In anatomy, a foramen is any opening. Foramina inside the body of humans and other animals typically allow muscles, nerves, arteries, veins, or other structures to connect one part of the body with another.
The human skull has numerous foramina through which cranial nerves, arteries, veins, and other structures pass. The skull bones that contain foramina include the frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, maxilla, palatine, temporal, and occipital lobes.
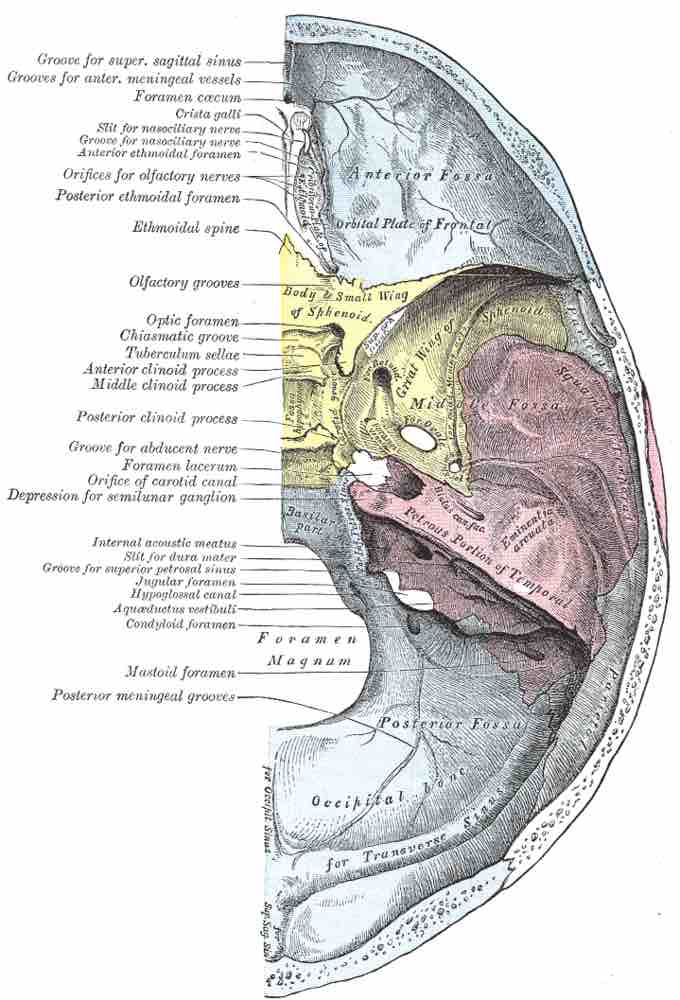
Base of the skull (upper surface)
This image details the foramina of the skull.
Key foramina in the skull include:
- Supraorbital foramen: Located in the frontal bone, it allows passage of the supraorbital vein, artery, and nerve into the orbit.
- Optic foramen: Located in the sphenoid, it allows the passage of the ophthalmic artery and nerve from the optic canal into the orbit.
- Foramen magnum: Located in the occipital bone, it allows the passage of the spinal and vertebral arteries and the spinal cord to pass from the skull into the vertebral column.
- Foramina of cribriform plate: Located in the ethmoid bone, it allows the passage of the olfactory nerve.
- Foramen rotundum: Located in the sphenoid bone, it allows passage of the maxillary nerve.