Chapter 7
Skeletal System: Parts of the Skeleton
By Boundless
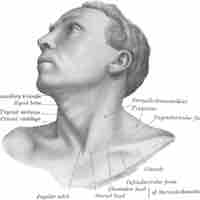
The human skull is the part of the skeleton that supports the structures of the face and forms a cavity for the brain.
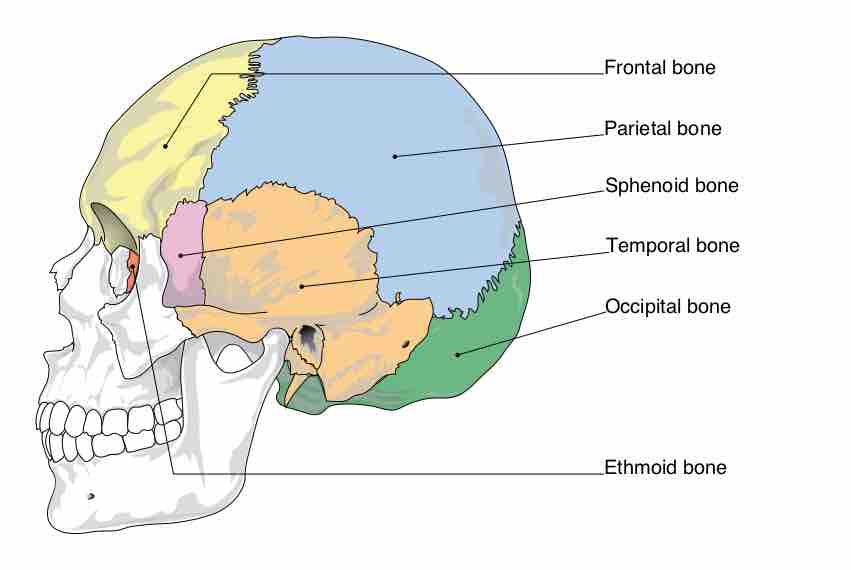
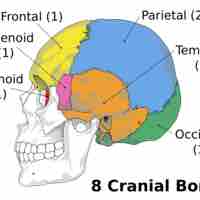
The neurocranium is comprised of eight bones: occipital, two temporal bones, two parietal bones, sphenoid, ethmoid, and the frontal bone.
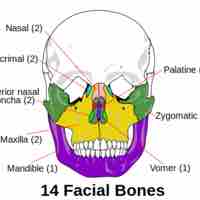
The viscerocranium (face) includes these bones: vomer, 2 inferior nasal conchae, 2 nasals, maxilla, mandible, palatine, 2 zygomatics, and 2 lacrimals.
The orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated.
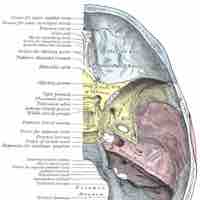
The human skull has numerous holes known as foramina through which cranial nerves, arteries, veins, and other structures pass.

A suture is a type of fibrous joint (or synarthrosis) that only occurs in the skull (or cranium).
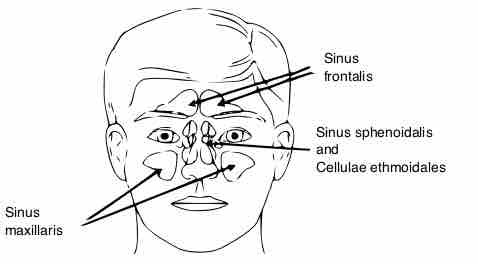
The paranasal sinuses (four, paired, air-filled spaces) surround the nasal cavity, and are located above and between the eyes, and behind the ethmoids.
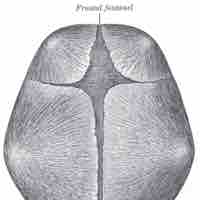
A fontanelle (or fontanel) is an anatomical feature on an infant's skull.

The spine is made of vertebrae that link together to protect the spinal cord.
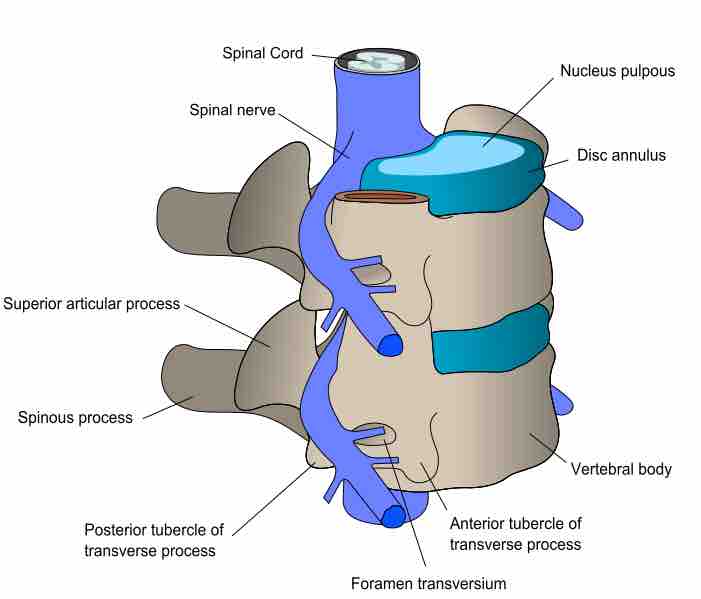
A vertebra consists of two parts: an anterior segment, or the vertebral body; and a posterior part, or the vertebral (neural) arch.
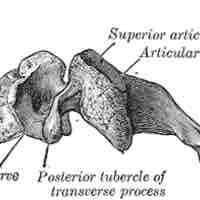
The vertebrae of the spinal column are divided into five regions: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccyx.
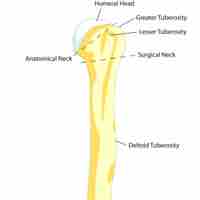
The bone forming the upper arm is the humerus.
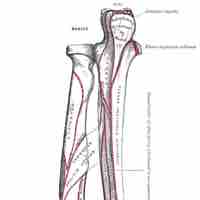
The forearm contains two bones, the radius and the ulna.
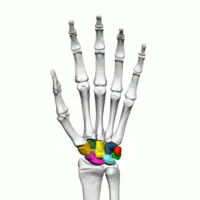
Each hand consists of 27 bones, divided between the wrist bones (carpals), the palm bones (metacarpals), and the finger bones (phalanges).
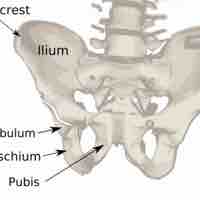
The ilium is the uppermost and largest bone of the pelvis.
The ischium forms the lower and posterior portion of the hip bones of the pelvis.
The pubis is the lowest and most anterior portion of the hip bones of the pelvis.
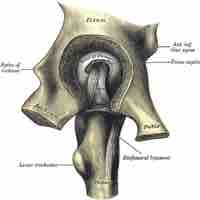
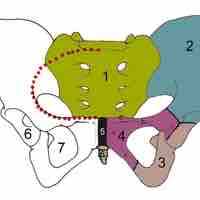
The false (greater) pelvis is larger and superior to the true (lesser) pelvis where the pelvic inlet is located.
The female pelvis has evolved to its maximum width for childbirth and the male pelvis has been optimized for bipedal locomotion.
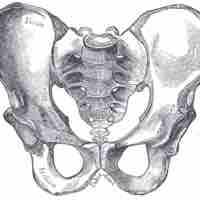
The human pelvis has evolved to be narrow enough for efficient upright locomotion, while still being wide enough to facilitate childbirth.
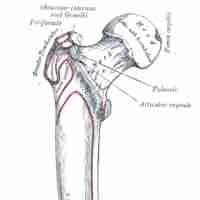
The femur—the bone of the upper leg—is the longest bone in the human body and one of the strongest.
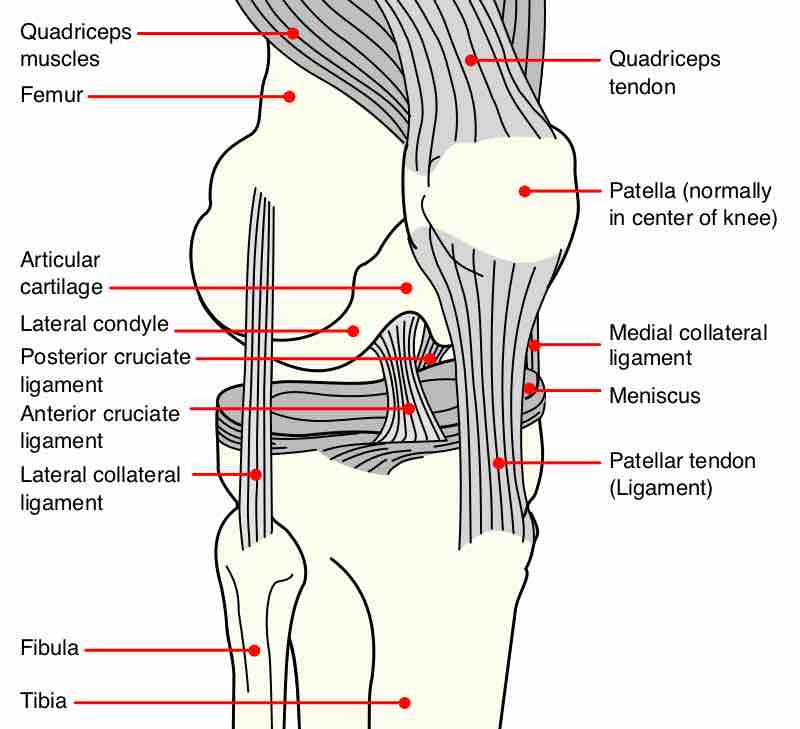
The patella (knee cap) is the bone between the fibula and femur.
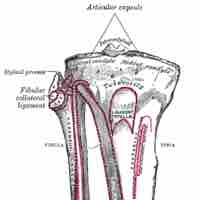
The tibia and the smaller fibula bones comprise the lower leg and articulate at the knee and ankle.
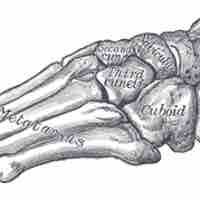
The human ankle and foot bones include tarsals (ankle), metatarsals (middle bones), and phalanges (toes).

The arches of the foot are formed by the tarsal and metatarsal bones; they dissipate impact forces and store energy for the subsequent step.