This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Dan Hickey. Dan Hickey is a Writer and Humorist based in Chicago, Illinois. He has published pieces on a variety of online satire sites and has been a member of the wikiHow team since 2022. A former teaching artist at a community music school, Dan enjoys helping people learn new skills they never thought they could master. He graduated with a BM in Clarinet Performance from DePauw University in 2015 and an MM from DePaul University in 2017.
There are 13 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, several readers have written to tell us that this article was helpful to them, earning it our reader-approved status.
This article has been viewed 836,470 times.
Learn more...
In theory, a dock isn’t a complicated structure. But just how do you get those sturdy posts (called pilings) securely rooted in the ground at the bottom of your pond or lake? Unless you have the heavy equipment to drive the pilings into the ground, you’ll need to use a jet of water to dig a deep hole or set the pilings in concrete footers—jetting is best for sandy soil, while concrete is more stable for muddy beds.[1] Although this project may require some special tools and a couple of people to lend a helping hand, you’ll be able to enjoy fun on the waterfront for years to come!
Things You Should Know
- To install wood posts (pilings), stand the piling in the desired spot and use a water jet to clear away sand and silt so it sinks 4–6 ft (1.2–1.8 m) below the lakebed.
- To pour concrete posts, push a PVC pipe 2 ft (0.61 m) into the lakebed, then bail out the water and remove sand and silt with a post-hole digger.
- Then, pour 10 in (25 cm) of concrete into the pipe and lower in your wood piling. Continue pouring concrete around the piling and let it cure for 3 days.
Steps
Installing Pressure-Treated Wood Pilings
-
1Choose round dock pilings made of pressure-treated wood. Pressure-treated wood has been preserved with special chemicals that help it last longer when it’s exposed to harsh outdoor conditions, like constantly being waterlogged or subjected to tiny wood-eating organisms. Round pilings aren’t cut to expose the interior of the wood, making them hardier than square-cut ones. Pressure-treated wood is also the most cost-effective option.[2]
- Other options for pilings include plastic-coated wood and heavy-duty aluminum.
- Buy pilings 6–8 in (15–20 cm) in diameter if your dock will weigh less than 10,000 lb (4,500 kg). If it’ll weigh more, choose 10–12 in (25–30 cm) pilings.[3]
- Get enough pilings to place one about every 10 ft (3.0 m) along the dock on both sides to support its weight.[4]
-
2Rent a 2–3 in (5.1–7.6 cm) water jetter from a home improvement store. Often, your local home improvement store will allow you to rent high-powered tools like a water jetter (also called a hydro jet) for a short amount of time. This prevents you from paying full price for a tool you won’t use very often—water jetters can be pricy![5]
- These high-powered water pumps typically run on gasoline and come with either a 2 in (5.1 cm) or 3 in (7.6 cm) diameter hose. Either size will work, but since the hose gets heavy when it’s full of water, the 2 in (5.1 cm) hose may be easier to use.
- The cost of renting a water jet will vary depending on your location and the length of time you need it. A 1,500 PSI jet might be $100 to $200 per day.
- If you don’t have access to a water jetter, use a power washer or high-pressure garden hose instead. The process will probably take longer this way, though.
Advertisement -
3Spray paint your pilings at 12 in (30 cm) intervals to monitor their depth. As you start to sink the pilings, it can be hard to keep track of how far they’ve gone into the ground. By marking them with spray paint, it’s easier to make sure your pilings are all installed at the same depth.[6]
-
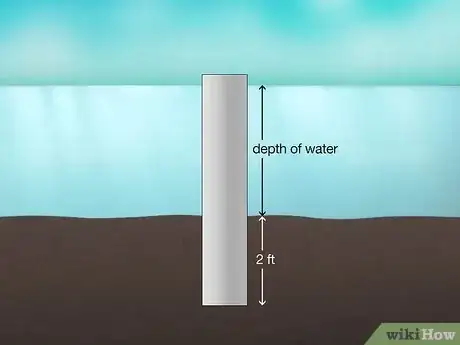
4Cut the pilings tall enough to hold the dock 3–4 in (7.6–10.2 cm) above water. Ideally, your dock will hover above the highest level the water will reach (taking tides, flooding, or heavy rainfall into account).[7] Use a long measuring tape or a marker float to find the depth of the water from the lakebed to the surface. Then, add 4 in (10 cm) plus the length of piling that will go underground (4–6 ft (1.2–1.8 m)) to find the total height.[8]
- For example, if the water is 6 ft (1.8 m) deep, you’d need pilings that are between about 124 in (3.1 m) and 148 in (3.8 m) tall.
- Cut the beams a little longer than you think you’ll need them to be. You can always trim them later if needed.
- Even in a body of water that isn’t affected by tides, the water level may still fluctuate. If you’re not sure what the maximum water line is, ask other pier or dock owners in your area.
-
5Stand the first piling in the water and push it into the lakebed. If possible, recruit 1-2 strong people to help you hold the piling in place (try bribing a few friends with lemonade and the promise of spending sunny days on the water!). Once the post is in the right location, gently push or hammer it a few inches or so into the lakebed for some stability before you jet the sand and silt away.[9]
- If you don’t have anyone who can help you, use sturdy pieces of wood and a pulley system to create a tripod that can lift and hold the pilings in place.
- If the lakebed is hard or compact, use the water jetter to “pre-jet” a starter hole to help the piling settle.
-
6Aim the water jetter at the bottom of the piling and turn on the pump. The water will blow out of the hose with enough force to push the sand and silt out from under the piling. As this is happening, guide the piling further down into the earth until you reach the desired depth. If you need to, move the tip of the hose from side to side so the piling can go in evenly.[10]
- If the force of the water isn’t enough to remove the sand, attach a PVC pipe with a 1 in (2.5 cm) diameter to the end of the hose to increase the pressure.
- Some people attach a metal brace to the piling 4–6 ft (1.2–1.8 m) above the bottom so it doesn’t sink further into the lakebed. This is optional.
- Use the water jetter to push some of the dirt back into place around the piling after it’s set. This helps stabilize the piling even more.
- Repeat this process for the remaining pilings.
Pouring Concrete Pilings
-
1Measure the total length of PVC pipe you’ll need for every piling. Measure from the bed beneath the water to the highest level the water reaches in your area. Depending on how soft the earth is below the water, add another 1–2 ft (0.30–0.61 m) to that length (closer to 2 ft (0.61 m) for soft, silty beds). Multiply this length by the number of beams you will need to get the total length of PVC.[11]
- When you’re choosing the pilings that go inside of the concrete, add another 3–4 in (7.6–10.2 cm) to account for the height of the pier or dock above the water.
-
2Purchase heavy-duty PVC with a diameter of 12–18 in (30–46 cm). For standard 8 ft (2.4 m) docks, a PVC pipe with a diameter of 12 in (30 cm) and an interior post with a diameter of 4 in (10 cm) is sufficient.[12]
- If your dock is longer than 8 ft (2.4 m), start with a PVC pipe of 18 in (46 cm) and and posts that are about 6 in (15 cm).
-
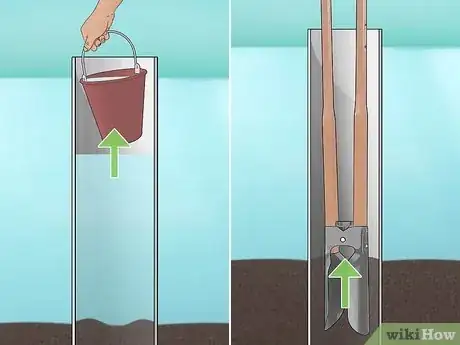
3Drive the PVC pipe about 2 ft (0.61 m) into the lakebed. If you can’t push the pipe into the ground by hand, lay a spare piece of wood on top of the PVC and hit it squarely with a sledgehammer until you reach the desired depth.[13]
- Spray paint the pipe in 1 ft (0.30 m) increments before placing it so you can tell how deep it is.
-
4Remove water and mud from the pipe with a bucket and post-hole digger. Bail out the water that’s inside of the PVC pipe with a bucket, then use a post-hole digger to remove sand, silt, or mud from the bottom of the pipe. The pipe should be clear down to the bottom.[14]
- While you can use a pump to clear out the pipe, doing it by hand is safer, since you don’t have to have electrical equipment near the water.
- If the ground is very hard, you may need to rent a mini-excavator.
-
5Mix quick-set concrete in buckets according to the package directions. It’s easy to mix quick-set concrete, like Quikrete, by hand—just pour the concrete mix into a bucket and dig a small hole in the mix, then add in water according to the instructions.[15]
- The amount of concrete you’ll need depends on the size of your project. For a PVC pipe with a diameter of 12 in (30 cm) and a post of 4 in (10 cm), estimate about 2 bags of Quikrete per 1 ft (0.30 m) of height.
- If your pipe is 18 in (46 cm) in diameter and your post is 6 inches (15 cm), you’ll need about 5 bags per 1 ft (0.30 m).
- It may be a good idea to rent a concrete mixer for this project.
-
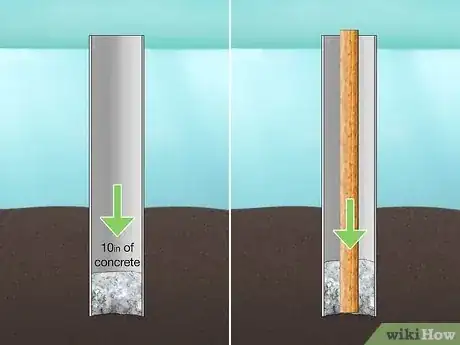
6Pour 10 in (25 cm) of concrete into the pipe, then insert a post. Lower the post into the PVC pipe and push it down into the concrete mix. By pouring concrete into the pipe first, the post will be more stable when you put it into place.[16]
- The PVC pipe will keep the water out of the concrete as it cures.
-
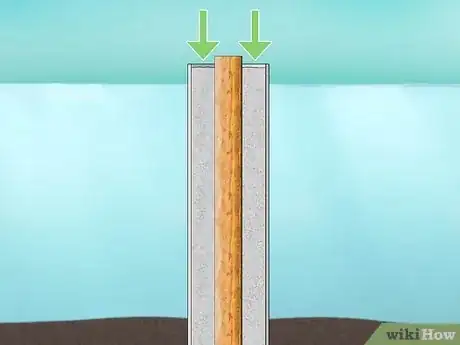
7Continue to pour concrete around the piling. Keep working until you fill the PVC pipe all the way to the maximum water line. Work slowly to ensure you don’t end up with any air pockets in the concrete.[17]
- This part of the process will take awhile, so it’s probably a good idea to get some friends to help you fill and carry buckets of concrete.
- You may have some excess pipe at the top. Cut this off with a reciprocating saw after the concrete dries if needed.
-
8Repeat for each post, then let the concrete cure for 3-4 days. No matter how excited you are about having a pier to lounge on, it’s important to let the concrete completely cure before you continue building your structure. After you poured all of that concrete, though, you’ll probably be glad to have a couple of days to rest before you start building the framework![18]
Community Q&A
-
QuestionIs a water jetter the same as a pressure washer?
 wikiHow Staff EditorThis answer was written by one of our trained team of researchers who validated it for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
wikiHow Staff EditorThis answer was written by one of our trained team of researchers who validated it for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
Staff Answer wikiHow Staff EditorStaff AnswerA water jetter is more powerful than a typical pressure washer, but in a pinch, a pressure washer could work. Since it's weaker, it'll probably take longer to jet the piling into place than with a jetter.
wikiHow Staff EditorStaff AnswerA water jetter is more powerful than a typical pressure washer, but in a pinch, a pressure washer could work. Since it's weaker, it'll probably take longer to jet the piling into place than with a jetter. -
QuestionWhy does the PVC only have to go into the ground 1 to 2 feet and the pilings much deeper?
 wikiHow Staff EditorThis answer was written by one of our trained team of researchers who validated it for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
wikiHow Staff EditorThis answer was written by one of our trained team of researchers who validated it for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
Staff Answer wikiHow Staff EditorStaff AnswerSince you're adding concrete inside the PVC, you'll have a much heavier and sturdier "foot" for the piling to rest on. However, if the lakebed is extra sandy or soft, you may have to go deeper than 2 feet.
wikiHow Staff EditorStaff AnswerSince you're adding concrete inside the PVC, you'll have a much heavier and sturdier "foot" for the piling to rest on. However, if the lakebed is extra sandy or soft, you may have to go deeper than 2 feet. -
QuestionHow do I build a shoreline dock attach without ice heave moving it?
 wikiHow Staff EditorThis answer was written by one of our trained team of researchers who validated it for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
wikiHow Staff EditorThis answer was written by one of our trained team of researchers who validated it for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
Staff Answer wikiHow Staff EditorStaff AnswerInstall an ice eater (a motor that bubbles the water around the dock and brings warmer water from below up to the surface) near your dock. It'll keep the water around the dock from freezing over, though it may not protect against a giant sheet of ice drifting into the dock.
wikiHow Staff EditorStaff AnswerInstall an ice eater (a motor that bubbles the water around the dock and brings warmer water from below up to the surface) near your dock. It'll keep the water around the dock from freezing over, though it may not protect against a giant sheet of ice drifting into the dock.
Warnings
- Since jetting will loosen the soil around the pilings, your pier or dock may not be able to support as much weight as one with cement pilings.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- In some areas, jetting is discouraged because it can disturb wildlife. Check to see if there are regulations in your area. Often, low-pressure jetting is still permitted.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ https://cabinlife.com/articles/article/should-you-build-your-own-dock
- ↑ https://www.decks-docks.com/the-ultimate-guide-to-dock-piling-materials
- ↑ http://www.piledrivers.org/files/9971afc0-2754-41db-a9bc-849f87c51217--c38abc5c-4dca-402f-b252-e7e8f85df9f8/timberpilemanual.pdf
- ↑ https://cabinlife.com/articles/article/should-you-build-your-own-dock
- ↑ https://www.forbes.com/home-improvement/plumbing/hydrojet-sewer-line-cost/
- ↑ https://www.oregon.gov/ODOT/Construction/Doc_BridgeInspectorManual/07_bridge.pdf
- ↑ https://www.jlconline.com/deck-builder/building-a-stationary-dock_o
- ↑ https://jrh-e.com/docks-%26-seawalls
- ↑ https://youtu.be/UMHrENlhttw?t=203
- ↑ https://fixitwise.com/dock-piling-installation-using-waterjetting/
- ↑ https://www.jlconline.com/deck-builder/building-a-stationary-dock_o
- ↑ https://www.jlconline.com/deck-builder/building-a-stationary-dock_o
- ↑ https://www.jlconline.com/deck-builder/building-a-stationary-dock_o
- ↑ https://www.thisoldhouse.com/fences/21017133/how-to-use-a-post-hole-digger
- ↑ https://www.bobvila.com/articles/how-to-mix-concrete/
- ↑ https://www.jlconline.com/deck-builder/building-a-stationary-dock_o
- ↑ https://www.jlconline.com/deck-builder/building-a-stationary-dock_o
- ↑ https://documents.coastal.ca.gov/assets/water-quality/permits/Pilings%20-%20Treated%20Wood%20&%20Alternatives%20-%20Factsheet%20Appl%202015r3.pdf
- ↑ https://www.cabinlife.com/articles/should-you-build-your-own-dock
About This Article
If you need to install posts in the water for a dock or a pier, measure and cut pilings made of pressure-treated wood. The pilings should be the length you need to support your structure, plus an extra 4-6 feet that you can bury in the ground. Have some friends help you stand the first piling in the water, then aim the tip of a high-powered hose or a water jetter at the base of the piling and turn on the pump. The force of the water should blast away the sand and mud beneath the wood, creating a hole so you can sink the piling. Keep reading to learn how to pour concrete posts!