VARIATION
Pancreatic tissue is present in all vertebrate species, but its precise form and arrangement vary widely. There may be up to three separate pancreases, two of which arise from ventral buds, and the other dorsally. In most species (including humans), these fuse in the adult, but there are several exceptions. Even when a single pancreas is present, two or three pancreatic ducts may persist, each draining separately into the duodenum (or equivalent part of the foregut). Birds, for example, typically have three such ducts. In teleosts, and a few other species (such as rabbits), there is no discrete pancreas at all, with pancreatic tissue being distributed diffusely across the mesentery and even within other nearby organs, such as the liver or spleen.
ANATOMY OF THE PANCREAS
The pancreas lies in the epigastrium or upper central region of the abdomen. It is composed of several parts.
- The head lies within the concavity of the duodenum.
- The uncinate process emerges from the lower part of head, and lies deep to superior mesenteric vessels.
- The neck is the constricted part between the head and the body.
- The body lies behind the stomach.
- The tail is the left end of the pancreas. It lies in contact with the spleen.
The superior pancreaticoduodenal artery from gastroduodenal artery and the inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery from superior mesenteric artery run in the groove between the pancreas and the duodenum and supply the head of pancreas. The pancreatic branches of splenic artery also supply the neck, body and tail of the pancreas. The body and neck of the pancreas drain into splenic vein; the head drains into the superior mesenteric and portal veins. Lymph is drained via the splenic, celiac and superior mesenteric lymph nodes.
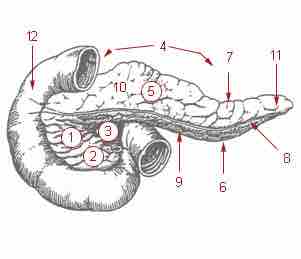
Parts of a Pancreas
1: Head of pancreas 2: Uncinate process of pancreas 3: Pancreatic notch 4: Body of pancreas 5: Anterior surface of pancreas 6: Inferior surface of pancreas 7: Superior margin of pancreas 8: Anterior margin of pancreas 9: Inferior margin of pancreas 10: Omental tuber 11: Tail of pancreas 12: Duodenum.