Chapter 10
Fluids
By Boundless
Pressure is scalar quantity which is defined as force per unit area where the force acts in a direction perpendicular to the surface.
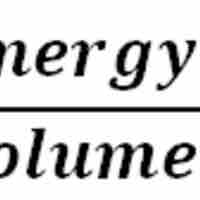
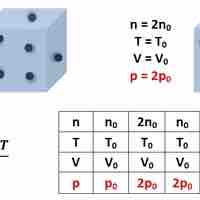
Pressure within static fluids depends on the properties of the fluid, the acceleration due to gravity, and the depth within the fluid.
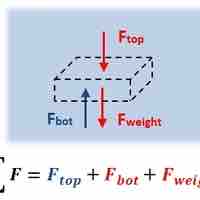
Any region or point, or any static object within a static fluid is in static equilibrium where all forces and torques are equal to zero.
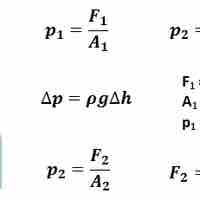
Pascal's Principle states that pressure is transmitted and undiminished in a closed static fluid.
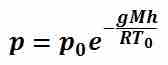
Pressure is often measured as gauge pressure, which is defined as the absolute pressure minus the atmospheric pressure.
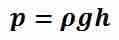
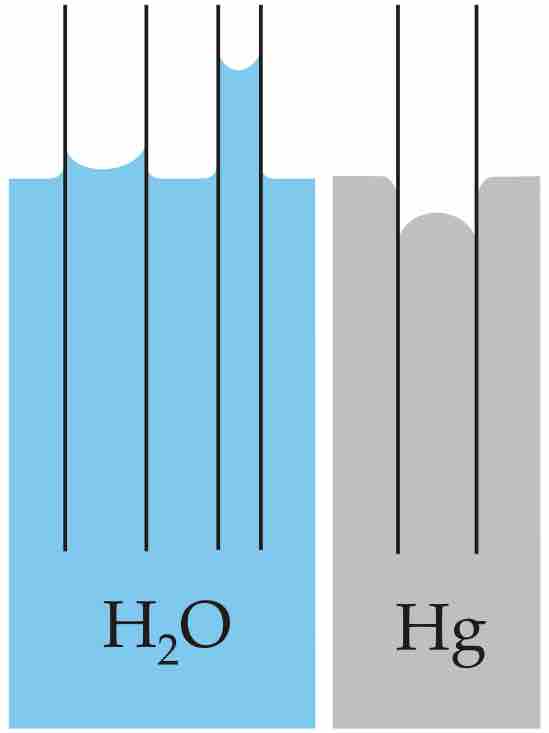
Barometers are devices used for measuring atmospheric and gauge pressure indirectly through the use of hydrostatic fluids.
Pressure plays an essential role in a number of critical bodily functions including respiration and blood circulation.

The buoyant force on an object can be calculated using the Archimedes principle.
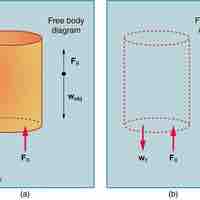
The buoyancy force on a completely submerged object of volume is

An object floats if the buoyancy force exerted on it by the fluid balances its weight.

Length is one of the basic dimensions used to measure an object.
The shape of an object is a description of space that the object takes up; the shape can change if the object is deformed.

Volume is a measure of the three-dimensional space an object occupies, usually taken in terms of length, width and height.
A point charge creates an electric field that can be calculated using Coulomb's Law.