Chapter 5
Gases
By Boundless
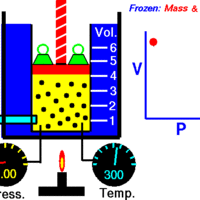
Boyle's Law describes the inverse relationship between the pressure and volume of a fixed amount of gas at a constant temperature.

Charles' and Gay-Lussac's Law states that at constant pressure, temperature and volume are directly proportional.
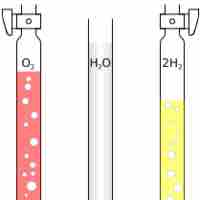
Avogadro's Law states that at the same temperature and pressure, equal volumes of different gases contain an equal number of particles.
The ideal gas equation is given by

A reformulation of the Ideal Gas Equation involving density allows us to evaluate the behaviors of ideal gases of unknown quantity.
We can derive a form of the Ideal Gas Equation, PV=nRT, that incorporates the molar mass of the gas (M,
Dalton's Law of Partial Pressure states the total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressure of each individual gas.
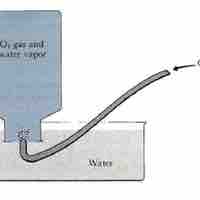
The amount of gas present can be determined by collecting a gas over water and applying Dalton's Law.
Kinetic Molecular Theory explains the macroscopic properties of gases and can be used to understand and explain the gas laws.
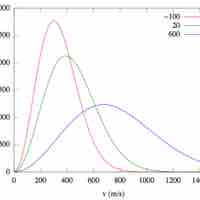
The Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution describes the average molecular speeds for a collection of gas particles at a given temperature.
The root-mean-square speed measures the average speed of particles in a gas, defined as
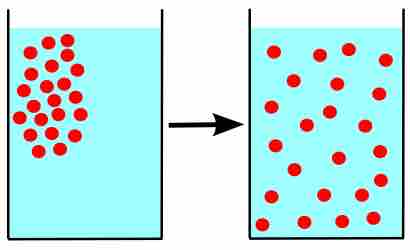
Due to their constant, random motion, gas molecules diffuse into areas of lower concentration, and effuse through tiny openings.
Real gases deviate from the ideal gas law due to the finite volume occupied by individual gas particles.
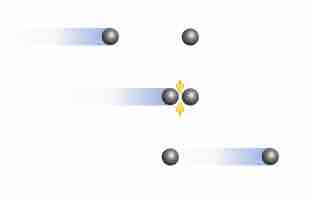
At high pressures and low temperatures, intermolecular forces between gas particles can cause significant deviation from ideal behavior.

The van der Waals equation modifies the Ideal Gas Law to correct for the excluded volume of gas particles and intermolecular attractions.
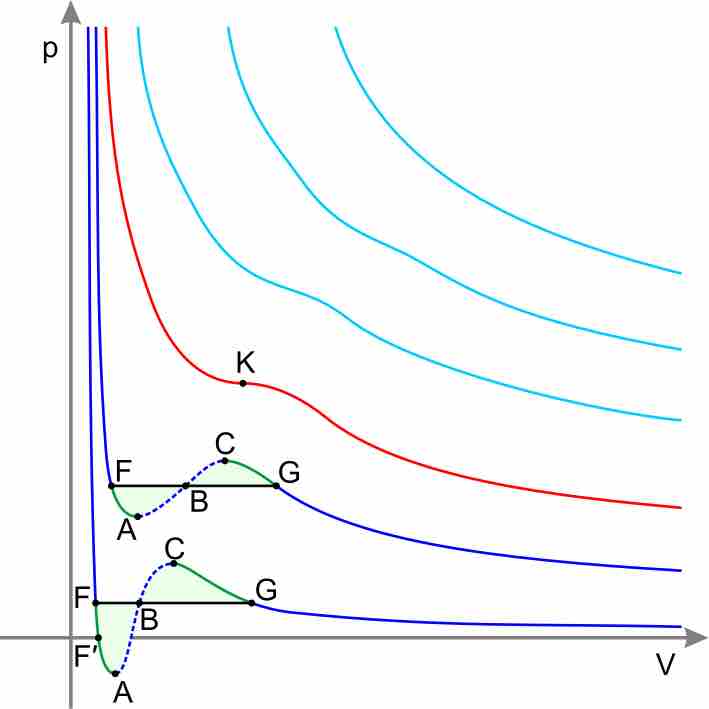
Equations other than the Ideal Gas Law model the non-ideal behavior of real gases at high pressures and low temperatures.

Air pollution results from increasing levels of harmful molecules and particulates in the atmosphere.
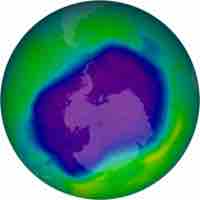
Free radicals in the upper stratosphere act as catalysts for ozone decomposition, thereby depleting the ozone layer.
- Types of Aqueous Solutions
- Precipitation Reactions
- Acid-Base Reactions
- Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
- Solution Concentration