This article was medically reviewed by Danielle Jacks, MD and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD. Danielle Jacks, MD is a Surgical Resident at Ochsner Clinic Foundation in New Orleans, Louisiana. She has over six years of experience in general surgery. She received her MD from Oregon Health and Science University in 2016.
There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 243,709 times.
When you visit a loved one in the hospital, you're likely to find your eye drawn to the monitor at their bedside. If you're wondering what all those wavy lines, numbers, and abbreviations mean, you've come to the right place! Read on to learn how to read and understand the patient monitor so you'll know what all those values can tell you about your loved one's condition. And if you have any questions or concerns, don't hesitate to ask a doctor or nurse on duty.
Things You Should Know
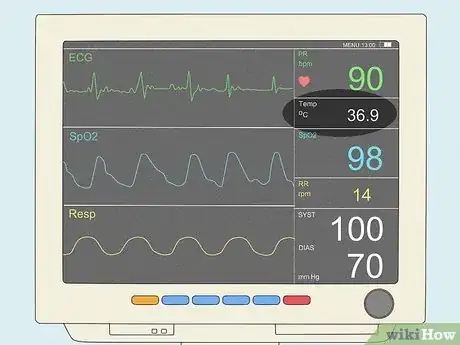
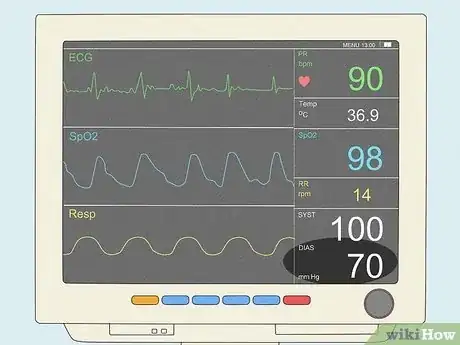
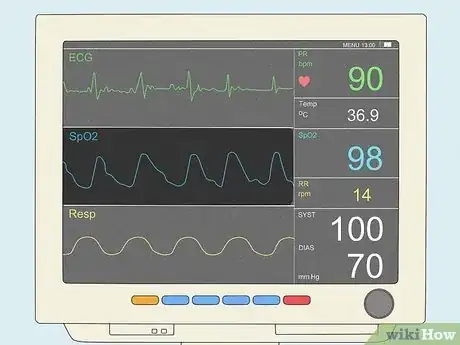
- Read the numbers on the right-hand side of the monitor to learn the patient's pulse rate, body temperature, and blood pressure.
- Use the respiratory and oxygen saturation rates to keep tabs on the patient's breathing and circulatory system.
- Watch the waveforms for any signs of irregular heartbeat or breathing.
Steps
Warnings
- Avoid focusing too much on a single number. Doctors and nurses will look at the vital signs together and take the context into consideration. A single number out of normal range usually isn't cause for concern.[14]⧼thumbs_response⧽
- If the monitor or another piece of equipment starts beeping, call a nurse to come and check it out.[15]⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002341.htm
- ↑ https://www.columbiadoctors.org/treatments-conditions/vital-signs-body-temperature-pulse-rate-respiration-rate-blood-pressure
- ↑ https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/vital-signs-body-temperature-pulse-rate-respiration-rate-blood-pressure
- ↑ https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/22447-blood-oxygen-level
- ↑ https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/vital-signs-body-temperature-pulse-rate-respiration-rate-blood-pressure
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002341.htm
- ↑ https://www.columbiadoctors.org/treatments-conditions/vital-signs-body-temperature-pulse-rate-respiration-rate-blood-pressure
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002341.htm
- ↑ https://www.columbiadoctors.org/treatments-conditions/vital-signs-body-temperature-pulse-rate-respiration-rate-blood-pressure
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK2214/
- ↑ https://www.nursespost.com/reading-a-patient-monitor/
- ↑ https://www.nursespost.com/reading-a-patient-monitor/
- ↑ https://www.healthywa.wa.gov.au/Articles/F_I/Intensive-care-units-ICUs
- ↑ https://www.nursespost.com/reading-a-patient-monitor/
- ↑ https://healthywa.wa.gov.au/Articles/F_I/Intensive-care-units-ICUs
































































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...