There are a number of properties that can be observed in a material that identify what state the matter is in -- solid, liquid, gas, or plasma.
Solids
A solid is in a state of matter that maintains a fixed volume and shape. A solid's particles fit closely together . The forces between the particles are so strong that the particles can not move freely; they can only vibrate. This causes a solid to be a stable, non-compressible shape with definite volume.

Solid
Solids are in a state of matter that maintains a fixed volume and shape.
Liquids
A liquid maintains a fixed volume, but its shape will mold to the shape of the container it is being held in. In , you can see that even though the liquid's shape is determined by the container, it has a free surface that is not controlled by the container. The particles are close together but not as close as in solids; they are still able to move around, which causes the liquid to flow. Liquids usually have a higher volume than their solid counterparts, except for certain molecules, such as H2O (water).

Liquid
Liquids maintain a fixed volume, but their shape will mold to the shape of the container they are being held in.
Gases
shows a gas, whose particles move around a lot and are much farther apart from each other, usually farther apart than the diameter of the particles themselves. The gas behaves like a liquid; the particles are moving but are still attracted to each other, so they still flow. Unlike a solid or a liquid, the gas will try to fill whatever container it is in, adapting its volume accordingly.
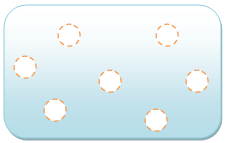
Gas
The particles are much farther from each other, usually a farther length than the size of the particles, and move a lot
Plasma
Plasma is a gas that has been ionized. That is to say, sufficient energy has been supplied to the gas such that the electrons have enough energy to escape their atoms or molecules. Plasma contains ions and electrons that can move around freely. Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape. Plasma is the most common form of visible matter in the universe . Lightning, sparks, neon lights, and the sun are all examples of matter in the plasma state.
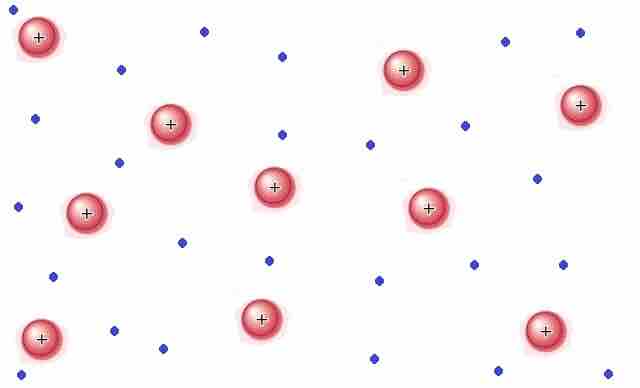
Plasma
Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape, but as well as neutral atoms, it contains a significant number of ions and electrons, both of which can move around freely.
Phase Transitions
shows the different states of matter and how they can change from one to another as a function of enthalpy and pressure and temperature changes. A solid can change to a liquid with an enthalpy increase. The process of a liquid going to a solid is known as melting. A liquid can change into a gas when it hits its boiling point or can even enter a plasma state if the enthalpy is increased enough. When the enthalpy is lowered, a liquid can transform into a solid through freezing. Sometimes, a solid can skip freezing and go directly to a gaseous state; this process is called sublimation.
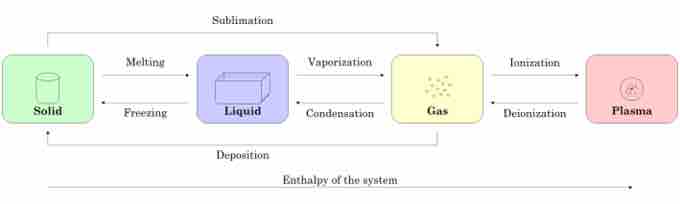
States of Matter
This figure illustrates the relationship between the enthalpy of a system and the state of matter that the system is in.