This article was co-authored by Pippa Elliott, MRCVS. Dr. Elliott, BVMS, MRCVS is a veterinarian with over 30 years of experience in veterinary surgery and companion animal practice. She graduated from the University of Glasgow in 1987 with a degree in veterinary medicine and surgery. She has worked at the same animal clinic in her hometown for over 20 years.
This article has been viewed 26,205 times.
Gerbils are a popular variety of small animal kept as pets. As with many small animals they prefer the company of others of their kind. Normally it’s best to keep two animals of the same gender together, but if you have a male and female together they may end up mating. There are a number of signs to look for.[1] [2] [3] [4]
Steps
Attracting the Mate
-
1Listen for thumping sounds. You may also observe the gerbil pounding both rear feet. The sound is usually a quick thump, but can vary in tempo and volume. This can be mistaken for the gerbil being excited for reasons other than mating.[5]
- Sometimes gerbils other than the mating pair will “catch on” and start pounding their feet too.
-
2Watch for the male gerbil rubbing themselves around the cage. This is scent marking, and may be a sign of the male signaling his suitability as a mate to the female gerbil. You may also see the gerbil rubbing their stomach on cage objects.[6]
- The male gerbil, however, could also be doing this to establish dominance and/or mark territory.
Advertisement -
3Look for aggressive behavior in the male. The male may be reacting to the female’s readiness to mate. The first sign of aggressive behavior is usually a loud squeak from the male. The male gerbils may appear to “box” or wrestle with other males to ward off rivals for mating. Do not let this go on too long. Separate them if necessary.[7]
- The aggressive behavior could also be for a perceived threat unrelated to mating.
Observing the Mating Act
-
1Watch for the female gerbil to run ahead of the male. This will usually occur later in a day.[8]
- Gerbils tend to mate in the evening.
-
2Look for the male gerbil to follow the female. He should approach her from the rear.[9]
- The male will attempt to mount the female in line from behind to get into the correct mating position.
-
3See if the female gerbil accepts the mount or turns and faces the male. Either can occur with a squeak.[10]
- If she turns and faces the male she has rejected the male as a mate.
- If the female does not turn, but stays in place, she has accepted the mating pair.
-
4Listen for mating sounds. Both the male and female gerbils can make these sounds. The male may thump his rear feet softly during mating. The female may squeak. Both of the male and female behaviors are signs of sexual excitement.[11]
-
5Look for the gerbils to groom themselves. Both male and female gerbils should groom themselves after the mating act. The male and female gerbil should be allowed to groom their own genitalia. [12]
Detecting Pregnancy in Gerbils
-
1Look at the gerbil’s belly. Gerbils can mate frequently. A female can be in heat every 6 weeks for 4 day periods. If she is with a male partner and not mating you should check for pregnancy. You’ll have to wait about a week to notice any visible body changes. Hold a piece of food or seed above the female’s head after a 2-3 week period to find the bulge in her belly.[13] [14]
-
2Weigh the female gerbil regularly. You’ll observe increases in weight of the female gerbil as she carries her litter. Weight the gerbil in a small pet scale or ask your veterinarian to do it. Either way, re-weight the gerbil every 10 days.[15]
-
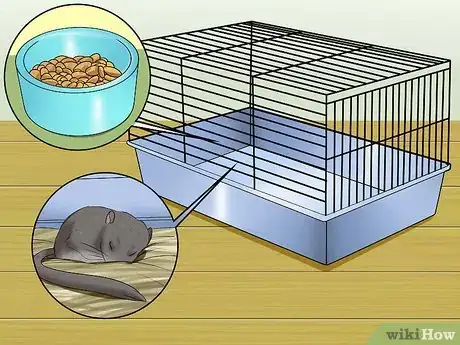
3Provide extra privacy and comfort. The gerbil parents will want more privacy and female will require more nutrition during the pregnancy. Acquire a hideaway from a pet store, and provide extra tissues for bedding to let the gerbils build a nest. You can also put up a cloth or paper as a privacy drape on their cage. Check the food that you are providing for them is balanced for pregnant gerbils. It should have at least 18 percent protein.[16]
-
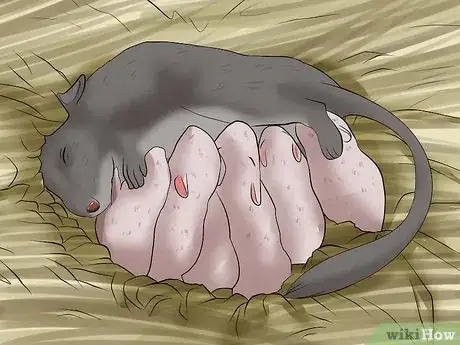
4Provide measured help for the litter. Birth usually will happen at night and can take a couple of hours. The gerbil will stretch until the baby is about to come out, reach to help it out, and then bite and eat the placenta. The babies will be born hairless, blind, deaf, and helpless. They will depend on their parents for weening for 21-35 days. Try to disturb this process as little as possible for a couple of weeks except for changing food, water, and overly wet bedding.[17]
- Don’t be surprised to see the two parents mate again right away. The male will then often get expelled from the hideaway for a few days before the female lets him help with the babies.
- Cannibalism is a concern with gerbil mothers and their babies. This is rare and usually only occurs with dead babies or if the mother is highly disturbed or sick.
Warnings
- Do not allow one male to mate with multiple females in close proximity. The females may kill the babies of the others.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Don’t interfere with the mating act once it’s started.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ http://www.peteducation.com/article.cfm?c=18+1799&aid=1620
- ↑ http://www.petplace.com/article/small-mammals/general/reproduction-breeding/breeding-your-gerbils
- ↑ http://thegerbils.com/breeding4mating.htm
- ↑ http://cpr-nc.org/pet-care-info/gerbils
- ↑ http://www.peteducation.com/article.cfm?c=18+1799&aid=1620
- ↑ http://www.peteducation.com/article.cfm?c=18+1799&aid=1620
- ↑ http://www.peteducation.com/article.cfm?c=18+1799&aid=1620
- ↑ http://thegerbils.com/breeding4mating.htm
- ↑ http://thegerbils.com/breeding4mating.htm
- ↑ http://thegerbils.com/breeding4mating.htm
- ↑ http://thegerbils.com/breeding4mating.htm
- ↑ http://thegerbils.com/breeding4mating.htm
- ↑ http://www.thegerbils.com/breeding5gestation.htm
- ↑ http://www.gopetsamerica.com/small-animals/gerbils.aspx
- ↑ http://www.thegerbils.com/breeding5gestation.htm
- ↑ http://www.thegerbils.com/breeding5gestation.htm
- ↑ http://www.thegerbils.com/breeding5gestation.htm