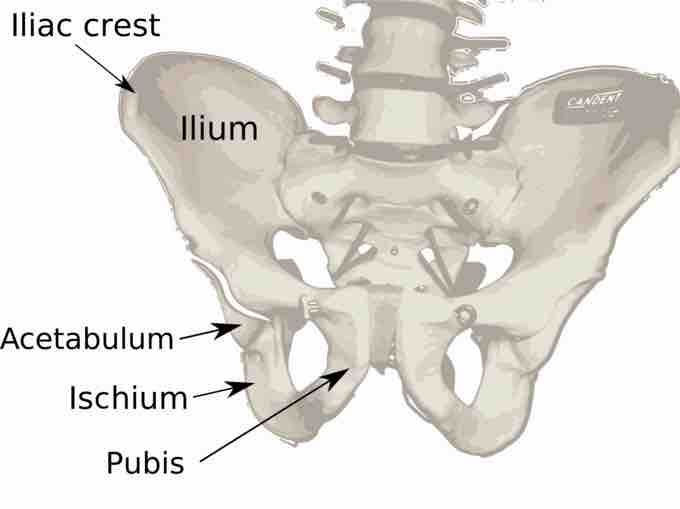
The ischium forms the lower and back part of the hip bone . Situated below the ilium and behind the pubis, the superior portion of this bone forms approximately one third of the acetabulum, which articulates with the femoral head to form the hip joint.
Lateral view of ischium
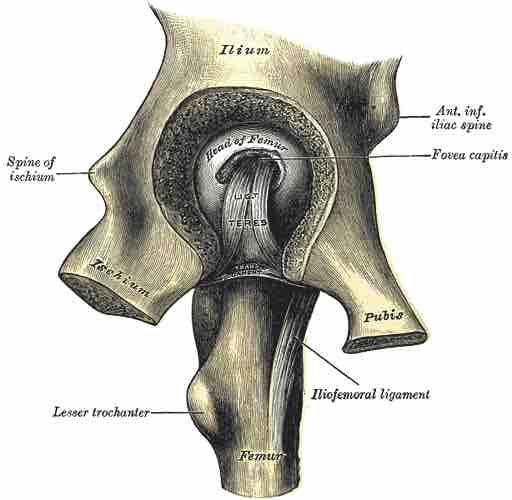
Left hip joint, opened by removing the floor of the acetabulum from within the pelvis. The ischium is labeled at the bottom left of the ilium.
The ischium is divisible into three portions; the body, and the superior and inferior rami.
The body contains a prominent spine that is the origin for the gemellus superior muscle. Two indentations run parallel to the spine—superiorly ,the greater sciatic notch and, inferiorly, the lesser sciatic notch, through which key nervous and vascular vessels pass.
The superior ramus of the ischium extends inferiorly and posteriorly from the body. It is the partial origin for the obturator internus and obturator externus muscles.
Posteriorly the ramus forms a large swelling termed the tuberosity of the ischium, or ischial tuberosity, which supports weight while sitting and is the origin for the gemellus inferior and adductor magnus muscles.
Dorsally, the ramus contributes to the obturator foramen, a large opening in the pelvis through which key nervous and vascular vessels pass.
The inferior ramus of the ischium is thin and flattened and ascends from the superior ramus of the ischium to join the inferior ramus of the pubis. It is the partial origin for the gracillis and adductor magnus muscles.
Ischium
The ischium is located below the ilium and behind the pubis.