Chapter 30
APPENDIX B: Development and Aging of the Organ Systems
By Boundless
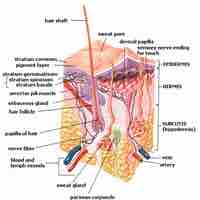
The integumentary system develops from all embryonic layers (ectoderm, mesoderm and neural crest cells).
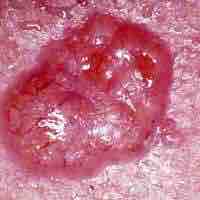
Intrinsic and extrinsic aging describe cutaneous aging of the integumentary system primarily involving the dermis.
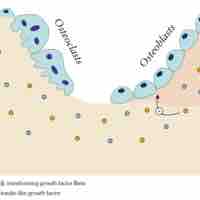
Although bone initially forms during fetal development, it undergoes secondary ossification after birth and is remodeled throughout life.

Bones adapt to the muscle force loads placed on them, becoming thicker and stronger under stress/use and weaker and thinner when unused.
As individuals age, bone resorption can outpace bone replacement, which can lead to osteoporosis and fractures.
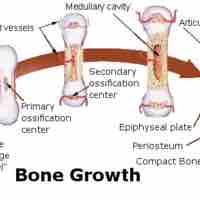
Early in gestation, a fetus has a cartilaginous skeleton that becomes skeletal bones in the gradual process of endochondral ossification.

In osteoporosis, bone mineral density (BMD) is reduced and the integrity of bone proteins is altered, increasing the risk of fracture.
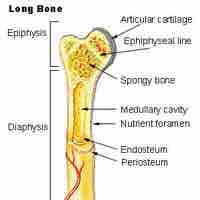
Movable joints are formed at the intersection of bones and are covered by cartilage, which allows the joint to move freely.
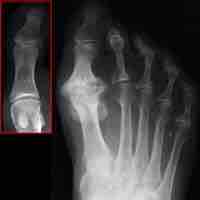
Aging is a common cause of chronic joint pain, as wear and tear on the joints from use results in inflammation and osteoarthritis.
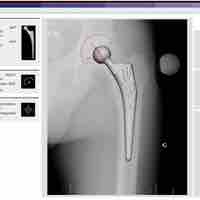
Arthroplasty is an operative procedure in which the arthritic or dysfunctional joint surface is replaced or repaired.

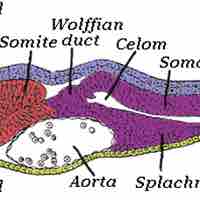
The CNS originally develops from a longitudinal groove on the neural plate that forms the rudimentary nervous system.
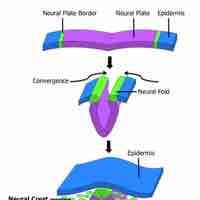
The peripheral nervous system develops from two strips of tissue called the neural crest, running lengthwise above the neural tube.
The peripheral nervous system is able to repair and regenerate itself, but the central nervous system is incapable of doing so.
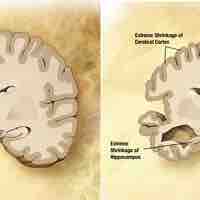
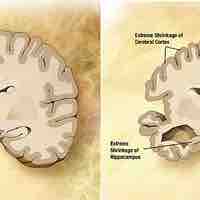
One of the effects of aging on the nervous system is the loss of neurons in cerebral cortex.
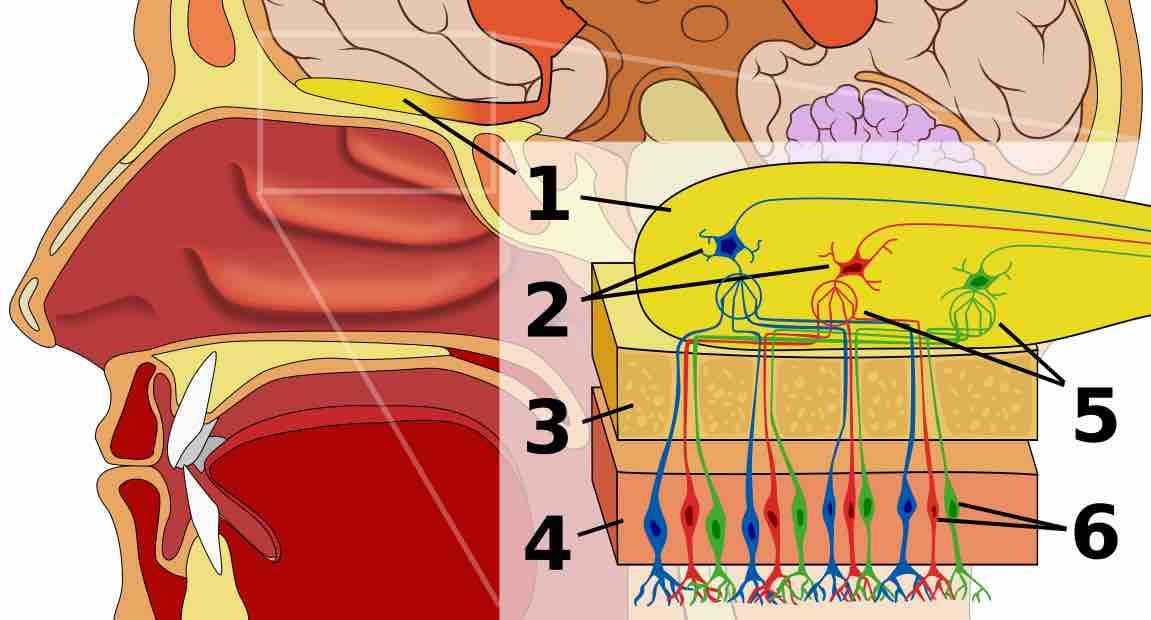
The senses of taste and smell develop in the intrauterine environment and can deteriorate with age.
The eye forms from the neural tube, epidermis, and the periocular mesenchyme, with sequential inductions of tissue during development.
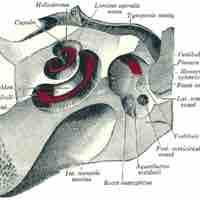
Critical periods have been identified for the development of the hearing and vestibular system.
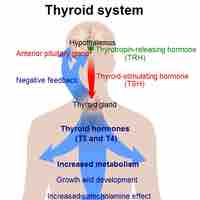
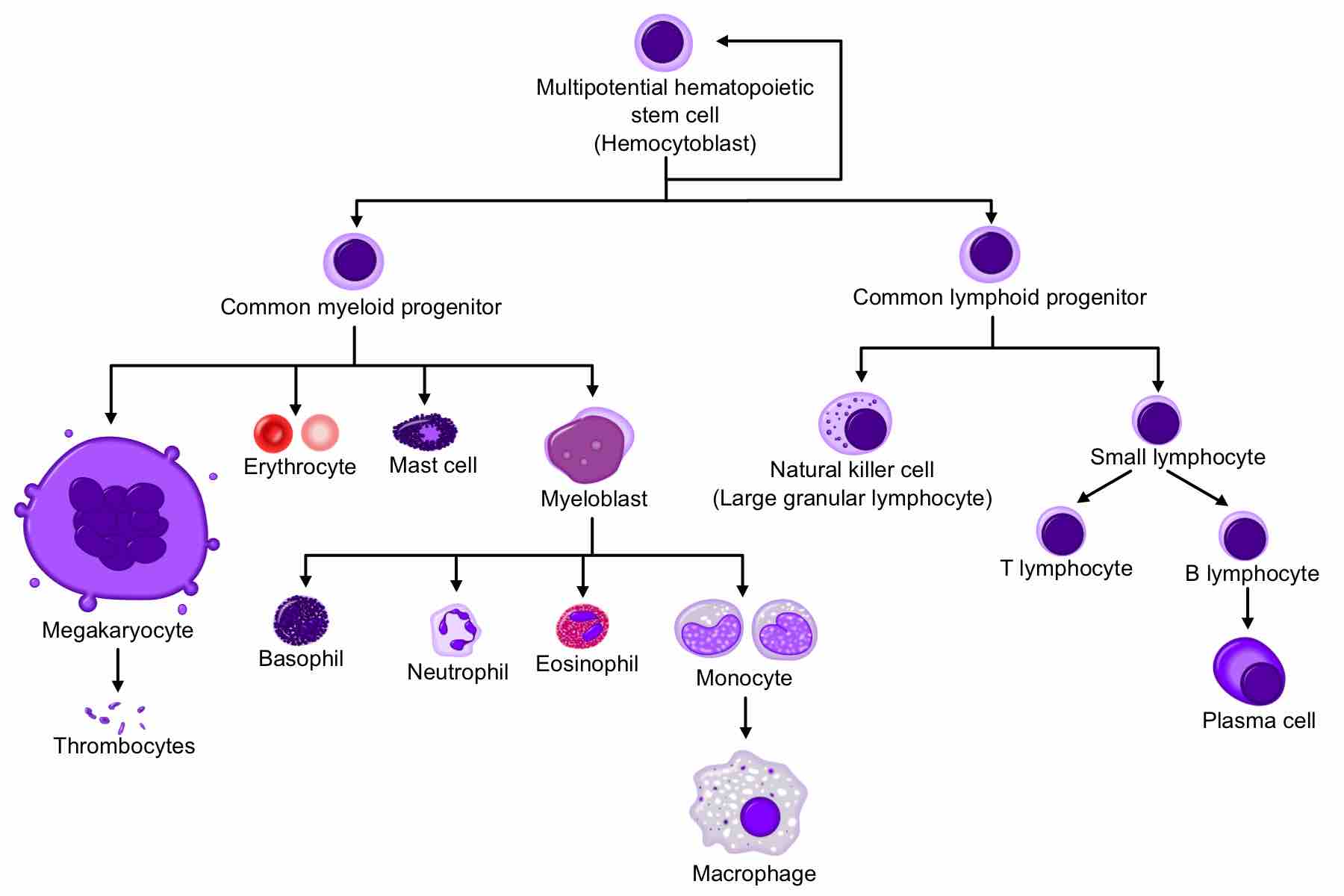
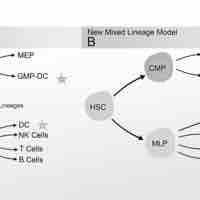
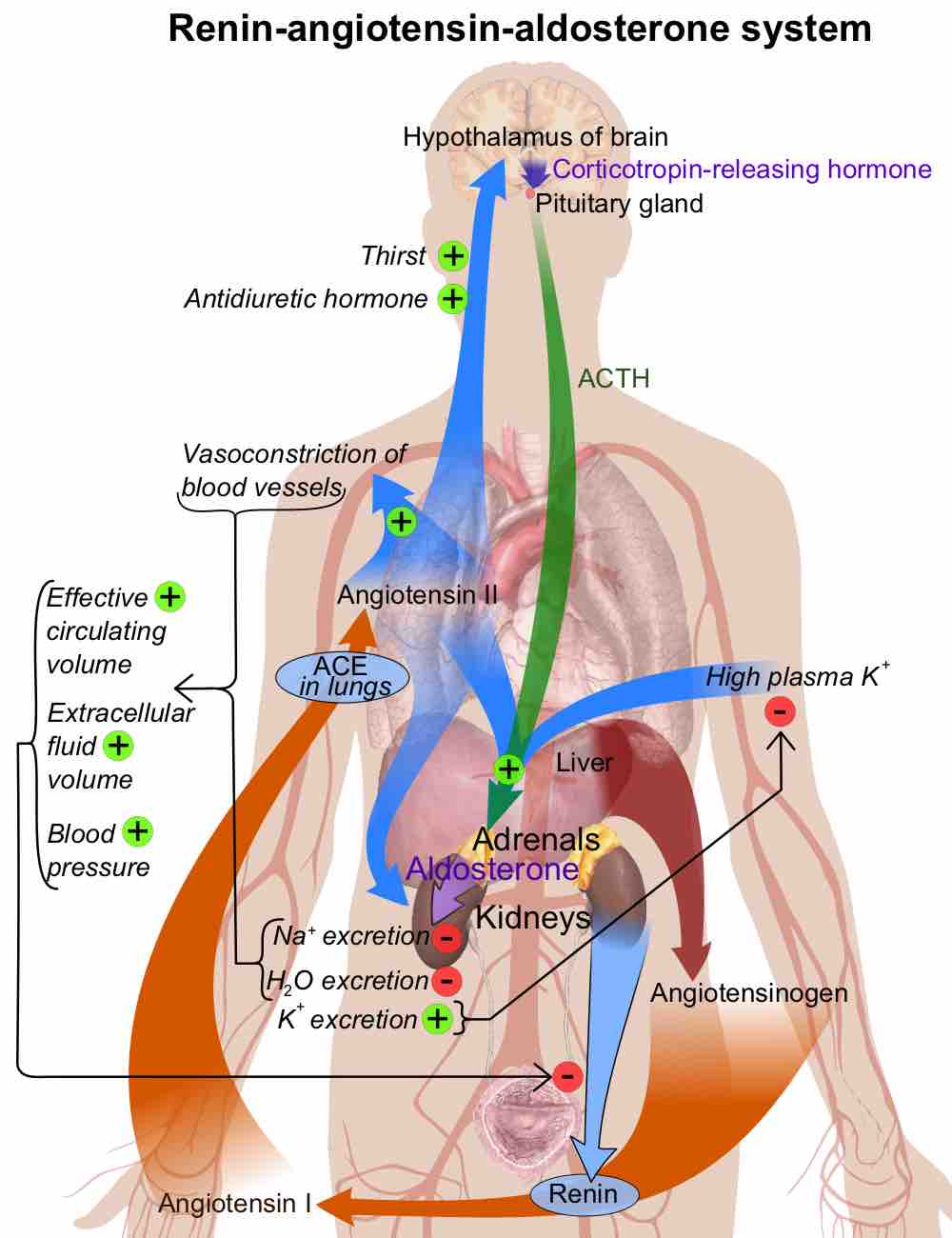
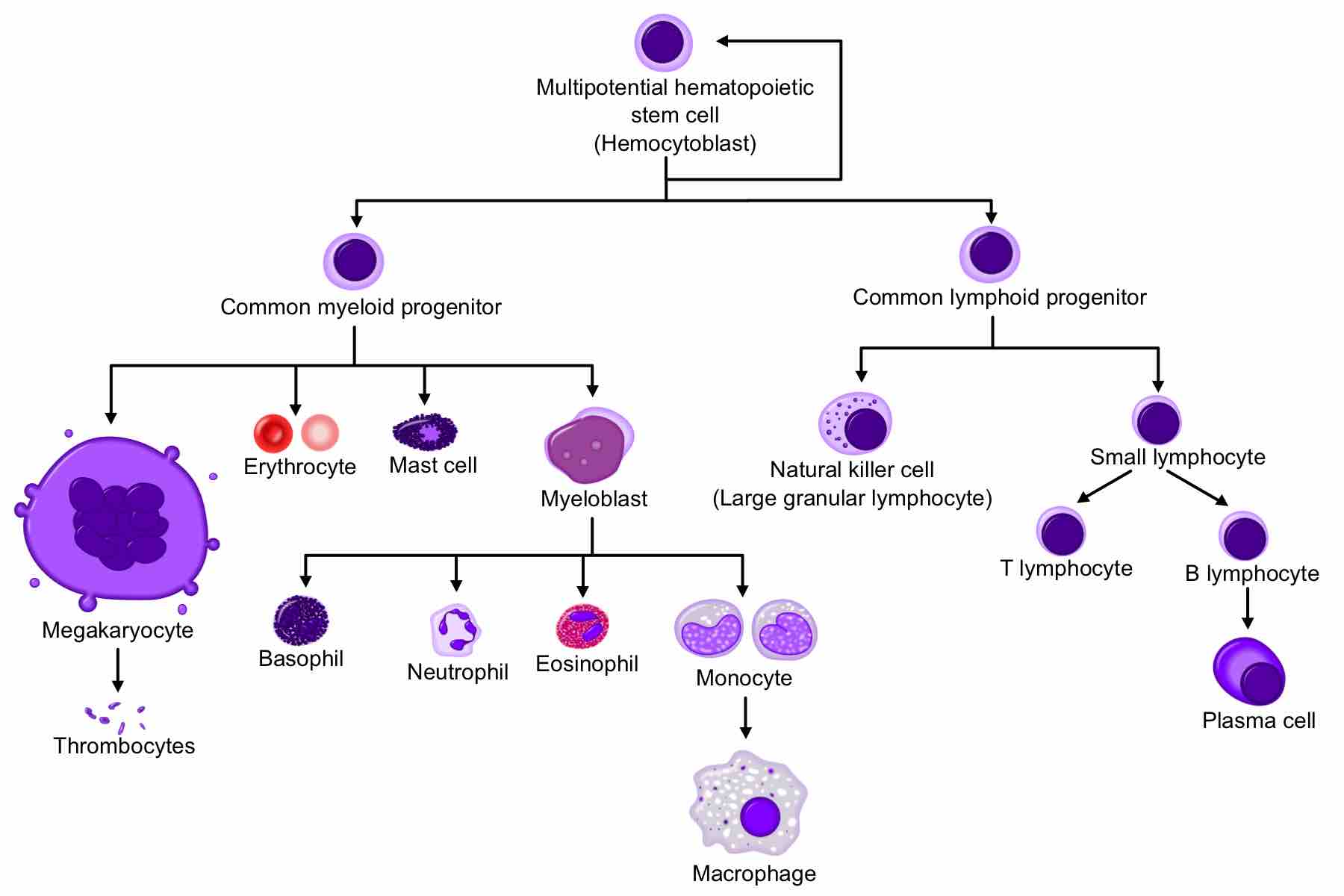
The endocrine system regulates growth, metabolism, and body homeostasis using hormones that effectively target organs via the bloodstream.
Three hormone axes are affected by aging: growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor I, cortisol/dehydroepiandrosterone, and testoterone/estradiol.

As a person ages, the walls of the heart thicken, the heart becomes heavier, valves stiffen and leak, and the aorta becomes larger.
Vasculogenesis is the development of new blood vessels.
Heart failure is defined as the inability of the heart to supply blood to the organs of the body.
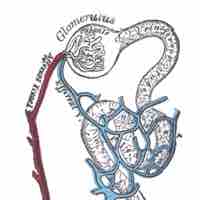
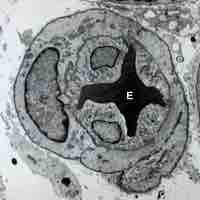
New blood vessels are formed from endothelial stem cells, which give rise to the endothelial cells which line the vessels.
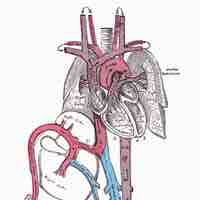
The fetal circulation includes the blood vessels within the placenta and the umbilical cord that carry fetal blood.
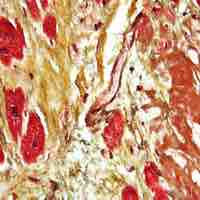
The health of the myocardium can be impaired with age as the arteries narrow or become clogged due to atherosclerosis.

Lung development can be divided into distinct stages: the pseudoglandular period, the canalicular period, and the terminal saccular period.
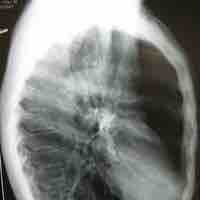
In mammals, breathing in is due to a flattening of the diaphragm and lung expansion. Lung elasticity declines with aging.

The digestive system is an endoderm-derived structure that begins developing about the fourth week of embryogenesis.
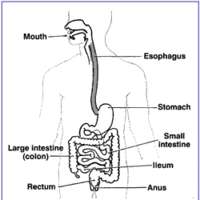
Aging can result in changes of the digestive system due to decreased nerve sensitivity, loss of muscle, and increased infection rate.