This article was co-authored by wikiHow Staff. Our trained team of editors and researchers validate articles for accuracy and comprehensiveness. wikiHow's Content Management Team carefully monitors the work from our editorial staff to ensure that each article is backed by trusted research and meets our high quality standards.
There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 28,885 times.
Learn more...
Creating Bismuth crystals is a fascinating science project that can be done entirely at home. The end result is a spectacular array of miniature towers of multicolored metal all gleaming in the light. The reason this is possible to do at home is due to Bismuth’s relatively low melting point. All it takes is a few tools, a little bit of safety equipment, and some knowledge on how it all works, and it’s possible to create an iridescent mini sculpture of your own.
Steps
Materials
-
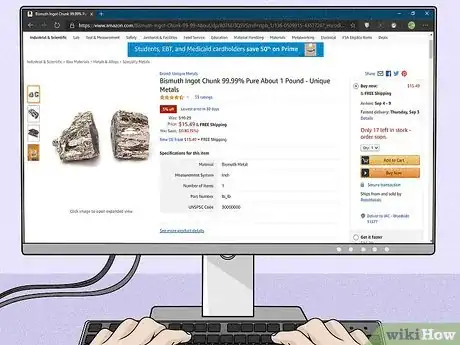
1Buy 3 kilograms (6.6 lb) of Bismuth. Bismuth is a fairly cheap metal but it is also very dense (it is often used as a substitute for lead).[1] As such, you should buy several pounds/kilograms of it, to ensure you have enough to do the experiment again if you want to.
- Because it is such a dense metal, be aware that you may need to buy more weight than you think as the pieces may be smaller than you were expecting.
- To achieve the highest quality crystals, try and get hold of Bismuth that is of the highest purity (around the 99.99% mark).[2]
- The easiest way to buy Bismuth is online.
-
2Have the right safety equipment around. The experiment does involve dealing with molten metal at a temperature of around 271 °C (520 °F). Like any liquid on a stove, it is not unusual for the metal to spatter and end up outside the vessel. As such, using appropriate safety equipment is extremely important.[3] This includes:
- Goggles
- Sturdy gloves
- Apron
- Fire extinguisher
Advertisement -
3Use a low-quality pot that you don’t mind not seeing clean again. Once you have melted the Bismuth in your pot, it’s highly unlikely that you will ever get that pot totally clean again so a cheap pot you don’t mind throwing out afterward is probably best.[4]
- Tall pots with a smaller diameter work better as the crystals form downwards from the surface of the molten metal.
-
4Work outside if possible. Working outside will give you more freedom to make mistakes and also be much safer.
- Be aware that some cheaper portable electric stoves don't have enough power to melt the Bismuth.[5]
- If you do work inside, make sure you have a fire extinguisher nearby.
Bismuth Melting
-
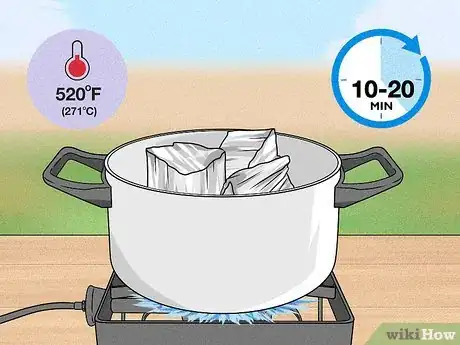
1Put the Bismuth in your pot and begin to heat the container. The melting point of Bismuth is 271 °C (520 °F) and it will take 10-20 minutes to get the Bismuth up to this temperature.[6] Use a fork to stir any remaining bits of Bismuth in with the rest of it.
- Be aware that as the Bismuth melts it may bubble and spatter so use a lid if you can.
-
2Scrape away the shiny layer that has formed on the Bismuth. The impurities in the Bismuth will rise to the top as the Bismuth melts. Once it is completely melted, these impurities will form a layer on top of the liquid. Use a spoon or other utensil to scrape this layer away and discard elsewhere on a non-flammable surface.[7]
- This is extremely important to make sure that the Bismuth crystals start forming at the right time.
-
3Turn off the heat once all the Bismuth is melted. In order to allow crystals to start forming the heat must be turned off. This occurs as the Bismuth starts moving back to a solid state from its molten state.[8]
- In order to reduce the speed at which the temperature of the Bismuth drops, some people turn the heat down gradually rather than straight off.
Crystal Formation
-
1Wait for a solid layer to form on top. The Bismuth will cool from the outside in and a firm layer will form on top which should then be removed. Moving the pot unnecessarily can mean ending up with smaller crystals so try gently pushing on the top layer with a fork. This will give you an indication of whether a top layer has solidified or not.[9]
- The reason you need to remove the top layer is so that the crystals forming on the bottom don’t link up with the top layer. If this happens, your crystals will be trapped in.
- Use a fork or spoon to scoop the top layer out from the rest of the Bismuth.
-
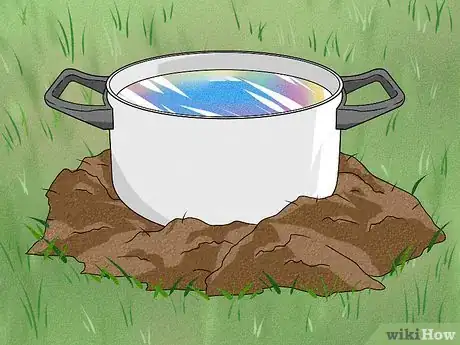
2Cool the Bismuth as slowly as possible for larger crystals. This can be done by insulating the pot from the outside as this is where most of the heat is lost. Placing the pot into a tin foil mold or into a pile of sand are both good options for insulation.
-
3Pour the rest of the liquid Bismuth into a separate bowl. As you have already removed the top layer, there will be a pool of liquid Bismuth underneath it. To create the largest crystals, pour the liquid out when the whole pot of Bismuth is about halfway between its molten and solid state.[10]
- Getting the timing correct here can take a little bit of practice so don't worry if you don't get it quite right the first time.
- If the separate bowl is not metal then you should heat it so it doesn’t crack from heat shock.
-
4Examine your crystals. Once you've removed the liquid from your pot, the Bismuth that solidified in the time you gave it will have formed crystals in your pot. These will initially appear to be silver but will quickly change color depending on the temperature that they were first exposed to oxygen at.[11]
- Use a pair of pliers to pull crystals out of the pot.
- Alternatively, place the pot face down and bang firmly on the base of it a few times. With any luck, the whole solid piece of Bismuth will come out and you’ll be left with a large chunk with many crystals inside it.
Warnings
- Appropriate safety equipment should always be worn.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- In this experiment, you're working with molten metal at an extremely hot temperature so take extra care when transporting the liquid from one place to another.⧼thumbs_response⧽
Things You'll Need
- 3 kilograms (6.6 lb) of Bismuth
- Disposable metal pot with lid
- Stove
- Safety goggles
- Thick safety gloves
- Apron
- Secondary pot for draining
References
- ↑ https://io9.gizmodo.com/5952428/grow-an-iridescent-crystal-from-a-plain-metal-fishing-sinker?IR=T
- ↑ http://www.amazingrust.com/Experiments/how_to/Bismuth_Crystals.html
- ↑ https://steemit.com/steemit/@kenikat/making-bismuth-crystals
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v8KYZHMkTHw
- ↑ https://edu.rsc.org/elements/bismuth/2000017.article
- ↑ https://steemit.com/steemit/@kenikat/making-bismuth-crystals
- ↑ https://io9.gizmodo.com/5952428/grow-an-iridescent-crystal-from-a-plain-metal-fishing-sinker
- ↑ https://steemit.com/steemit/@kenikat/making-bismuth-crystals
- ↑ http://periodictable.com/Stories/083.4/index.html
About This Article
To make bismuth crystals, start by melting the bismuth in a tall, narrow pot over a stove outdoors. Once the bismuth has melted, scrape off and dispose of the shiny layer on top. Then, wait until a solid layer forms on top of the bismuth as it cools before scraping the layer off with a fork. Next, pour the remaining liquid into a metal bowl so you're left with a solid chunk of bismuth in the bottom of the pot. Finally, turn the pot upside down and bang on it to remove the solid bismuth, along with the crystals. For tips on how to purchase bismuth, read on!