A recent episode of more than three days in bed
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Cigarette smoking
- High cholesterol levels
- Genetic risk factors, such as clotting factor deficiencies
- Long periods of sitting, such as on an airplane
- Obesity
- Recent surgery
When to Seek Medical Care
-
1Check with your doctor before using herbal supplements. While herbal supplements are generally safe, they aren’t right for everyone. They may trigger an allergic reaction, interfere with your medications, or worsen a condition you’re treating. Talk to your doctor about your desire to use herbal supplements, and make sure they’re safe for you to take.[13]
- Tell your doctor all of the medications and supplements you’re taking.
- Let your doctor know that you’re hoping to prevent DVT.
-
2Get immediate medical care if you have symptoms of DVT. Try not to worry because you can get treatment for DVT. However, you need to see your doctor as soon as you notice symptoms because a blood clot can become life threatening. To get prompt treatment, see your doctor as soon as you notice the following symptoms:[14]
- Swelling in your leg or around your ankle (if the DVT is in your leg)
- Swelling in your wrist or finger (if the DVT is in your arm)
- Pain, cramps, or throbbing in your calf or forearm
- Redness
- Tenderness
- Warmth
-
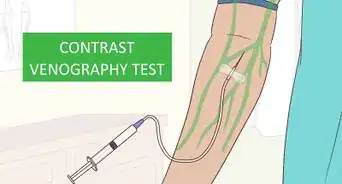
3Let your doctor conduct diagnostic tests to confirm it’s DVT. These symptoms may be caused by other conditions, so your doctor will likely recommend some tests. They will likely do these tests in their office, but you may get them done at a hospital. Your doctor will likely do the following tests to confirm you have DVT:[15]
- An ultrasound to view the clot
- A blood test to find out if you have D dimer in your blood
- Venography, which is an X-ray of your veins while they have dye in them
- CT scan or MRI to look for a clot
-
4Get emergency medical care if you have symptoms of a pulmonary embolism. In some cases, a DVT blood clot can travel from your arm or leg to your lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism. This is always an emergency medical condition, so you need to get immediate care. Try not to worry, but go to the emergency room as soon as you recognize the following symptoms:[16]
- Sudden shortness of breath
- Chest pain or pressure that worsens when you breathe or cough
- Lightheadedness, dizziness, or fainting
- Rapid heartbeat
- Coughing up blood
Warnings
- Some supplements may interact with other medications that you are taking. Be sure to check with your doctor before adding a supplement to your regimen.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8593442
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2123064
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18154917
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19783511
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8737632
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8034203
- ↑ https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/deep-vein-thrombosis-dvt/
- ↑ https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/deep-vein-thrombosis-dvt/
- ↑ https://newsinhealth.nih.gov/2017/01/how-spot-prevent-deep-vein-thrombosis
- ↑ https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/deep-vein-thrombosis-dvt/
- ↑ https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/dvt/facts.html
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/deep-vein-thrombosis/basics/risk-factors/con-20031922
- ↑ https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/herbal-medicine
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/deep-vein-thrombosis/basics/symptoms/con-20031922
- ↑ https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/deep-vein-thrombosis/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20352563
- ↑ https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/deep-vein-thrombosis/symptoms-causes/syc-20352557
-Step-1.webp)
-Step-2.webp)
-Step-3.webp)
-Step-4.webp)
-Step-5.webp)
-Step-6.webp)
-Step-7.webp)
-Step-8.webp)
-Step-9.webp)
-Step-10.webp)
-Step-11.webp)
-Step-14.webp)
-Step-12.webp)
-Step-13.webp)








-Step-16.webp)











































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...