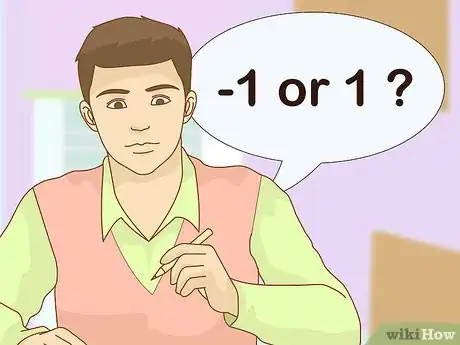wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, 61 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time.
There are 11 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 1,323,364 times.
Learn more...
Pi (π) is one of the most important and fascinating numbers in mathematics. Roughly 3.14, it is a constant that is used to calculate the circumference of a circle from that circle's radius or diameter.[1] It is also an irrational number, which means that it can be calculated to an infinite number of decimal places without ever slipping into a repeating pattern.[2] This makes it difficult, but not impossible, to calculate precisely.
Steps
Calculating Pi Using the Measurements of a Circle
-
1Make sure you are using a perfect circle. This method won't work with ellipses, ovals, or anything but a real circle. A circle is defined as all the points on a plane that are an equal distance from a single center point. The lids of jars are good household objects to use for this exercise. You should be able to calculate pi roughly because in order to get exact results of pi, you will need to have a very thin lead (or whatever you are using). Even the sharpest pencil graphite could be huge to have exact results.[3]
-
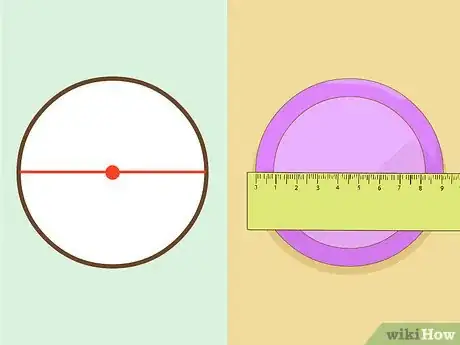
2Measure the circumference of a circle as accurately as you can. The circumference is the length that goes around the entire edge of the circle. Since the circumference is round, it can be difficult to measure (that's why pi is so important).[4]
- Lay a string over the circle as closely as you can. Mark the string off where it circles back around, and then measure the string length with a ruler.
Advertisement -
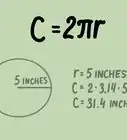
3Measure the diameter of the circle. The diameter runs from one side of the circle to the other through the circle's center point.[5]
-
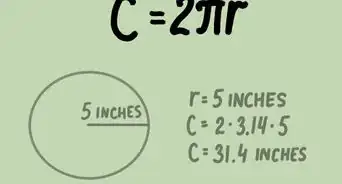
4Use the formula. The circumference of a circle is found with the formula C=πd=2πr. Thus, pi equals a circle's circumference divided by its diameter. Plug your numbers into a calculator: the result should be roughly 3.14.[6]
-
5Repeat this process with several different circles, and then average the results. This will give you more accurate results. Your measurements might not be perfect on any given circle, but over time they should average out to a pretty accurate calculation of pi.
Calculating Pi Using an Infinite Series
-
1Use the Gregory-Leibniz series. Mathematicians have found several different mathematical series that, if carried out infinitely, will accurately calculate pi to a great number of decimal places. Some of these are so complex they require supercomputers to process them. One of the simplest, however, is the Gregory-Leibniz series.[7] Though not very efficient, it will get closer and closer to pi with every iteration, accurately producing pi to five decimal places with 500,000 iterations. Here is the formula to apply.
- π=(4/1)-(4/3)+(4/5)-(4/7)+(4/9)-(4/11)+(4/13)-(4/15) ⋯
- Take 4 and subtract 4 divided by 3. Then add 4 divided by 5. Then subtract 4 divided by 7. Continue alternating between adding and subtracting fractions with a numerator of 4 and a denominator of each subsequent odd number. The more times you do this, the closer you will get to pi.
-
2Try the Nilakantha series. This is another infinite series to calculate pi that is fairly easy to understand. While somewhat more complicated, it converges on pi much quicker than the Leibniz formula.[8]
- π=3+4/(2·3·4)-4/(4·5·6)+4/(6·7·8)-4/(8·9·10)+4/(10·11·12)-4/(12·13·14) ⋯
- For this formula, take three and start alternating between adding and subtracting fractions with numerators of 4 and denominators that are the product of three consecutive integers which increase with every new iteration. Each subsequent fraction begins its set of integers with the highest one used in the previous fraction. Carry this out even a few times and the results get fairly close to pi.
Calculating Pi Using a Limit
-
1Pick a large number. The bigger the number, the more accurate your calculation will be.
-
2Plug your number, which we'll call x, into this formula to calculate pi: x * sin(180 / x). For this to work, make sure your calculator is set to Degrees. The reason this is called a Limit is because the result of it is 'limited' to pi. As you increase your number x, the result will get closer and closer to the value of pi.
Using Arcsine Function/Inverse Sine Function
-
1Pick any number between -1 and 1. This is because the Arcsin function is undefined for arguments greater than 1 or less than -1.[11]
-
2Plug your number into the following formula, and the result will be roughly equal to pi.[12]
- π={arcsin[√(1 - x²)]+ abs[arcsin x]}·2.
- Arcsin refers to the inverse sine in radians
- Sqrt is short for square root
- Abs is short for absolute value
- x^2 refers to an exponent, in this case, x squared.
- π={arcsin[√(1 - x²)]+ abs[arcsin x]}·2.
Community Q&A
-
QuestionIs twenty two over seven equal to pi?
 Community AnswerIt is not precisely equal to pi. While it does look like pi at first (3.14285...), pi is 3.14159... It cannot be equal to pi because 3.14285 ends up repeating. Pi is an irrational number, meaning it goes on forever and does not repeat. Remember that irrational numbers are defined as "not being able to be written as a ratio between two numbers." 22/7 is a ratio of two numbers, so it cannot be exactly equal to pi.
Community AnswerIt is not precisely equal to pi. While it does look like pi at first (3.14285...), pi is 3.14159... It cannot be equal to pi because 3.14285 ends up repeating. Pi is an irrational number, meaning it goes on forever and does not repeat. Remember that irrational numbers are defined as "not being able to be written as a ratio between two numbers." 22/7 is a ratio of two numbers, so it cannot be exactly equal to pi. -
QuestionHow can I figure out pi as a fraction?
 Community AnswerYou can't. Pi cannot be a fraction because it is irrational. This means that it cannot be expressed as a ratio of two rational numbers. Pi is sometimes expressed as the fraction 22/7, but that is just an approximation.
Community AnswerYou can't. Pi cannot be a fraction because it is irrational. This means that it cannot be expressed as a ratio of two rational numbers. Pi is sometimes expressed as the fraction 22/7, but that is just an approximation. -
QuestionWhat does the word irrational mean?
 Community AnswerAn irrational number is a number that cannot be expressed as a ratio of whole numbers (i.e., as a fraction). The root of the word 'irrational' is 'ratio', and the prefix 'ir' means 'not'. The word can have different meanings outside of math.
Community AnswerAn irrational number is a number that cannot be expressed as a ratio of whole numbers (i.e., as a fraction). The root of the word 'irrational' is 'ratio', and the prefix 'ir' means 'not'. The word can have different meanings outside of math.
References
- ↑ https://www.mathsisfun.com/definitions/pi.html
- ↑ http://mathworld.wolfram.com/IrrationalNumber.html
- ↑ https://www.mathscareers.org.uk/calculating-pi/
- ↑ https://www.mathscareers.org.uk/calculating-pi/
- ↑ https://www.mathsisfun.com/numbers/pi.html
- ↑ http://www.mathsisfun.com/numbers/pi.html
- ↑ https://crypto.stanford.edu/pbc/notes/pi/glseries.html
- ↑ http://www.mathscareers.org.uk/article/calculating-pi/
- ↑ https://mste.illinois.edu/activity/buffon/
About This Article
Pi is roughly 3.14, but it's actually an infinite number that never slips into a repeating pattern. If you want to calculate pi, first measure the circumference of a circle by wrapping a piece of string around the edge of it and then measuring the length of the string. Then, measure the diameter of the circle, which is the distance between one side and the other that runs through the center. Once you've got the circumference and diameter, plug them into the formula π=c/d, where "π" is pi, "c" is circumference, and "d" is diameter. Just divide the circumference by the diameter to calculate pi! To learn how to calculate pi using a limit or sine function, keep reading the article!