Chapter 28
Introduction to Quantum Physics
By Boundless
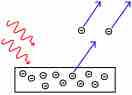
Electrons are emitted from matter that is absorbing energy from electromagnetic radiation, resulting in the photoelectric effect.

The electromagnetic (EM) spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation.

A photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of light, which carries momentum and energy.

Quantum mechanics has had enormous success in explaining microscopic systems and has become a foundation of modern science and technology.
Wave–particle duality postulates that all physical entities exhibit both wave and particle properties.

De Broglie's hypothesis was that particles should show wave-like properties such as diffraction or interference.
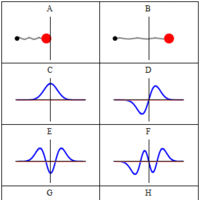
A wave function is a probability amplitude in quantum mechanics that describes the quantum state of a particle and how it behaves.
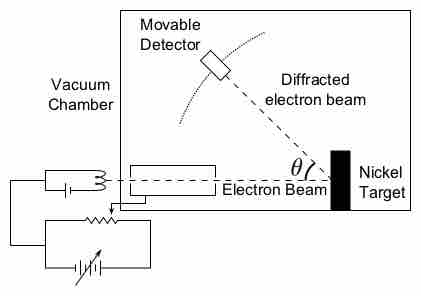
The concept of "matter waves" or "de Broglie waves" reflects the wave-particle duality of matter.
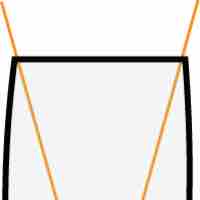
The uncertainty principle asserts a basic limit to the precision with which some physical properties of a particle can be known simultaneously.

Since its inception, many counter-intuitive aspects of quantum mechanics have provoked strong philosophical debates.
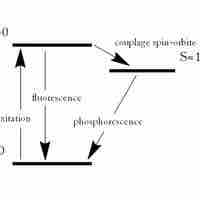
Fluorescence and phosphorescence are photoluminescence processes in which material emits photons after excitation.

A laser is a device that emits monochromatic light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons.
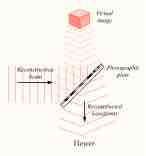
Holography is an optical technique which enables three-dimensional images to be made.
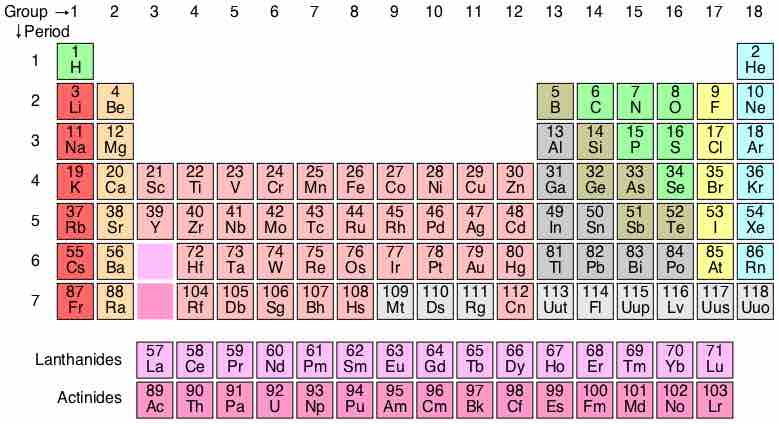
A periodic table is a tabular display of elements organized by their atomic numbers, electron configurations, and chemical properties.
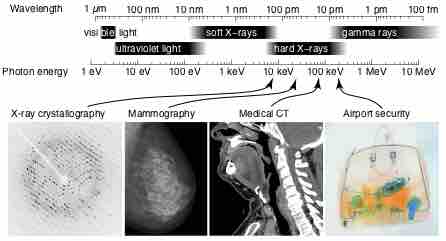
X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation and have wavelengths in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers.
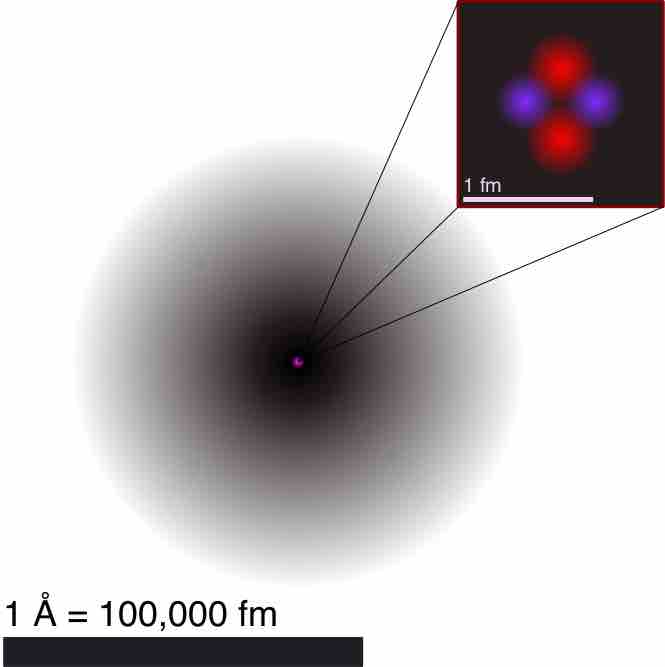
Atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electron cloud, commonly called atomic orbitals.