This article was co-authored by Payam Daneshrad, MD. Dr. Payam Daneshrad is a board certified Otolaryngologist, a board eligible Facial Plastic Surgeon, and the Owner and Director of Daneshrad Clinic in Los Angeles, California. With over 19 years of experience, Dr. Daneshrad specializes in adult and pediatric Otolaryngology-head and neck surgery, packing-less nasal surgery, minimally invasive sinus surgery, and snoring treatment. He also uses the newest surgical ENT techniques for tonsillectomy, adenoidectomy, thyroidectomy, and parathyroidectomy. Dr. Daneshrad graduated with a BS and the highest honors from the University of California, Berkeley. He earned his Doctor of Medicine (MD) from Tulane University School of Medicine, where he was accepted into the AOA, the medical honor's society, and the Tulane University School of Public Health. Dr. Daneshrad received his medical training from the University of Southern California, where he currently serves as an Associate Clinical Professor. Dr. Daneshrad is the Otolaryngologist and Facial Plastic Surgeon for the Los Angeles Sparks and the athletic teams of Loyola Marymount University.
There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 281,896 times.
People of all ages may have difficulty hearing the TV. Turning up the volume too loudly on your TV can disrupt your neighbors or make it difficult for you to watch TV with other people. Assistive Listening Devices (ALDs) allow you to hear the TV better without affecting other people. There are many different options available; find an option that meets your needs.
Steps
Using a TV Amplifying System
-
1Choose an amplifier that meets your needs. If you do not wear hearing aids but need some assistance, an amplifier may be a good idea for you.[1] These devices use a transmitting base that plugs into your television's headphone jack, and you wear a headset or neckloop. You can adjust the sound and tone to a comfortable level without disturbing the volume on your TV.
- When searching for an amplifier, consider if you prefer headphones or a neckloop, the range of the transmitter (e.g. can you leave the room and still hear the TV?), the battery life, and the warranty.
- Popular brands include TV Ears, Sennheiser, Serene, and Innovations.[2]
- These devices differ from everyday headphones because they enhance the speech and reduce background noise.
- The connection cables, transmitter, listening device, and instructions are all included in the package when you purchase your amplifying system.
-
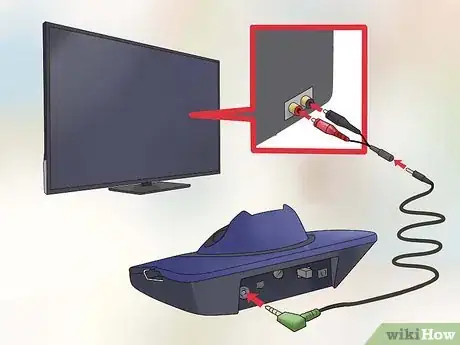
2Set up your transmitter. The transmitter should be placed near the TV, but not close to any metal objects as they can decrease the range of the transmitter. Turn off your TV before connecting. Plug one end of the cable into your transmitter and the other end into your TV. Depending on your TV, you will plug into the headphone socket, RCA socket, or the SCART socket.
- Always read the directions before connecting your transmitter to the TV.
Advertisement -
3Set up your receiver. Your receiver may be rechargeable or run on batteries. Adjust the sound and tone to a comfortable level. You should also test the amplifying range now. Make sure the sound is clear. If it sounds fuzzy, the audio jack may not be plugged all the way into the transmitter or the TV or your transmitter may not be in a good spot.
-
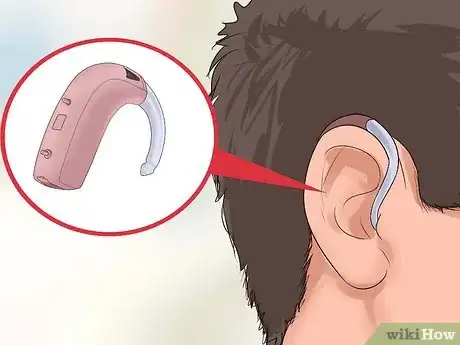
4Use the T-coil position on hearing aid if applicable. If you wear hearing aids, your amplifier can be connected directly to your hearing aids. Most hearing aids have a t-coil that can pick up the signal to your transmitter. Switch your hearing aid to the "T" position to use them with your amplifier. The TV sound should now be directly transmitted to your hearing aid.
- If you are having trouble using your t-coil, talk to your audiologist or healthcare professional. He or she can make sure that your t-coil is working properly and can program and adjust the volume of the t-coil.[3] The t-coil function may not automatically be turned on when you start wearing hearing aids.
Using FM Systems
-
1Decide if an FM system is a good option. FM systems use radio waves and are best for noisy environments. If you usually watch TV in a busy home or a home with a lot of commotion, this may be a good option for you. The FM system uses a transmitter microphone and a receiver. The receiver can be used as headphones or used with your hearing aids.[4]
- FM systems are also portable and can be used in other environments (e.g. restaurants, school, work)
- FM systems are more expensive than TV amplifiers.
- You can buy an FM system online, in electronics stores, or through a hearing professional.[5]
-
2Connect the transmitter to your TV. The microphone can be connected to the TV using an audio jack, or you can place the microphone next to the TV speaker. A 3.5mm stereo socket is usually used to connect the transmitter to the TV. Many transmitters will allow you to select a frequency as well. Frequency options are helpful as certain frequencies can be noisy.
-
3Set up your receiver. FM systems typically use headphones, earbuds, or neckloops. If your FM system has different frequency options, make sure that your receiver and transmitter are set to the same frequency. You can control the volume using your receiver. The receiver can be worn around your neck or sometimes clipped onto your pants.
- Radio waves can go through walls, so you may be able to hear the TV from another room.
- Test the range of your receiver once everything is set up. The transmission range can be up to 1,000 feet (300 m).[6]
-
4Use the FM system with your hearing aid. If you are using hearing aids, turn your hearing aids to the "T" position [7] Plug either a neckloop or silhouette inductor into the receiver. Neckloops are worn around the neck, and silhouette inductors are worn behind the ear. Silhouettes are most useful for people with severe hearing loss.[8]
Using Other Technologies
-
1Try using a phone app. TV Louder is an iPhone app that can be used as a personal amplifier. Download the app, set your TV to a normal volume, and connect your headphones to your phone. You can then adjust the volume using your phone. This is a free app, but it is not a substitute for hearing aids. This is an inexpensive option you can try before you invest in another system.
-
2Consider an infrared system. Infrared systems work just like FM systems. However, instead of using radio waves to transmit the signal, light waves are used. Light waves cannot pass through walls, so these systems can only be used in one room. The signal is also interrupted if a person or object blocks the signal. These systems also do not work well with sunlight.[9] [10]
-
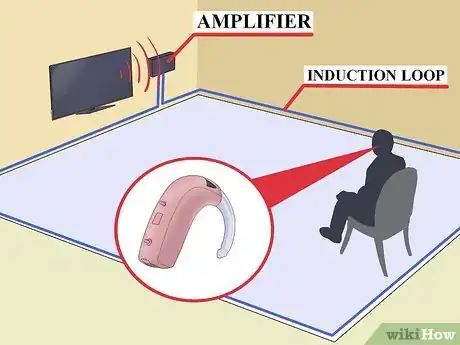
3Try an induction loop system. An induction loop wire is installed around a room to transmit a signal that can be picked up by your hearing aids or a receiver. If you wear a hearing aid, you will not need to wear a receiver with this system..[11] Switch your hearing aid to the "T" position to hear the TV.[12] If you do not use hearing aids, you will need to wear a receiver to hear the TV.
-
4Consider video streaming service. The streaming service, Roku, comes with a remote with headphone jack. When you plug your headphones directly into the Roku remote, the TV mutes. You can listen to the TV without anyone else hearing.[13] This is very helpful if you are in the room with other people, but no one else wants to watch TV.
-
5Use closed captioning. Closed captioning will allow you to read the spoken words on the screen. Although this method does not allow you to hear better, it will increase your understanding of what you are watching on the TV. This is also helpful if the background music or noise is interfering with your amplified signal.[14]
- This is also the best choice if you want to protect your hearing. Turning a TV up too high can lead to ear and hearing damage over time.
References
- ↑ http://www.healthyhearing.com/help/assistive-listening-devices/headphones-for-tv
- ↑ http://www.harriscomm.com/newsletter/faq/tvamps.pdf
- ↑ http://www.assist2hear.com/loop-systems-residential-commercial
- ↑ http://www.healthyhearing.com/help/assistive-listening-devices/fm-systems
- ↑ http://www.healthyhearing.com/help/assistive-listening-devices/fm-systems
- ↑ http://www.astate.edu/dotAsset/08b7234b-302a-402f-af8b-cf7932dc3efc.pdf
- ↑ http://www.healthyhearing.com/help/assistive-listening-devices/fm-systems
- ↑ http://www.astate.edu/dotAsset/08b7234b-302a-402f-af8b-cf7932dc3efc.pdf
- ↑ http://www.healthyhearing.com/report/52538-Top-five-assistive-listening-devices
- ↑ http://www.astate.edu/dotAsset/08b7234b-302a-402f-af8b-cf7932dc3efc.pdf
- ↑ http://www.astate.edu/dotAsset/08b7234b-302a-402f-af8b-cf7932dc3efc.pdf
- ↑ http://www.asha.org/public/hearing/Induction-Loop-Systems/
- ↑ http://www.businessinsider.com/roku-versus-apple-tv-2015-4?_ga=1.120748488.1117458754.1449378063
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4285000/