Chapter 9
Rotational Kinematics, Angular Momentum, and Energy
Book
Version 3
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Physics
Physics
by Boundless
Section 1
Quantities of Rotational Kinematics

Angular Position, Theta
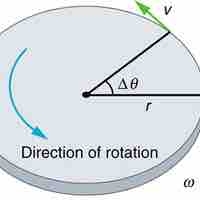
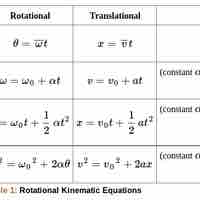
The angle of rotation is a measurement of the amount (the angle) that a figure is rotated about a fixed point— often the center of a circle.
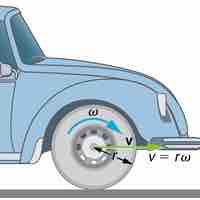
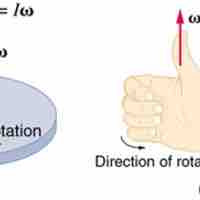
Angular Velocity, Omega
Angular velocity ω is the rate of change of an angle, mathematically defined as ω =
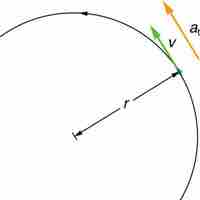
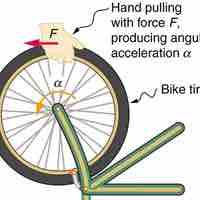
Angular Acceleration, Alpha
Angular acceleration is the rate of change of angular velocity, expressed mathematically as
Section 5
Rotational Kinetic Energy
Rotational Kinetic Energy: Work, Energy, and Power
The rotational kinetic energy is the kinetic energy due to the rotation of an object and is part of its total kinetic energy.
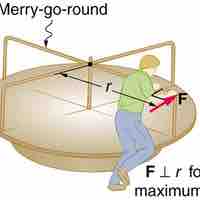
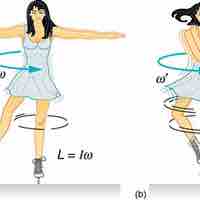
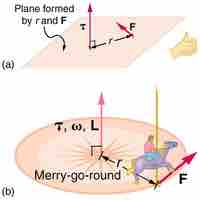
Moment of Inertia
The moment of inertia is a property of a mass that measures its resistance to rotational acceleration about one or more axes.
You are in this book
Boundless Physics
by Boundless