This article was co-authored by Zora Degrandpre, ND. Dr. Zora Degrandpre is a Natural Health Doctor and Licensed Naturopathic Physician in Vancouver, Washington. She is a grant reviewer for the National Institutes of Health and the National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine. She received her ND from the National College of Natural Medicine in 2007.
There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 20,713 times.
Insulin resistance, as the name suggests, is a condition when the cells in your body don’t respond well to the hormone insulin, meaning they don’t absorb glucose from your blood. Over time, this causes your blood sugar to rise, and could lead to type-2 diabetes.[1] Fortunately, the condition is manageable and won’t progress to diabetes with proper treatment. Even better, many of the recommended treatments are completely natural. Your doctor will almost certainly suggest dietary and lifestyle changes to regulate your blood sugar and improve your insulin sensitivity. They might also prescribe medication, so always follow your doctor’s treatment advice to manage your condition effectively.
Steps
Simple Dietary Changes
If you’re diagnosed with insulin resistance, your doctor will almost certainly recommend some dietary changes to manage your condition. In fact, besides medication, the most common treatment for insulin resistance is a controlled diet. Your doctor may even suggest that you try some dietary adjustments before prescribing medication to see if that helps you. Regardless of whether or not you take medication, it’s extremely important to follow a healthy diet. Incorporate as many fresh fruits and vegetables as possible while controlling your intake of sugary or high glycemic foods. This can help improve your insulin sensitivity and control your weight to make developing diabetes less likely.
-
1Eat whole wheat products instead of enriched flours. Enriched flours have a high glycemic index and cause your blood sugar to spike. Replace all enriched products like white breads and rice with whole wheat or grain varieties for more complex carbohydrates.[2]
-
2Add more natural fiber to your diet. Studies show that people with high fiber diets have a lower incidence of insulin resistance. Add more fresh fruits and vegetables, beans, whole grain products, and fiber-enriched cereals to your diet.[3]
- You can also take supplements to increase your fiber intake. However, doctors recommend getting as much fiber as possible from your normal diet before resorting to supplements.
Advertisement -
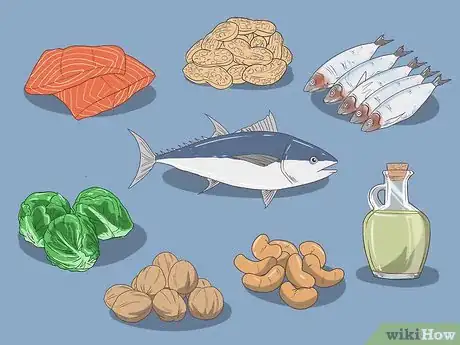
3Eat foods high in omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3s help regulate your body’s glucose levels. You can get this nutrient from oily fish like salmon and sardines, nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils.[4]
- You can also take fish oil supplements to increase your omega-3 intake, but doctors recommend getting as much as possible from your diet first.
-
4Follow an anti-inflammatory diet to see if that helps. Since diabetes and insulin resistance can increase the inflammation in your body, an anti-inflammatory diet might help your symptoms. Follow a mostly plant-based diet rich in fresh fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts. Get your animal protein from lean sources like poultry or fish.[5]
- Also avoid processed, fried sugary, or fatty foods. These are associated with higher levels of inflammation.
-
5Reduce your intake of saturated fats. High-fat diets can make diabetes and insulin resistance worse, as well as cause weight-gain. Eliminate fried or processed foods that are high in saturated fats.
- Try to replace saturated fats with polyunsaturated “healthy” fats from nuts, fish, vegetable oil, and dairy products.
-
6Eliminate sugary foods with a high glycemic index (GI). These foods spike your blood sugar. Foods with a high GI include desserts and sodas, enriched white products, rice, potatoes, breakfast cereals.
Lifestyle Remedies
In addition to dietary changes, some lifestyle changes are a completely natural way to raise your insulin sensitivity. Mainly, staying active and controlling your bodyweight can improve your condition significantly. You should follow these lifestyle remedies along with a careful diet and any medication that your doctor prescribes. That way, you’ll have a well-rounded treatment regimen in place to improve your insulin sensitivity.
-
1Maintain a healthy bodyweight. Being overweight is a major risk factor for insulin resistance and diabetes. Speak to your doctor to find the ideal bodyweight, then follow a diet and exercise regimen to reach and maintain that weight.[6]
- Most of the methods for improving insulin resistance, like following a healthy diet and exercising regularly, will also help you lose weight at the same time.
-
2Get at least 30 minutes of exercise each day. Exercise is proven to improve insulin sensitivity. Try to get 30 minutes of aerobic exercise like running or biking every day, or at least 5 days out of the week.[7]
- Aerobic exercise is best but some light resistance or weight training is also effective for boosting your metabolism.
-
3Reduce your stress to improve your condition. High stress is linked to poor insulin sensitivity. If you often feel stressed, try doing some relaxation exercises like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing to improve your anxiety.[8]
- If you have trouble controlling your stress, then consider speaking to a professional therapist to learn more stress-reduction techniques.
-
4Sleep for 7-8 hours each night. Regular sleep helps your body operate better and could improve your insulin sensitivity. Do your best to get a full sleep every night so your body can recharge itself.[9]
- If you suffer from insomnia, try doing quiet, relaxing activities for an hour before bed like reading, listening to calm music, or taking a bath. Try not to look at your phone or computer, since the screen light can stimulate your brain
Hypoglycemic Herbs
While medication, diet, and lifestyle changes are the primary treatments for insulin resistance, there are also some herbal treatments that may be effective. Clinical trials are limited, but studies do suggest that these remedies could improve your insulin sensitivity and regulate your blood sugar. If you’d like to supplement your regular treatment regimen, try some of the following herbs. Always ask your doctor before you start taking herbs because they can potentially interact with other medications or be harmful with long-term use. If you experience any adverse reactions, then stop taking them right away.
-
1Take fish oil supplements to boost your omega-3s. If you don’t get enough omega-3 fatty acids from your diet, then daily fish oil supplements can boost your intake.[10]
-
2Use ginseng to regulate your blood sugar levels. Studies suggest that ginseng is an effective treatment for diabetes and insulin resistance because it can help control your blood sugar. Try taking a daily supplement to see if it improves your symptoms.[11]
- The strength of ginseng depends on where it was produced, so follow the dosage instructions on the product you use or ask your doctor for guidance.
-
3Eat bitter melon to lower your blood glucose. Lowering your blood sugar can help improve insulin resistance. Either eat bitter melon plain or take supplements with the nutrient extracted.[12]
-
4Take jiangtang keli to improve your insulin sensitivity. This herb is commonly used in China and other Asian countries to manage insulin resistance. It may help you as well.[13]
Medical Takeaways
Insulin resistance is a manageable condition that you can treat with a variety of natural remedies. By following the right diet, getting enough exercise, and reducing your stress, you could improve your condition significantly. In fact, doctors usually recommend these treatments for people with insulin resistance. You could also try some herbal treatments to regulate your blood sugar but always check with your doctor before doing so. Your doctor may also want you to take medication, so make sure you follow the treatment regimen that you’re prescribed to see the best results possible.
References
- ↑ https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/prediabetes/symptoms-causes/syc-20355278
- ↑ https://familydoctor.org/condition/insulin-resistance/
- ↑ https://www.aafp.org/afp/2001/0315/p1159.html
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3320694
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20234036
- ↑ https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/what-is-diabetes/prediabetes-insulin-resistance
- ↑ https://www.aafp.org/afp/2001/0315/p1159.html
- ↑ https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/insulin-resistance.html
- ↑ https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/insulin-resistance.html


































































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...