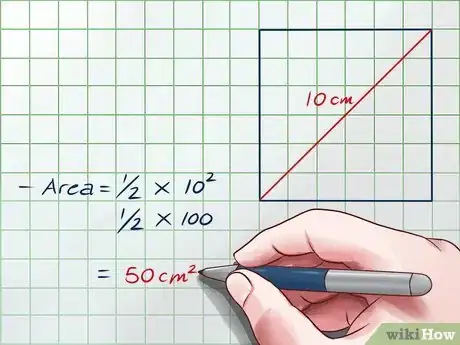This article was co-authored by David Jia. David Jia is an Academic Tutor and the Founder of LA Math Tutoring, a private tutoring company based in Los Angeles, California. With over 10 years of teaching experience, David works with students of all ages and grades in various subjects, as well as college admissions counseling and test preparation for the SAT, ACT, ISEE, and more. After attaining a perfect 800 math score and a 690 English score on the SAT, David was awarded the Dickinson Scholarship from the University of Miami, where he graduated with a Bachelor’s degree in Business Administration. Additionally, David has worked as an instructor for online videos for textbook companies such as Larson Texts, Big Ideas Learning, and Big Ideas Math.
There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 1,054,431 times.
The most common formula for the area of a square is simple: it's the length of the side squared, or s2.[1] But sometimes you only know the length of the square's diagonal, running between opposite vertices. If you've studied right triangles, you can find a new area formula that uses this diagonal as its only variable.
Steps
Finding the Area from the Diagonal
-
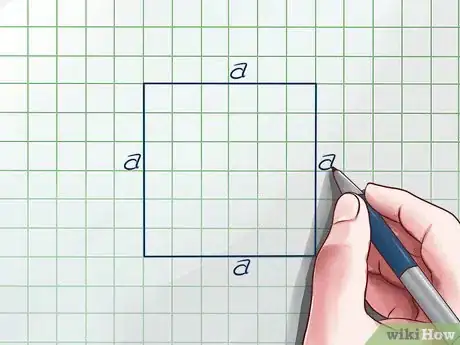
1Draw your square. A square has four equal sides.[2] Let's say each one has a length of "s".
-
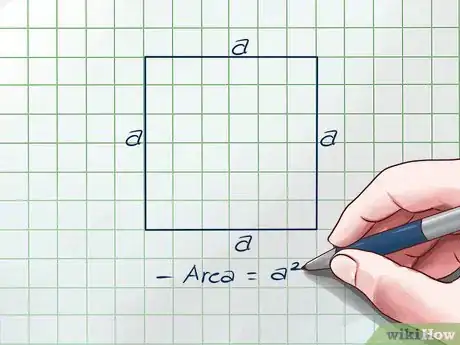
2Review the basic formula for a square's area. A square's area is equal to its length times its width. Since each side is s, the formula is Area = s x s = s2. This will be useful later on.[3]Advertisement
-
3Join any two opposite corners to make a diagonal. Let the measure of this diagonal be d units. This diagonal divides the square into two right-triangles.
-
4Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to one of the triangles. The Pythagorean theorem[4] is a formula for finding the hypotenuse (longest side) of a right triangle: (side one)2 + (side two)2 = (hypotenuse)2, or . Now that the square is divided in half, you can use this formula on one of the right triangles:
- The two shorter sides of the triangle are the sides of the square: each one has a length of s.
- The hypotenuse is the diagonal of the square, d.
-
5Arrange the equation so s2 is on one side. Remember that we already know the square's area is equal to s2. If you can get s2 alone on side, you'll have a new equation for area:
- Simplify:
- Divide both sides by two:
- Area =
- Area =
-
6Use this formula on an example square. These steps have proven that the formula Area = works for all squares. Just plug in the length of the diagonal for d and solve.[5]
- For example, let's say a square has a diagonal that measures 10 cm.
- Area =
=
= 50 square centimeters.
Additional Info
-
1Find the diagonal from the length of a side.[6] The Pythagorean theorem for a square with side s and diagonal d gives you the formula . Solve for d if you know the side lengths and want to find the length of the diagonal:
-
- For example, if a square has sides of 7 inches, its diagonal d = 7√2 inches, or about 9.9 inches.
- If you don't have a calculator, you can use 1.4 as an estimate for √2.
-
-
2Find the side length from the diagonal. If you are given the diagonal and you know that the diagonal of a square is , you can divide both sides by to get .[7]
- For example, a square with a diagonal of 10cm has sides with length cm.
- If you need to find both the side length and the area from the diagonal, you can use this formula first, then quickly square the answer to get the area: Area square centimeters. This is a bit less accurate, since is an irrational number that can lead to rounding errors.
-
3Interpret the area formula. The math checks out for the formula Area = , but is there a way to test this directly? Well, is the area of a second square with the diagonal as a side. Since the full formula is , you can reason that this second square has exactly twice the area of the original square. You can test this yourself:
- Draw a square on a piece of paper. Make sure all the sides are equal.
- Measure the diagonal. Draw a second square using that measurement as the length of the square.
- Trace a copy of your first square so you have two of them. Cut all three squares out.
- Cut apart the two smaller squares into any shapes so you can arrange them to fit inside the large square. They should fill the space perfectly, showing that the area of the larger square is exactly twice the area of the smaller square.
Community Q&A
-
QuestionA square has side lengths of 26.2 m, 21.4m, 27m, and 24.3m. How can I get the diagonal of square?
 Community AnswerThis shape is not a square, since it does not have equal sides. It is an irregular quadrilateral, either a trapezoid or an irregular shape with no name. Draw a right triangle inside the shape with the diagonal as the hypotenuse. If you have enough information to calculate the height and base of this right triangle (usually with trigonometry), you can use Pythagoras' Theorem to find the diagonal. The two diagonals will be different lengths, since the shape is not symmetrical.
Community AnswerThis shape is not a square, since it does not have equal sides. It is an irregular quadrilateral, either a trapezoid or an irregular shape with no name. Draw a right triangle inside the shape with the diagonal as the hypotenuse. If you have enough information to calculate the height and base of this right triangle (usually with trigonometry), you can use Pythagoras' Theorem to find the diagonal. The two diagonals will be different lengths, since the shape is not symmetrical. -
QuestionWhat is the area of a school lawn with a width of 69 meters?
 DonaganTop AnswererAssuming it is a square or rectangle, you have to know the other dimension, too.
DonaganTop AnswererAssuming it is a square or rectangle, you have to know the other dimension, too. -
QuestionHow did I find the length of side of each square?
 LyKaxandra CaimoyCommunity AnswerSuppose that the diagonal is 8. Square 8, so you will get 64. Now divide 64 by 2, you will get 32. Get the square root of 32. That is the length of the side of a square. The square root of 32 is equal to 4 square root of 2.
LyKaxandra CaimoyCommunity AnswerSuppose that the diagonal is 8. Square 8, so you will get 64. Now divide 64 by 2, you will get 32. Get the square root of 32. That is the length of the side of a square. The square root of 32 is equal to 4 square root of 2.
References
- ↑ https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/square.html
- ↑ https://www.mathopenref.com/square.html
- ↑ https://www.cuemath.com/measurement/area-of-square/
- ↑ https://www.mathsisfun.com/pythagoras.html
- ↑ https://www.cuemath.com/measurement/area-of-square/
- ↑ http://www.coolmath.com/reference/squares#The_diagonal_of_a_square
- ↑ https://www.mathopenref.com/squarediagonals.html
- ↑ https://math.mit.edu/~stevenj/18.335/newton-sqrt.pdf
About This Article
To find the area of a square using the length of its diagonal, use the formula area = d^2 divided by 2, where d is the length of the diagonal. Just square the length of the diagonal and then divide that number by 2 to find the square's area. To learn how to find the length of a square's sides using the diagonal, scroll down!