There is some disagreement as to what constitutes the pelvis. Depending on what is included in the description these groupings are often termed true (lesser) or false (greater) pelves.
The True Pelvis
The true (or lesser) pelvis is bounded in front and below by the pubic symphysis and the superior rami of the pubis; above and behind, by the sacrum and coccyx; and laterally, by a broad, smooth, quadrangular area of bone, corresponding to the inner surfaces of the body and superior ramus of the ischium, and the part of the ilium below the arcuate line.
This cavity is a short, curved canal, deeper on its posterior than on its anterior wall, and contains the pelvic inlet. Some consider this region to be the entirety of the pelvic cavity. Others define the pelvic cavity as the larger space including the false greater pelvis, just above the pelvic inlet .
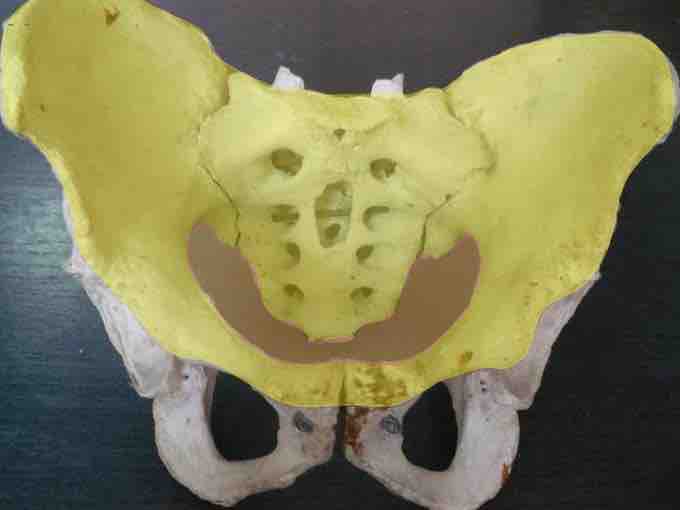
Greater and lesser pelvis
The greater pelvis (yellow) is larger and superior to the lesser pelvis (red) where the pelvic inlet is located.
The true pelvis contains the pelvic colon, rectum, bladder, and some of the reproductive organs. The rectum is at the back, in the curve of the sacrum and coccyx; the bladder is in front, behind the pubic symphysis.
In the female, the uterus and vagina occupy the interval between these viscera. The pelvic splanchnic nerves arising at S2–S4 are in the lesser pelvis.
The False Pelvis
The false (or greater) pelvis is bounded on either side by the ilium. In front it is incomplete, presenting a wide interval between the anterior borders of the ilia; behind is a deep notch on either side between the ilium and the base of the sacrum.
Some consider this region to be part of the pelvic cavity, while others consider it part of the abdominal cavity (hence the name false pelvis). Others compromise by referring to the area as the abdominopelvic cavity.
The false pelvis supports the intestines (specifically, the ileum and sigmoid colon), and transmits part of their weight to the anterior wall of the abdomen.