Chapter 20
Immune System
By Boundless
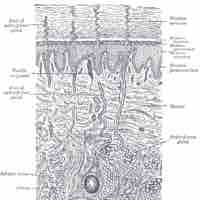
In mammals, the skin and mucosae constitute complex protective barriers that guard against infection and injury.
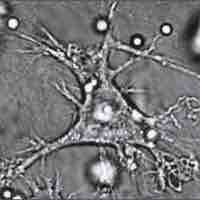
Phagocytes are the white blood cells that protect the body by ingesting harmful foreign particles and help initiate an immune response.

Natural killer (NK) cells are cytotoxic lymphocytes critical for the innate immune system.
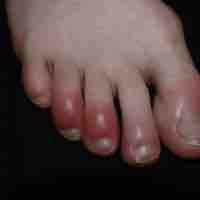
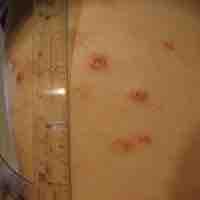
Inflammation is part of the biological response of vascular tissues to harmful stimuli.
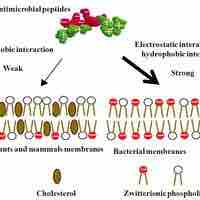
Antimicrobial peptides are an evolutionarily-conserved component of the innate immune response found among all classes of life.
Fever is an elevation of body temperature above the regulatory set point, mediated through the release of prostaglandin E2.
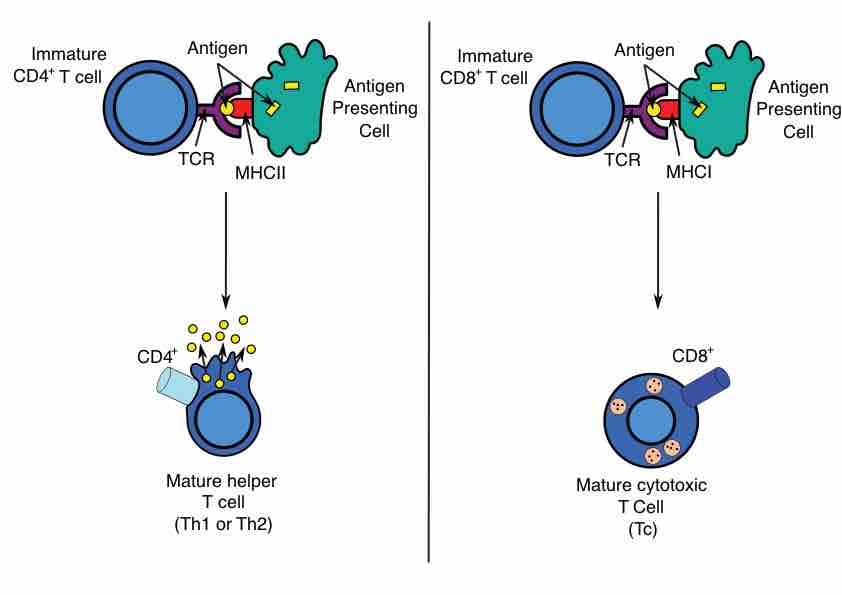
The adaptive immune system is composed of highly-specialized systemic cells and processes that eliminate or prevent pathogenic growth.

The adaptive immune response is mediated by B and T cells and creates immunity memory.
T cells originate from hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow and undergo positive and negative selection in the thymus to mature.
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell in the vertebrate immune system.

Antigen presentation is a process where immune cells capture antigens and then enable their recognition by T-cells.
Antigens are molecules that initiate the immune response and can be bound by antibodies.
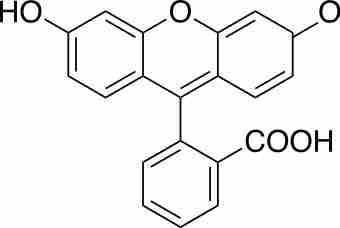
Haptens are molecules that create an immune response when attached to proteins.
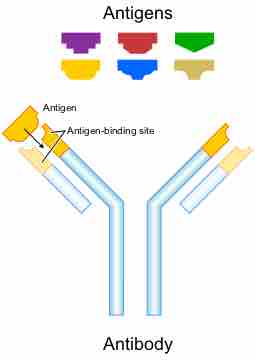
Antigen epitopes make it possible for the immune system to recognize pathogens.
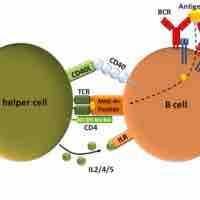
B cells mature in the bone marrow, where they undergo VDJ recombination to produce unique receptors that do not react to self-antigens.

An antibody is a Y-shaped protein produced by B cells to identify and neutralize antigens in the body.
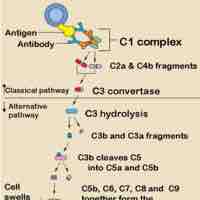
The complement system is the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to remove pathogens from an organism.
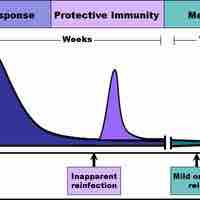
Immunological memory refers to the ability of B and T cells to produce long-lived memory cells that defend against specific pathogens.
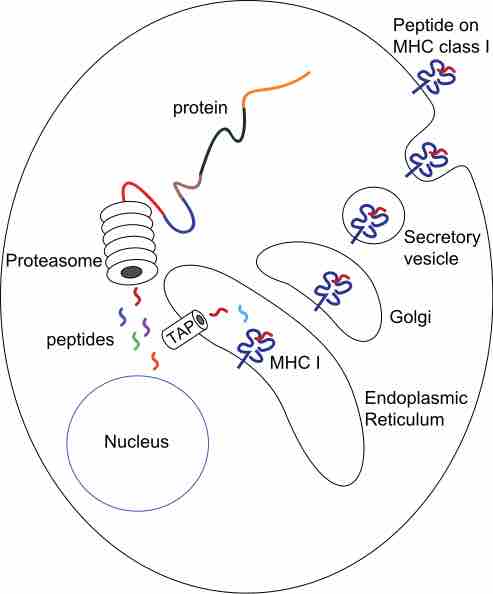
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a cell surface molecule that regulates interactions between white blood cells and other cells.
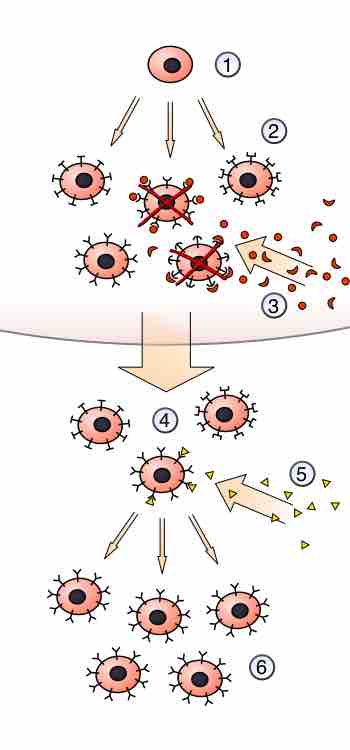
Antigens are selected to form clones of themselves, both memory and effector.
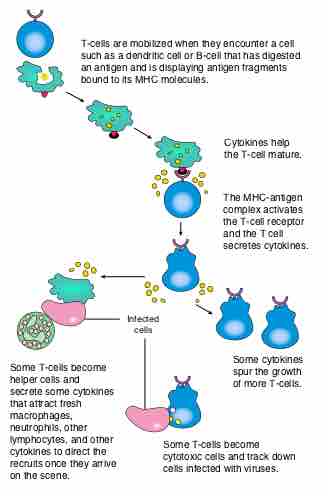
T helper cells assist the maturation of B cells and memory B cells while activating cytotoxic T cells and macrophages.
The humoral immune response is the aspect of immunity mediated by secreted antibodies.