Chapter 21
Respiratory System
By Boundless
Breathing allows for the delivery oxygen to internal tissues and cells where it is needed, and allows for the removal of CO2.
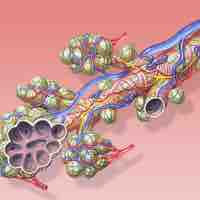
The respiratory system include lungs, airways and respiratory muscles. Ventilation is the rate at which gas enters or leaves the lung.
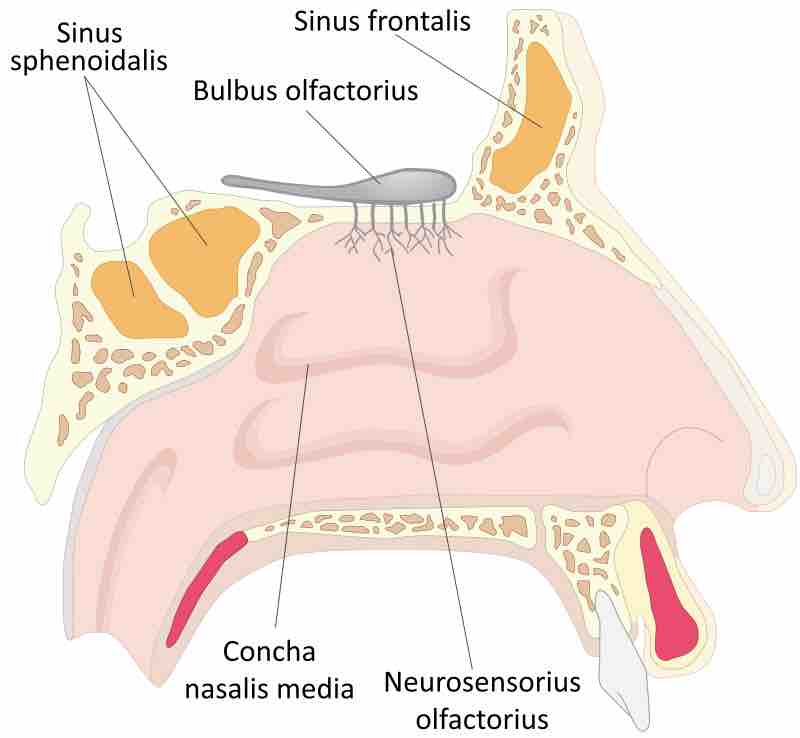
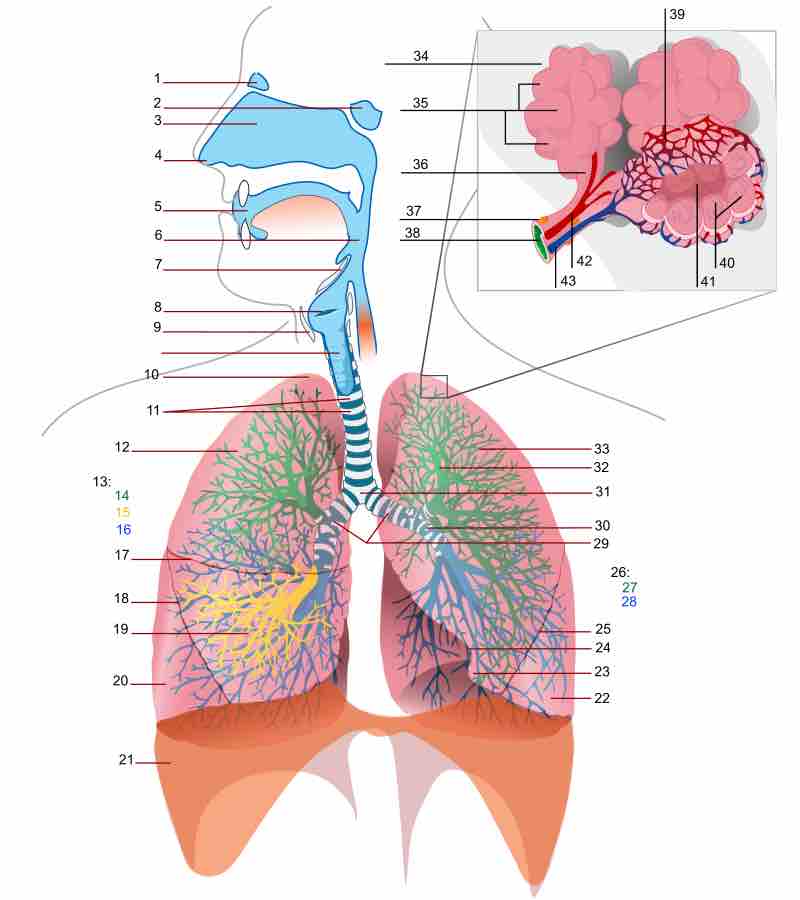
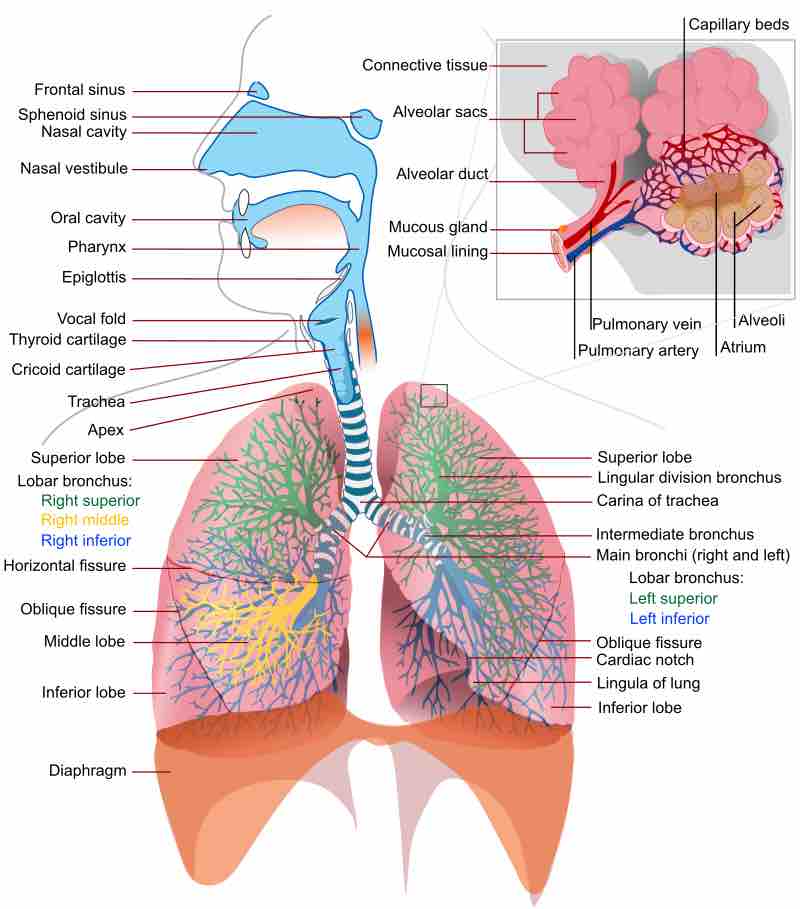
The shape of the nose is determined by the ethmoid bone and the nasal septum.
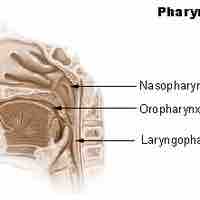
The human pharynx is part of the digestive system and also the respiratory system.
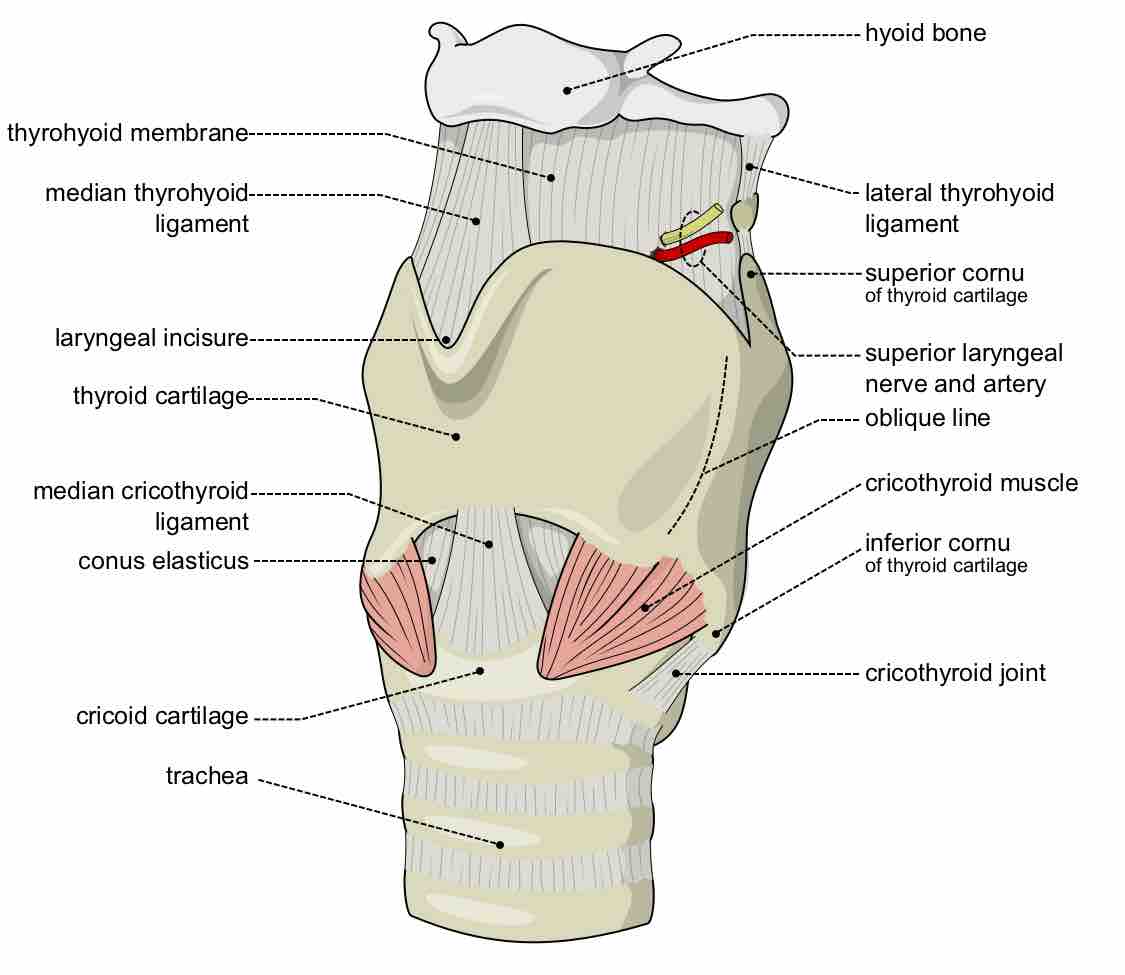
The larynx is an organ in the neck involved in breathing, sound production, and protecting the trachea against food aspiration.
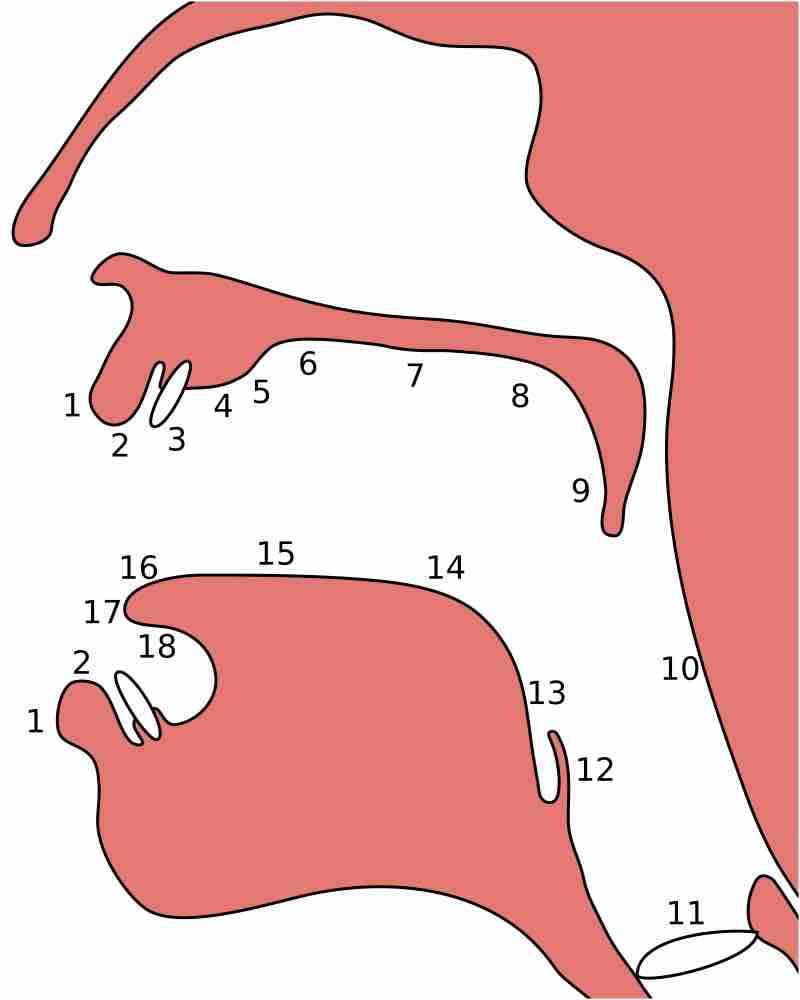
Voices produce sounds through a steady flow of air through the larynx, which causes vibrations and creates fluctuations in air pressure.
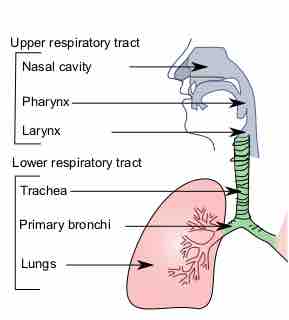
The trachea, or windpipe, is a tube that connects the pharynx or larynx to the lungs, allowing the passage of air.
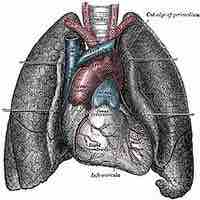
The lungs are an essential organ which is necessary for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide from the body.
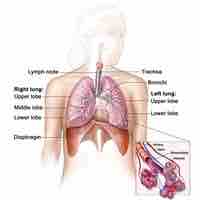
The lungs are located on either side of the heart and are separated by fissures into lobes, three in the right and two lobes in the left.
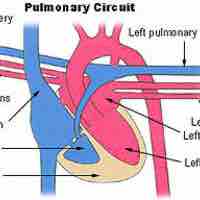
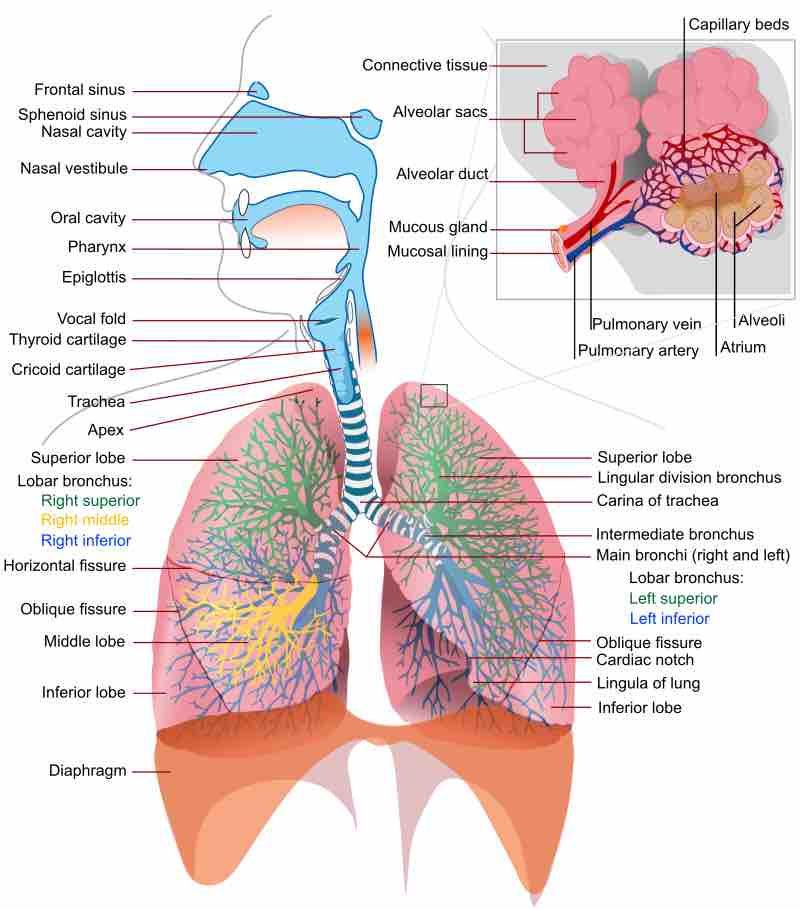
Pulmonary circulation transports oxygen-depleted blood away from the heart to the lungs and returns oxygenated blood back to the heart.
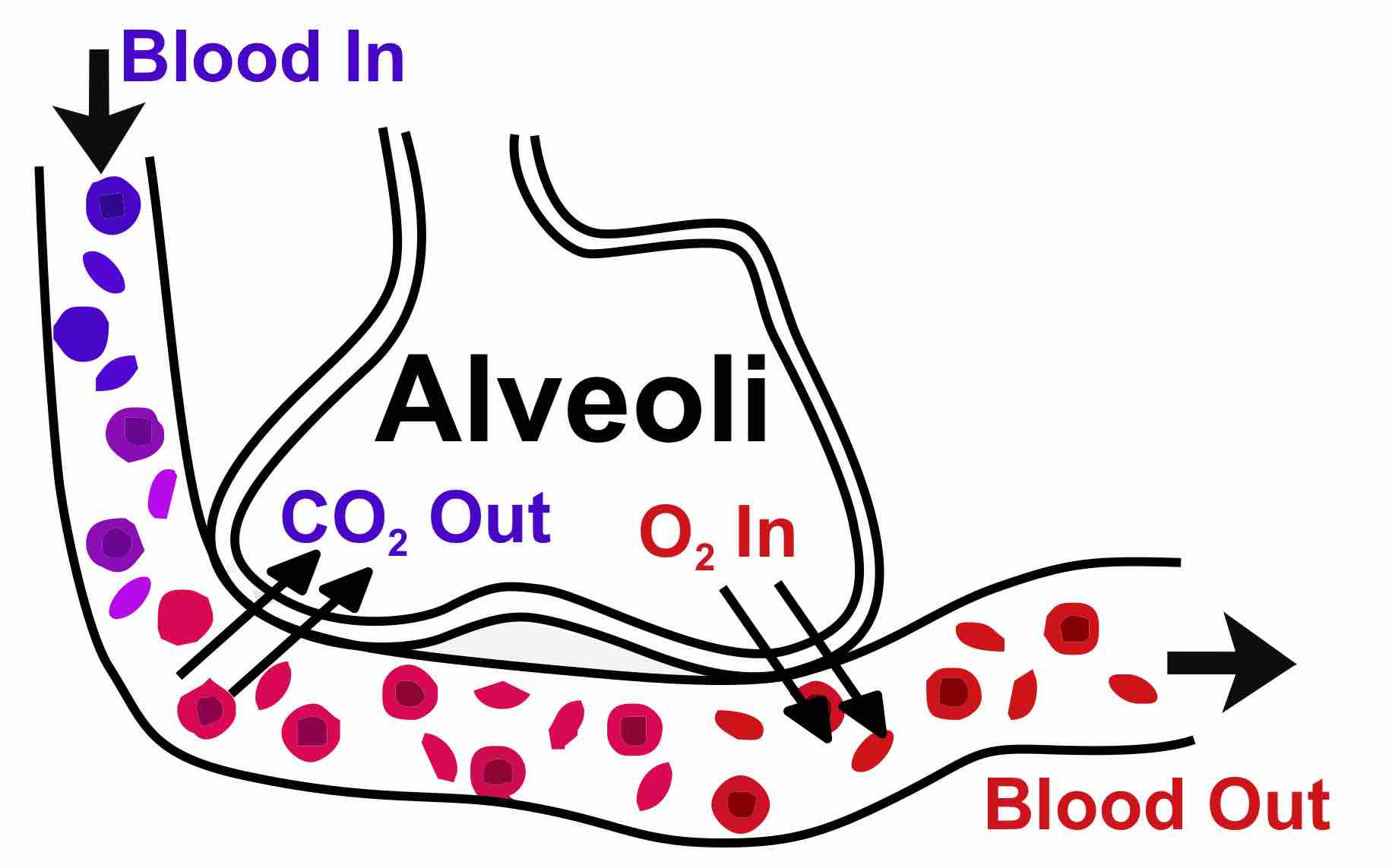
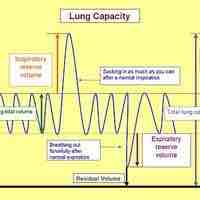
Ventilation is the rate at which gas enters or leaves the lung.
Inhalation is the flow of air into an organism which is generated due to pressure difference between the atmosphere and alveolus.
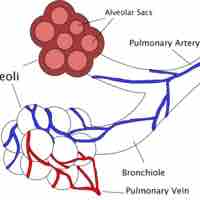
Exhalation (or expiration) is the flow of the respiratory current out of the organism.
Breathing is an autonomic process that moves air in and out of the lungs.
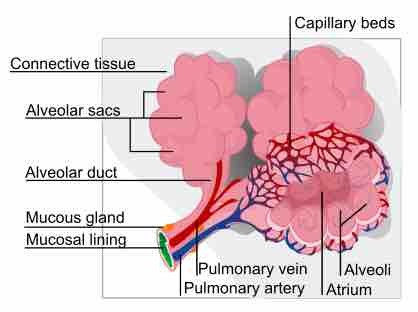
The surface tension of alveolar fluid is regulated by pulmonary surfactant, allowing efficient respiration.
Lung compliance refers to the magnitude of change in lung volume as a result of the change in pulmonary pressure.
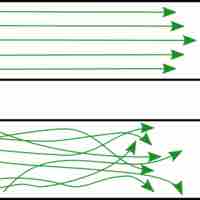
Airway resistance refers to resistance in the respiratory tract to airflow.

Dalton's law of partial pressures states that the pressure of a mixture of gases is the sum of the pressures of the individual components.
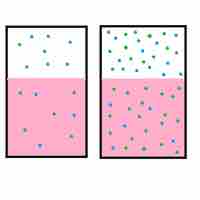
Henry's law states that the amount of a gas that dissolves in a liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of that gas.
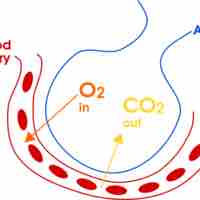
Respiration is the transport of oxygen to the cells within tissues and the transport of carbon dioxide in the opposite direction.
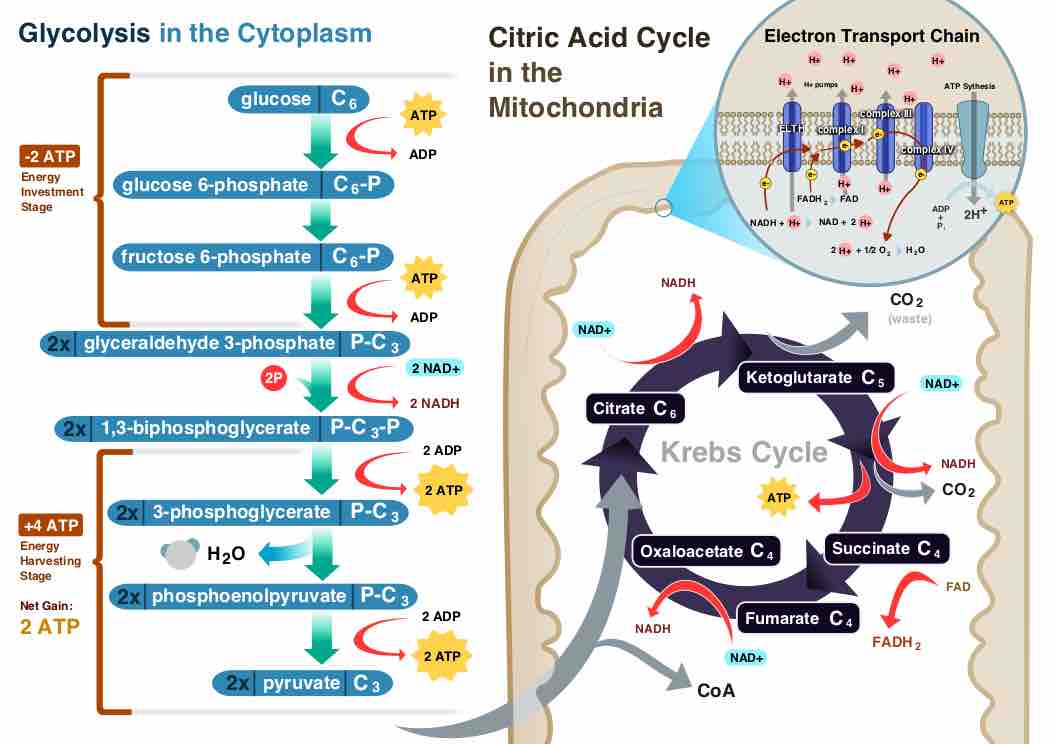
Cellular respiration is the metabolic process by which an organism obtains energy through the reaction of oxygen with glucose.
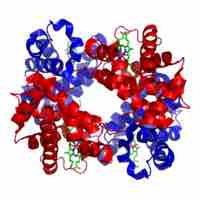
Hemoglobin is the primary transporter of oxygen with an oxygen binding capacity between 1.36 and 1.37 ml O2 per gram Hgb.
CO2 is carried in blood in three different ways: dissolved in plasma, bound to hemoglobin, or as a biocarbonate ion.
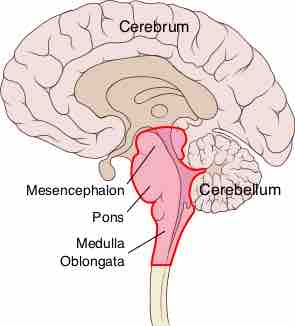
The medulla and the pons are involved in the regulation of the ventilatory pattern of respiration.
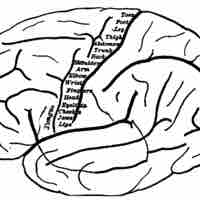
The cerebral cortex of the brain controls voluntary respiration.
Chemoreceptors detect the levels of carbon dioxide in the blood by monitoring the concentrations of hydrogen ions in the blood.
The Hering–Breuer inflation reflex prevents overinflation of the lungs.