Arthroplasty (literally "surgical repair of joint") is an operative procedure of orthopedic surgery performed, in which the arthritic or dysfunctional joint surface is replaced with something better or by remodeling or realigning the joint by osteotomy or some other procedure .
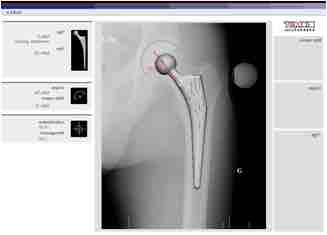
Planning Arthroplasty
CAD assisted planning for Total Hip Arthroplasty.
Previously, a popular form of arthroplasty was interpositional arthroplasty with interposition of some other tissue like skin, muscle, or tendon to keep inflammatory surfaces apart; or excisional arthroplasty in which the joint surface and bone were removed, leaving scar tissue to fill in the gap. Other forms of arthroplasty include resection(al) arthroplasty, resurfacing arthroplasty, mold arthroplasty, cup arthroplasty, and silicone replacement arthroplasty, among others. Osteotomy to restore or modify joint congruity is also an arthroplasty.
For the last 45 years, the most successful and common form of arthroplasty has been the surgical replacement of degenerated joint surfaces with prostheses. For example, a hip joint that is affected by osteoarthritis may be replaced entirely (total hip arthroplasty) with a prosthetic hip. This would involve replacing both the acetabulum (hip socket) and the head and neck of the femur. The purpose of this procedure is to relieve pain, to restore range of motion, and to improve walking ability; thus leading to the improvement of muscle strength.
One of the main problems with joint replacements is wear of the bearing surfaces of components. This can lead to damage to surrounding bone and contribute to eventual failure of the implant. Use of alternative bearing surfaces has increased in recent years, particularly in younger patients, in an attempt to improve the wear characteristics of joint replacement components. These include ceramics and all-metal implants (as opposed to the original metal-on-plastic). The plastic (actually ultra high-molecular-weight polyethylene) can also be altered in ways that may improve wear characteristics.