Chapter 22
Digestive System
By Boundless
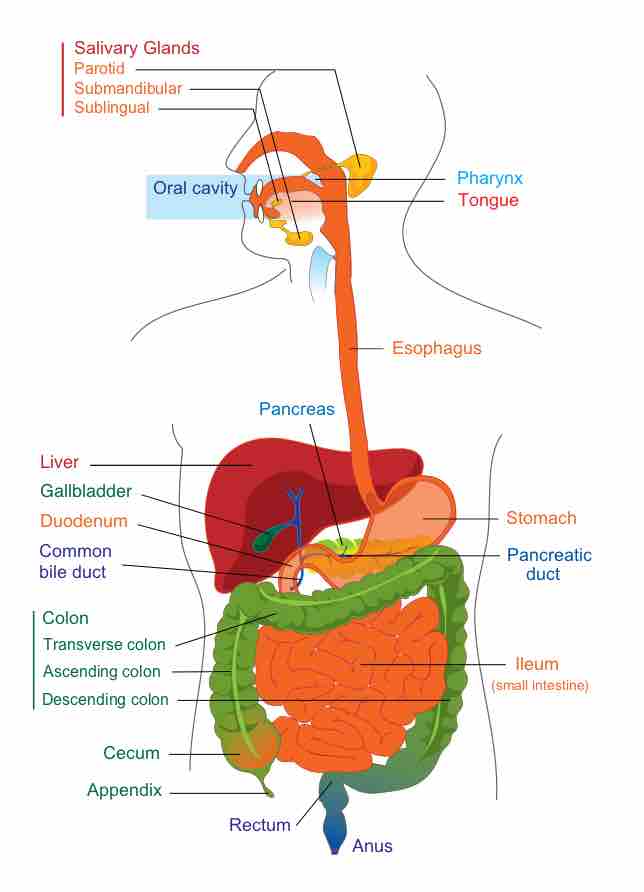
The human gastrointestinal tract refers to the stomach and intestine, and sometimes to all the structures from the mouth to the anus.
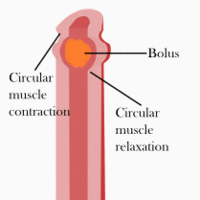
Digestion is necessary for absorbing nutrients from food, and occurs through two processes: mechanical and chemical digestion.
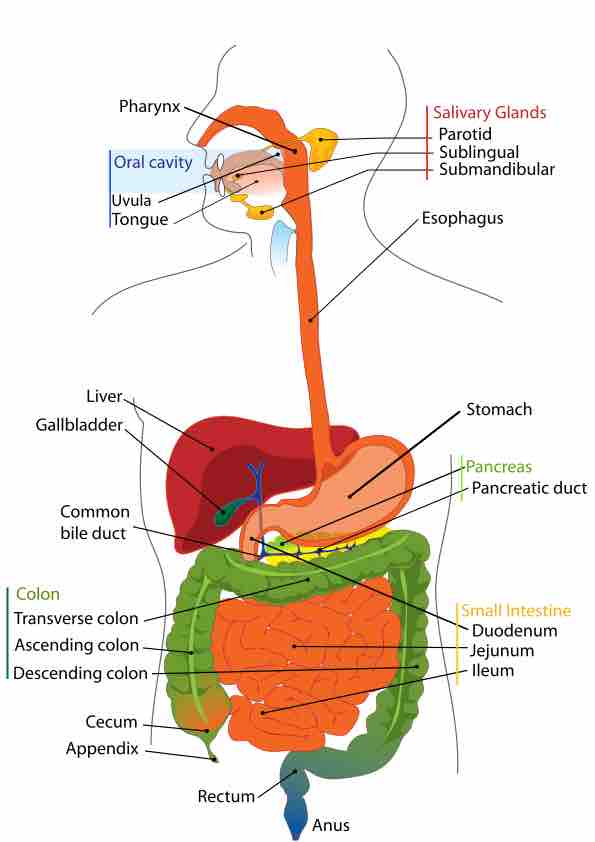
The organs of the digestive system can be divided into upper and lower digestive tracts. The upper digestive tract consists of the esophagus, stomach, and the small intestine, while the lower tract includes all of the large intestine, the rectum, and anus.
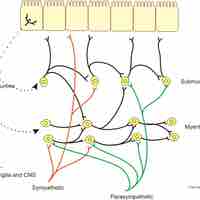
The enteric nervous system (ENS) is a subdivision of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) that directly controls the gastrointestinal system.
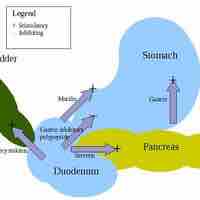
The digestive system functions via a system of long reflexes, short reflexes, and extrinsic reflexes from gastrointestinal (GI) peptides working together.
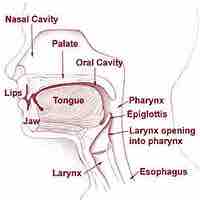
The mouth is the first portion of the alimentary canal, which receives and mechanically breaks down food, and produces saliva.
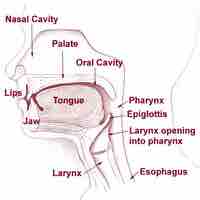
The pharynx is part of the digestive and respiratory systems and consists of three main parts: nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx.
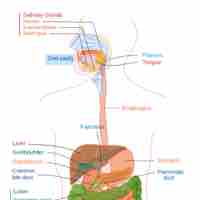
The esophagus is a muscular tube through which food passes from the pharynx via peristalsis to the stomach.
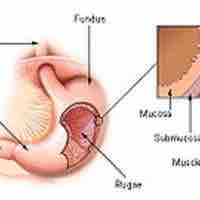
The mucosa is the innermost layer of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, composed of simple epithelium cells. It is the absorptive and secretory layer of the GI tract.
The submucosa is a dense irregular layer of connective tissue with large blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves that supports the mucosa.
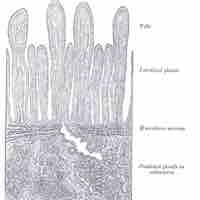
The muscularis is responsible for segmental contractions and peristaltic movement in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
Serosa consists of a secretory epithelial layer and a thin connective tissue layer that reduce the friction from muscle movement.
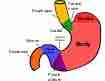
The stomach is divided into four sections, each of which has different cells and functions.
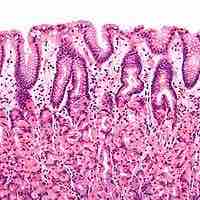
The layers of the stomach produce mucous to protect itself, enyzmes to break down the food for digestion, and muscles to 'churn' the food.

The movement and the flow of chemicals into the stomach is controlled by the autonomic nervous system and various digestive system hormones.
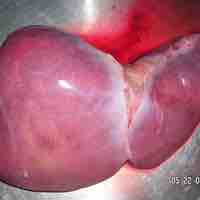
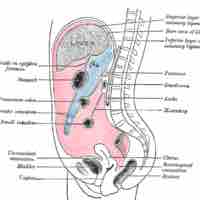
The liver makes bile, which is essential for the digestion of fats.
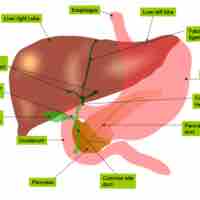
The liver is located in the abdomen; it has four lobes.
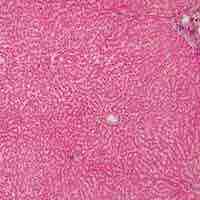
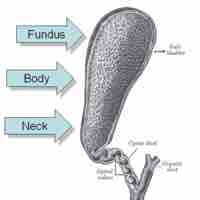
Hepatocytes are the main tissue cells of the liver; the gallbladder contains the mucosa, muscularis, perimuscular, and serosa layers.
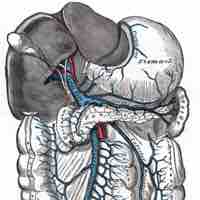
In the hepatic portal system, the liver receives a dual blood supply from the hepatic portal vein and hepatic arteries.
The liver is thought to be responsible for up to 500 separate functions.
Bile is a fluid produced by the liver that aids the process of digestion and absorption of lipids in the small intestine.
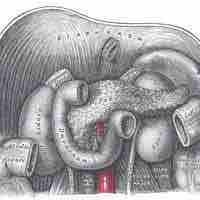
The pancreas is a gland organ in the digestive and endocrine systems.
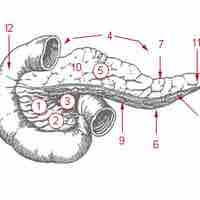
The pancreas lies in the epigastrium or upper central region of the abdomen and can vary in shape.
The pancreas serves digestive and endocrine functions, and it is composed of two types of tissue: islets of Langerhans and acini.
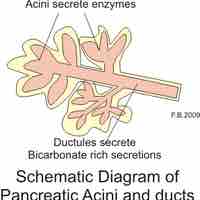
Pancreatic fluid contains digestive enzymes that help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.
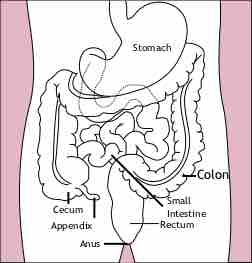
The small intestine is the part of the gastrointestinal tract where much of the digestion and absorption of food takes place.
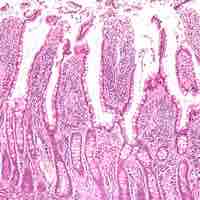
The small intestine wall has four layers: the outermost serosa, muscularis, submucosa, and innermost mucosa.

The small intestine uses different enzymes and processes to digest proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates.

The large intestine absorbs water from remaining indigestible food matter and compacts feces prior to defecation.
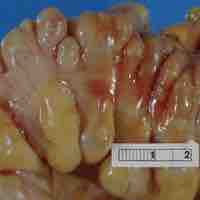
The large intestine has taeniae coli, and invaginations (the intestinal glands) as opposed to the small intestines.
The largest bacteria ecosystem in the human body is in the large intestine, where it plays a variety of important roles.
In the large intestine, a host of microorganisms known as "gut flora" help digest remaining food matter and create vitamins.

The large intestine absorbs water from the chyme and stores feces until they can be defecated.
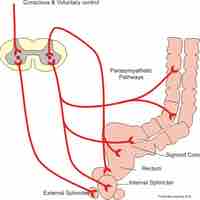
Defecation is a combination of voluntary and involuntary processes with enough force to remove waste material from the digestive system.

Chemical digestion is the process of breakdown of large macronutrients into smaller molecules by enzyme-mediated hydrolysis.
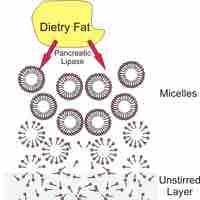
Chemical breakdown of macromolecules contained in food is completed by various enzymes produced in the digestive system.
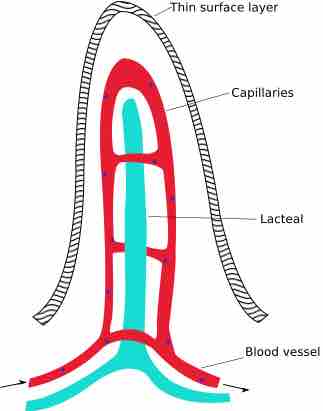
Absorption of nutrients occurs partially by diffusion through the wall of the small intestine.
Glucose, amino acids, fats, and vitamins are absorbed in the small intestine via the action of hormones and electrolytes.
The cephalic phase of gastric secretion occurs even before food enters the stomach via neurological signals.
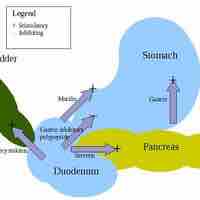
The gastric phase is a period in which swallowed food activates gastric activity in the stomach.
The intestinal phase occurs in the duodenum, responds to arriving chyme, and moderates gastric activity via hormones and nervous reflexes.
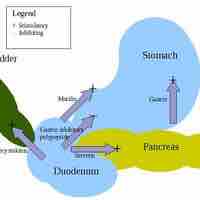
There are five main hormones that aid and regulate the digestive system in mammals.