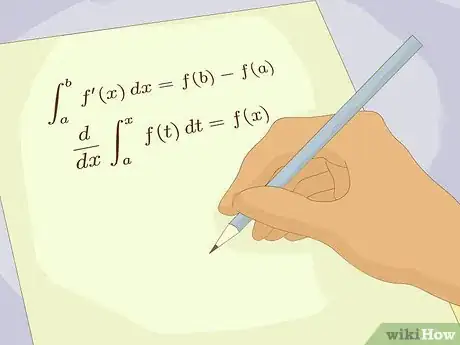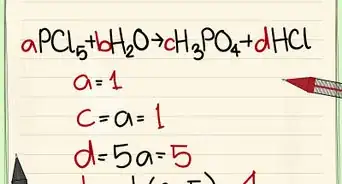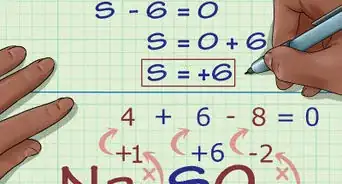This article was co-authored by Meredith Juncker, PhD. Meredith Juncker is a PhD candidate in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center. Her studies are focused on proteins and neurodegenerative diseases.
There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 43,062 times.
Learning chemistry will help you understand the different forms and properties of matter. Atoms are the small bits of matter that can be added to each other to build anything from water molecules to skyscrapers. The first steps of understanding the complexities of chemistry are to know the elements on the periodic table, understand atoms, and consider why some atoms bond together. This will give you a strong start to understanding chemical behavior.
Steps
Familiarizing Yourself With the Periodic Table
-
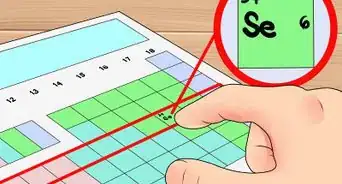
1Memorize the atomic symbols. An atom is the smallest unit of an element that retains the properties of that element. Each atom has its own spot on the periodic table, and its own one or two letter symbol. For example, the symbol for hydrogen is “H” and sodium is “Na.”[1]
- This often is a first assignment given to a chemistry class.
-
2Know how mass changes in the table. One of the important characteristics of an atom is how much mass it has. This tells you how many particles are in the nucleus of the atom (the particles outside the nucleus are so small that they do not count in the mass). The periodic table is arranged so that mass increases as you go from left to right (across a row) and from top to bottom (down a column).[2]Advertisement
-
3Understand the major types of elements. The periodic table is broken up into several different types of elements. The broadest categories are metals, metalloids, and nonmetals. The category that an atom belongs to can tell you about its physical properties and its reactivity.[3]
Knowing the Composition of Atoms
-
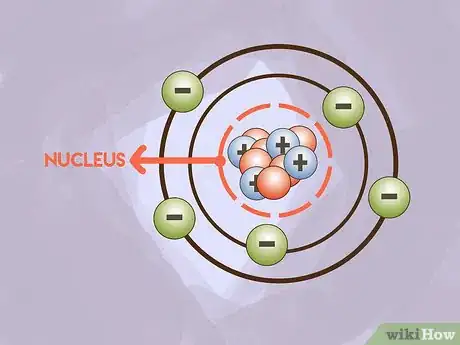
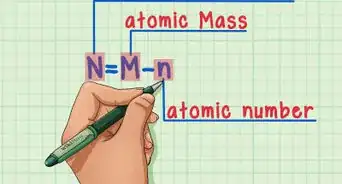
1Know what subatomic particles make an atom. Three different subatomic particles make up an atom. Protons have a positive charge, neutrons lack charge, and electrons have a negative charge. The sum of protons and neutrons is equal to the mass of the atom (in atomic mass units). The mass of electrons is so little that they are not counted.[4]
-
2Be able to locate each particle. The nucleus is the center of the atom. This is where you will find protons and neutrons. Electrons orbit the nucleus in electron orbitals. Electrons do not typically enter the nucleus and protons and neutrons do not typically leave the nucleus.[5]
-
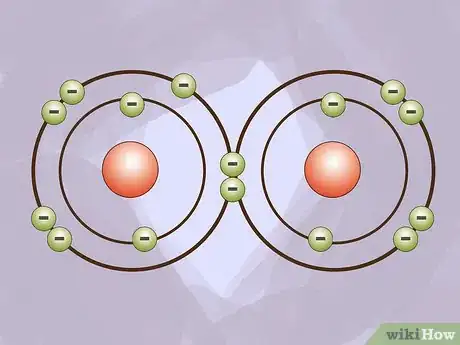
3Consider what happens when atoms bond. When two or more atoms join together, it is called bonding. Protons and neutrons are not directly involved in bonding. Electrons are shared or transferred between two or more atoms in a bond and this forms a molecule.[6]
Grasping Reactions and Bonding
-
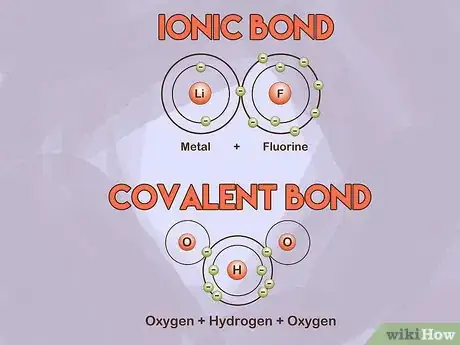
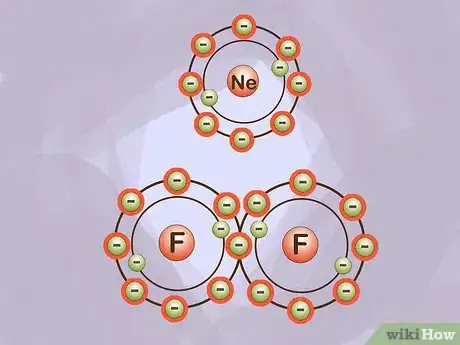
1Learn the major types of bonds. Ionic bonds occur between metals and nonmetals. Covalent bonds occur between two nonmetals. In an ionic bond, electrons are more likely to be found at one end of a molecule than the other. This results in a negatively charged and positively charged end of the molecule. Covalent bonds share electrons more evenly.[7]
-
2Utilize chemical formulas. Chemical formulae provide information about what elements are present in a molecule or reaction, and in what proportions. For example, hydrochloric acid has a chemical formula of HCl and the chemical reaction describing burning methane is CH4 + 2O2 → 2H2O + CO2. The numbers before the chemical symbols are known as coefficients and tell you how many of that molecule or atom is present. The number in subscripts tell you how many of particular atom is present in the molecule.[8]
-
3Consider stability as a reason for bonding. Atoms and molecules bond together to become more stable. That is to say that they try to attain the lowest possible energy state. To break a bond, you have to add enough energy to make the bond no longer favorable. For this reason, bonds are often hard to break.[9]
Getting a Chemistry Education
-
1Polish your math skills. To understand chemistry, you will need to have a working knowledge of algebra (at least) since you will be using it often. Understanding calculus, differential equations, and linear algebra is a huge plus in upper level chemistry courses, like physical chemistry. You will be required to take some of these courses to obtain your chemistry degree. You should also consider seeking a math minor (or even double major) to give yourself a leg up in your chemistry work.
-
2Choose a branch of chemistry. Chemists are broken up into several different categories of study. For example, there are physical chemists, biochemists, analytical chemists, etc. Decide what kind of chemistry you like the most, and concentrate on that topic. For example, if you really like organic chemistry, take more organic chemistry courses than what's required for your degree.[10]
- You can also pursue a master’s or doctorate to further narrow your scope and build your expertise in chemistry.
-
3Do research in chemistry. Classwork is a good place to start learning the concepts of chemistry. Lab classes will help to teach you the protocol for conducting yourself in a laboratory and apply concepts you’ve learned in class. Ultimately though, if you wish to understand chemistry, you will have to do research on a topic in chemistry. While research is required for most chemistry degrees, it is usually a minimal amount. Start doing research as early as you can under the supervision of a professor in the field you like most (e.g. biochemistry).[11]
Community Q&A
-
QuestionHow do I choose what field to pursue?
 Community AnswerYou will have to determine this for yourself. Pick an area you are interested and start studying it to see if you would like to do it.
Community AnswerYou will have to determine this for yourself. Pick an area you are interested and start studying it to see if you would like to do it. -
QuestionWhich topics will a doctor study?
 Community AnswerAlthough a potential doctor can have an undergraduate degree in any field, it's wise to study topics such as anatomy, physiology, biology, chemistry, and math, plus other college courses necessary for a degree, such as English and foreign languages. Other common courses are physics and related science classes.
Community AnswerAlthough a potential doctor can have an undergraduate degree in any field, it's wise to study topics such as anatomy, physiology, biology, chemistry, and math, plus other college courses necessary for a degree, such as English and foreign languages. Other common courses are physics and related science classes. -
QuestionIf I want to do medicine, which chemistry subject should I concentrate on?
 HannahCommunity AnswerThe most useful branch would be biochemistry, as it focuses on the chemical processes in living organisms. You will learn about protein structure, enzymes and their involvement in metabolic pathways, as well. For example, antibodies and the immune system - which are all important in medical school. But it is not mandatory to choose biochemistry! Decide for the branch of chemistry that you like most - they will all help you in medical school.
HannahCommunity AnswerThe most useful branch would be biochemistry, as it focuses on the chemical processes in living organisms. You will learn about protein structure, enzymes and their involvement in metabolic pathways, as well. For example, antibodies and the immune system - which are all important in medical school. But it is not mandatory to choose biochemistry! Decide for the branch of chemistry that you like most - they will all help you in medical school.
Warnings
- Chemistry takes time and effort to master.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- If you are doing experiments with real chemicals, make sure that you obtain a materials safety data sheet for every involved chemical.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Oregon_Institute_of_Technology/OIT%3A_CHE_101_-_Introduction_to_General_Chemistry/02%3A_Atoms_and_the_Periodic_Table/2.04%3A_Memorizing_Element_Names_and_Symbols
- ↑ https://mccord.cm.utexas.edu/chembook/page-nonav.php?chnum=1§=5
- ↑ https://www.angelo.edu/faculty/kboudrea/periodic/physical_metals.htm
- ↑ http://education.jlab.org/atomtour/listofparticles.html
- ↑ http://education.jlab.org/atomtour/listofparticles.html
- ↑ http://education.jlab.org/atomtour/listofparticles.html
- ↑ https://www.khanacademy.org/science/ap-biology/chemistry-of-life/introduction-to-biological-macromolecules/a/chemical-bonds-article
- ↑ http://www.elementalmatter.info/chemical-formulas.htm
- ↑ https://www.khanacademy.org/science/ap-biology/chemistry-of-life/introduction-to-biological-macromolecules/a/chemical-bonds-article